Astatine is a radioactive chemical element with symbol At and atomic number 85. It is the rarest naturally occurring element in the Earth's crust, occurring only as the decay product of various heavier elements. All of astatine's isotopes are short-lived; the most stable is astatine-210, with a half-life of 8.1 hours. A sample of the pure element has never been assembled, because any macroscopic specimen would be immediately vaporized by the heat of its own radioactivity.

Bromine is a chemical element with symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest halogen, and is a fuming red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured gas. Its properties are thus intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος ("stench"), referencing its sharp and disagreeable smell.

The halogens are a group in the periodic table consisting of five chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). The artificially created element 117 may also be a halogen. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17. The symbol X is often used generically to refer to any halogen.
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. This page is for the iodide ion and its salts, not organoiodine compounds. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability.
Halogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the addition of one or more halogens to a compound or material. The pathway and stoichiometry of halogenation depends on the structural features and functional groups of the organic substrate, as well as on the specific halogen. Inorganic compounds such as metals also undergo halogenation.
Fluoride toxicity is a condition in which there are elevated levels of the fluoride ion in the body. Although fluoride is safe for dental health at low concentrations, sustained consumption of large amounts of soluble fluoride salts is dangerous. Referring to a common salt of fluoride, sodium fluoride (NaF), the lethal dose for most adult humans is estimated at 5 to 10 g. Ingestion of fluoride can produce gastrointestinal discomfort at doses at least 15 to 20 times lower than lethal doses. Although it is helpful topically for dental health in low dosage, chronic ingestion of fluoride in large amounts interferes with bone formation. In this way, the most widespread examples of fluoride poisoning arise from consumption of ground water that is abnormally fluoride-rich.
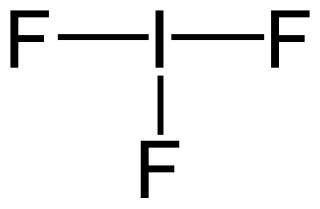
An interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.

Hydrogen halides are diatomic inorganic compounds with the formula HX where X is one of the halogens: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, or astatine. Hydrogen halides are gases that dissolve in water to give acids which are commonly known as hydrohalic acids.
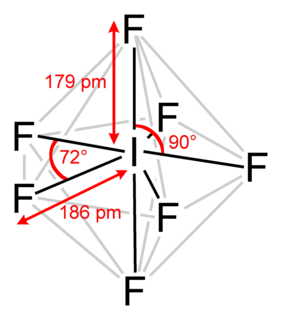
Iodine heptafluoride, also known as iodine(VII) fluoride or iodine fluoride, is an interhalogen compound with the chemical formula IF7. It has an unusual pentagonal bipyramidal structure, as predicted by VSEPR theory. The molecule can undergo a pseudorotational rearrangement called the Bartell mechanism, which is like the Berry mechanism but for a heptacoordinated system.
It forms colourless crystals, which melt at 4.5 °C: the liquid range is extremely narrow, with the boiling point at 4.77 °C. The dense vapor has a mouldy, acrid odour. The molecule has D5h symmetry.
Fluoride volatility is the tendency of highly fluorinated molecules to vaporize at comparatively low temperatures. Heptafluorides, hexafluorides and pentafluorides have much lower boiling points than the lower-valence fluorides. Most difluorides and trifluorides have high boiling points, while most tetrafluorides and monofluorides fall in between. The term "fluoride volatility" is jargon used particularly in the context of separation of radionuclides.
A cyanogen halide is a molecule consisting of cyanide and a halogen. Cyanogen halides are chemically classified as pseudohalogens.

Beryllium iodide is the chemical compound with the formula BeI2. It is very hygroscopic and reacts violently with water, forming hydroiodic acid.
Bismuth pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula BiF5. It is a white solid that is highly reactive. The compound is of interest to researchers but not of particular value.
In epidemiology, environmental diseases are diseases that can be directly attributed to environmental factors. Apart from the true monogenic genetic disorders, environmental diseases may determine the development of disease in those genetically predisposed to a particular condition. Stress, physical and mental abuse, diet, exposure to toxins, pathogens, radiation, and chemicals found in almost all personal care products and household cleaners are possible causes of a large segment of non-hereditary disease. If a disease process is concluded to be the result of a combination of genetic and environmental factor influences, its etiological origin can be referred to as having a multifactorial pattern.
A monofluoride is a chemical compound with one fluoride per formula unit. For a binary compound, this is the formula XF.
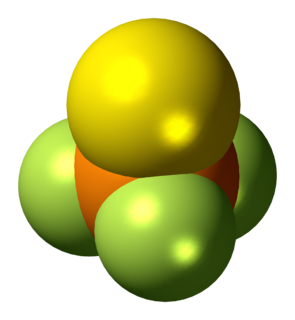
Thiophosphoryl fluoride is an inorganic molecular gas with formula PSF3 containing phosphorus, sulfur and fluorine. It spontaneously ignites in air and burns with a cool flame. The discoverers were able to have flames around their hands without discomfort, and called it "probably one of the coldest flames known". The gas was discovered in 1888.
Neptunium(V) fluoride or neptunium pentafluoride is a chemical compound of neptunium and fluorine with the formula NpF5.