
The Bronze Age is a historical period characterized by the use of bronze, and in some areas proto-writing, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age Stone-Bronze-Iron system, as proposed in modern times by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen, for classifying and studying ancient societies.
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age and the Bronze Age. The concept has been mostly applied to Europe and the Ancient Near East, and, by analogy, also to other parts of the Old World.

An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and greenhouse periods, during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the Quaternary glaciation, known in popular terminology as the Ice Age. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed "glacial periods", and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called "interglacials" or "interstadials", with both climatic pulses part of the Quaternary or other periods in Earth's history.

In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages lasted from the 5th to the 15th century. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and merged into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages.

The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make implements with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted roughly 3.4 million years and ended between 8700 BCE and 2000 BCE with the advent of metalworking.

Whisky or whiskey is a type of distilled alcoholic beverage made from fermented grain mash. Various grains are used for different varieties, including barley, corn, rye, and wheat. Whisky is typically aged in wooden casks, generally made of charred white oak.

Brandy is a spirit produced by distilling wine. Brandy generally contains 35–60% alcohol by volume and is typically drunk as an after-dinner digestif. Some brandies are aged in wooden casks. Others are coloured with caramel colouring to imitate the effect of aging, and some are produced using a combination of both aging and colouring. Varieties of wine brandy can be found across the winemaking world. Among the most renowned are Cognac and Armagnac from southwestern France.
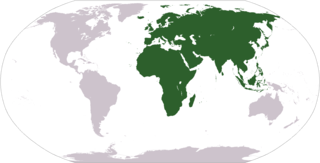
The term 'Old World' is used commonly in the West to refer to Africa, Asia and Europe, regarded collectively as the part of the world known to its population before contact with the 'New World'.

A student is primarily a person enrolled in a school or other educational institution who attends classes in a course to attain the appropriate level of mastery of a subject under the guidance of an instructor and who devotes time outside class to do whatever activities the instructor assigns that are necessary either for class preparation or to submit evidence of progress towards that mastery. In the broader sense, a student is anyone who applies themselves to the intensive intellectual engagement with some matter necessary to master it as part of some practical affair in which such mastery is basic or decisive.

A gymnasium is a type of school with a strong emphasis on academic learning, and providing advanced secondary education in some parts of Europe comparable to British grammar schools, sixth form colleges and US preparatory high schools. In its current meaning, it usually refers to secondary schools focused on preparing students to enter a university for advanced academic study. Before the 20th century, the system of gymnasiums was a widespread feature of educational system throughout many countries of central, north, eastern and southern Europe.

Kindergarten (, ; from German [ˈkɪndɐˌɡaːɐ̯tn̩] is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally created in the late 18th century in Bavaria and Strasbourg to serve children whose parents both worked outside home. The term was coined by the German Friedrich Fröbel, whose approach globally influenced early-years education. Today, the term is used in many countries to describe a variety of educational institutions and learning spaces for children ranging from one to seven years of age, based on a variety of teaching methods.
A middle school is an educational stage which exists in some countries, providing education between primary school and secondary school. The concept, regulation and classification of middle schools, as well as the ages covered, vary between, and sometimes within, countries.

The FIFA World Player of the Year was an association football award presented annually by the sport's governing body, FIFA, between 1991 and 2015. Coaches and captains of international teams and media representatives selected the player they deem to have performed the best in the previous calendar year.

The Nordic Bronze Age is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 1700–500 BC. The Bronze Age culture of this era succeeded the Nordic Stone Age culture and was followed by the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The archaeological legacy of the Nordic Bronze Age culture is rich, but the ethnic and linguistic affinities of it are unknown, in the absence of written sources. Some scholars also include sites in what is now Finland, Estonia, northern Germany and Pomerania as part of its cultural sphere.
Educational stages are subdivisions of formal learning, typically covering early childhood education, primary education, secondary education and tertiary education. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) recognizes seven levels of education in its International Standard Classification of Education system. UNESCO's International Bureau of Education maintains a database of country-specific education systems and their stages.

Confirmation or Chrismation is one of the seven sacraments of the Catholic Church. It is also one of the three sacraments of initiation into the Catholic Church, the other two being Baptism and Holy Communion.
Human prehistory is the period between the use of the first stone tools c. 3.3 million years ago by hominins and the invention of writing systems. The earliest writing systems appeared c. 5,300 years ago, but it took thousands of years for writing to be widely adopted, and it was not used in some human cultures until the 19th century or even until the present. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different dates in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently.














