| Look up pharyngeal in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Pharyngeal may refer to:
| Look up pharyngeal in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Pharyngeal may refer to:

The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a fan-shaped muscle located in the neck. It is one of three pharyngeal constrictors. Similarly to the superior and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles, the middle pharyngeal constrictor is innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus. The middle pharyngeal constrictor is smaller than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.
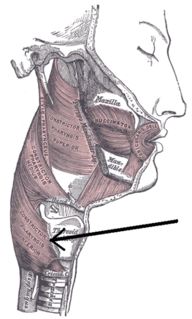
The Inferior pharyngeal constrictor, the thickest of the three constrictors, arises from the sides of the cricoid and thyroid cartilage. Similarly to the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscles, it is innervated by the vagus nerve, specifically, by branches from the pharyngeal plexus and by neuronal branches from the recurrent laryngeal nerve.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity and above the esophagus and larynx, or the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species.
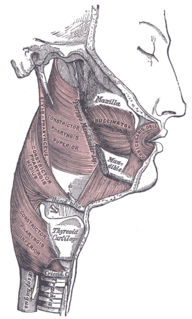
The pharyngeal muscles are a group of muscles that form the pharynx, which is posterior to the oral cavity, determining the shape of its lumen, and affecting its sound properties as the primary resonating cavity.

The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a muscle in the pharynx. It is the highest located muscle of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is a quadrilateral muscle, thinner and paler than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle.

A pharyngeal consonant is a consonant that is articulated primarily in the pharynx. Some phoneticians distinguish upper pharyngeal consonants, or "high" pharyngeals, pronounced by retracting the root of the tongue in the mid to upper pharynx, from (ary)epiglottal consonants, or "low" pharyngeals, which are articulated with the aryepiglottic folds against the epiglottis in the lower larynx, as well as from epiglotto-pharyngeal consonants, with both movements being combined.
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Pharyngeal. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing is an important part of eating and drinking. If the process fails and the material goes through the trachea, then choking or pulmonary aspiration can occur. In the human body the automatic temporary closing of the epiglottis is controlled by the swallowing reflex.
A Zenker's diverticulum, also pharyngeal pouch, is a diverticulum of the mucosa of the esophagus, just above the cricopharyngeal muscle. It is a pseudo diverticulum.

The stylopharyngeus is a muscle in the head that stretches between the temporal styloid process and the pharynx.
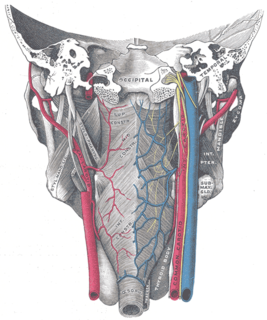
The pharyngeal raphe is a raphe that serves as the origin and insertion for several of the pharyngeal constrictors. Two sides of the pharyngeal wall are joined together posteriorly in the midline by the raphe. Its superior part is attached to the pharyngeal tubercle; it extends inferiorly to the level of vertebra C6 where it blends with the posterior wall of the esophagus.
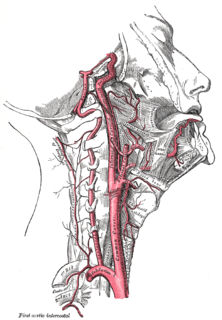
The ascending pharyngeal artery is an artery in the neck that supplies the pharynx, developing from the proximal part of the embryonic second aortic arch.

The ascending palatine artery is an artery in the head that branches off the facial artery and runs up the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.
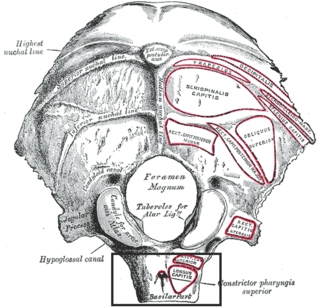
The pharyngeal tubercle is a part of the occipital bone of the head and neck. It is located on the lower surface of the basilar part of occipital bone, about 1 cm. anterior to the foramen magnum. The pharyngeal tubercle gives attachment to the fibrous raphe of the pharynx, also known as the pharyngeal raphe.

The pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve, the principal motor nerve of the pharynx, arises from the upper part of the ganglion nodosum, and consists principally of filaments from the cranial portion of the accessory nerve.

The pharyngeal plexus is a network of nerve fibers innervating most of the palate and pharynx.
The pharyngeal branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve are three or four filaments which unite, opposite the Constrictor pharyngis medius, with the pharyngeal branches of the vagus and sympathetic, to form the pharyngeal plexus.

The buccopharyngeal fascia is a fascia in the head.
The pharyngeal aponeurosis, is situated between the mucous and muscular layers.
Constrictor may refer to:
In the pharynx, the sinus of Morgagni is the enclosed space between the upper border of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle, the base of the skull and the pharyngeal aponeurosis.
Passavant's ridge is a mucous elevation situated behind the floor of the naso-pharynx.