Related Research Articles

The mkdir command in the Unix, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems is used to make a new directory. It is also available in the EFI shell and in the PHP scripting language. In DOS, OS/2, Windows and ReactOS, the command is often abbreviated to md.

In computing, at is a command in Unix-like operating systems, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS used to schedule commands to be executed once, at a particular time in the future.
In computing, rmdir is a command which will remove an empty directory on various operating systems.

ipconfig is a console application program of some computer operating systems that displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings.

In computing, XCOPY is a command used on IBM PC DOS, MS-DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, FreeDOS, ReactOS, and related operating systems for copying multiple files or entire directory trees from one directory to another and for copying files across a network.
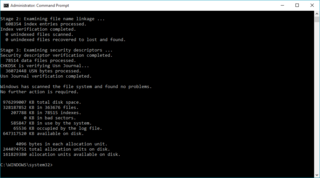
In computing, CHKDSK is a system tool and command in DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and related operating systems. It verifies the file system integrity of a volume and attempts to fix logical file system errors. It is similar to the fsck command in Unix and similar to Microsoft ScanDisk which co-existed with CHKDSK in Windows 9x and MS-DOS 6.x.

Microsoft Diagnostics (MSD) was a software tool developed by Microsoft to assist in the diagnostics of 1990s-era computers. Users primarily deployed this tool to provide detailed technical information about the user's software and hardware and to print the gathered information, usually for use by support technicians in troubleshooting and resolving problems. The assumptions made by the program were valid until the late 1990s: it does not handle plug-and-play USB or other new technologies that appeared around 2000.
In computing, SUBST is a command on the DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems used for substituting paths on physical and logical drives as virtual drives.
In computing, regsvr32 is a command-line utility in Microsoft Windows and ReactOS for registering and unregistering DLLs and ActiveX controls in the operating system Registry. Despite the suffix "32" in the name of the file, there are both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of this utility. regsvr32 requires elevated privileges.
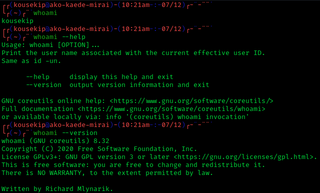
In computing, whoami is a command found on most Unix-like operating systems, Intel iRMX 86, every Microsoft Windows operating system since Windows Server 2003, and on ReactOS. It is a concatenation of the words "Who am I?" and prints the effective username of the current user when invoked.

In computing, ATTRIB is a command in Intel ISIS-II, DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS that allows the user to change various characteristics, or "attributes" of a computer file or directory. The command is also available in the EFI shell.

In computing, ren is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, 4NT and Windows PowerShell. It is used to rename computer files and in some implementations also directories. It can also move a file to a new path, if it is on the same device. It is analogous to the Unix mv command. However, unlike mv, ren cannot be used to move files, as a new directory for the destination file may not be used. Alternatively, move may be used if available. On versions of MS-DOS that do not support the move command, the user would simply copy the file to a new destination, and then delete the original file. A notable exception to this rule is DOSBox, in which ren may be used to move a file, since move is not supported.

In computing, type is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS/4NT and Windows PowerShell used to display the contents of specified files on the computer terminal. The analogous Unix command is cat.

In computing, del is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, NDOS, 4OS2, 4NT and Windows PowerShell. It is used to delete one or more files or directories from a file system.
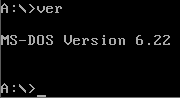
In computing, ver is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe and 4DOS/4NT. It prints the name and version of the operating system, the command shell, or in some implementations the version of other commands. It is roughly equivalent to the Unix command uname.

To shut down or power off a computer is to remove power from a computer's main components in a controlled way. After a computer is shut down, main components such as CPUs, RAM modules and hard disk drives are powered down, although some internal components, such as an internal clock, may retain power.

In computing, diskpart is a command-line disk partitioning utility included in Windows 2000 and later Microsoft operating systems, replacing its predecessor, fdisk. The command is also available in ReactOS.

In computing, net is a command in IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS used to manage and configure the operating system from the command-line. It is also part of the IBM PC Network Program for DOS.
In computing, recover is a primitive file system error recovery utility included in MS-DOS / IBM PC DOS versions prior to DOS 6.0 and a number of other operating systems.

In computing, replace is a command that is used to replace one or more existing computer files or add new files to a target directory. Files with a hidden or system attribute set cannot be replaced using replace. The command lists all files that are replaced.
References
- ↑ "MS-DOS and Windows command line systeminfo command".
- ↑ Bott, Ed; Carl Siechert; Craig Stinson (2004). Microsoft Windows XP inside out . Bpg-Inside Out Series (2 ed.). Microsoft Press. p. 1252. ISBN 978-0-7356-2044-5 . Retrieved 2011-03-24.
Systeminfo.exe is a command-line utility that displays information about your Windows version, BIOS, processor, memory, and a few more esoteric items.
- ↑ "Systeminfo".
- ↑ "Reactos/Reactos". GitHub . 3 January 2022.
- ↑ SYSTEMINFO - Windows CMD - SS64.com