
A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in project management and systems engineering, is a deliverable-oriented breakdown of a project into smaller components. A work breakdown structure is a key project deliverable that organizes the team's work into manageable sections. The Project Management Body of Knowledge defines the work-breakdown structure "A hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables."
Project planning is part of project management, which relates to the use of schedules such as Gantt charts to plan and subsequently report progress within the project environment.

The Project Management Body of Knowledge is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. The body of knowledge evolves over time and is presented in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, a book whose sixth edition was released in 2017. The Guide is a document resulting from work overseen by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offers the CAPM and PMP certifications.

The critical path method (CPM), or critical path analysis (CPA), is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is commonly used in conjunction with the program evaluation and review technique (PERT). A critical path is determined by identifying the longest stretch of dependent activities and measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish.
Project management software has the capacity to help plan, organize, and manage resource tools and develop resource estimates. Depending on the sophistication of the software, it can manage estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, decision-making, quality management and documentation or administration systems. Today, numerous PC and browser-based project management software and contract management software solutions exist, and are finding applications in almost every type of business.

In project management under the PRINCE2 methodology, a product breakdown structure (PBS) is a tool for analysing, documenting and communicating the outcomes of a project, and forms part of the product based planning technique.
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development is a process of writing and maintaining the source code, but in a broader sense, it includes all that is involved between the conception of the desired software through to the final manifestation of the software, sometimes in a planned and structured process. Therefore, software development may include research, new development, prototyping, modification, reuse, re-engineering, maintenance, or any other activities that result in software products.

A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents an algorithm, workflow or process. Flowchart can also be defined as a diagramatic representation of an algorithm.
A business analyst (BA) is someone who analyzes an organization or business domain and documents its business or processes or systems, assessing the business model or its integration with technology.

A technology roadmap is a flexible planning technique to support strategic and long-range planning, by matching short-term and long-term goals with specific technology solutions. It is a plan that applies to a new product or process and may include using technology forecasting/technology scouting to identify suitable emerging technologies. It is a known technique to help manage the fuzzy front-end of innovation. It is also expected that roadmapping techniques may help companies to survive in turbulent environments and help them to plan in a more holistic way to include non-financial goals and drive towards a more sustainable development. Here roadmaps can be combined with other corporate foresight methods to facilitate systemic change.

The Project Initiation Documentation (PID) - one of the most significant artifacts in project management, which provides the foundation for the business project.
Scrum is an agile framework for managing knowledge work, with an emphasis on software development, although it has wide application in other fields and is slowly starting to be explored by traditional project teams more generally. It is designed for teams of three to nine members, who break their work into actions that can be completed within timeboxed iterations, called sprints, no longer than one month and most commonly two weeks, then track progress and re-plan in 15-minute time-boxed stand-up meetings, called daily scrums.
Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS) - A hierarchically organised depiction of the identified project risks arranged by category.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
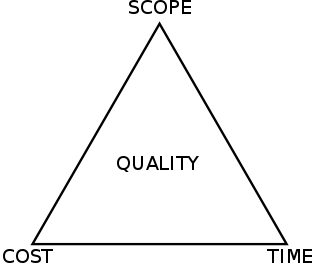
The Project Management Triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.
The Product flow diagram (PFD) representation of the order by which a sequence of products is created according to Product based planning principles. It is related to the Product breakdown structure (PBS).
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:
The Goals breakdown structure (GBS) is a hierarchical structure linking high-level objectives or goals to more detailed goals. The GBS was originally developed for project management, but applies to product development and the organization as a whole. The concept is based on the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) popular in the project management discipline. Like the WBS, project goals exhibit a hierarchical structure. The highest-level defines the overall goal or mission for the project. The next level down sets the goals the organization intends to achieve from the project. These might include such items as profit, market share, etc. The next layer down defines the features the products must exhibit to achieve the organization's goals. The next layer down defines the specifications each product or component of the product must have to meet the products features.









