The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is an agency of the United States Department of Labor. Congress established the agency under the Occupational Safety and Health Act, which President Richard M. Nixon signed into law on December 29, 1970. OSHA's mission is to "assure safe and healthy working conditions for working men and women by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education and assistance". The agency is also charged with enforcing a variety of whistleblower statutes and regulations. OSHA is currently headed by Acting Assistant Secretary of Labor Loren Sweatt. OSHA's workplace safety inspections have been shown to reduce injury rates and injury costs without adverse effects to employment, sales, credit ratings, or firm survival.
OSHA or Osha may refer to:

Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride) is a geminal organic compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a moderately sweet aroma is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.

Diacetyl (IUPAC systematic name: butanedione or butane-2,3-dione) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3CO)2. It is a yellow or green liquid with an intensely buttery flavor. It is a vicinal diketone (two C=O groups, side-by-side) with the molecular formula C4H6O2. Diacetyl occurs naturally in alcoholic beverages and is added to some foods to impart its buttery flavor.

The Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 is a US labor law governing the federal law of occupational health and safety in the private sector and federal government in the United States. It was enacted by Congress in 1970 and was signed by President Richard Nixon on December 29, 1970. Its main goal is to ensure that employers provide employees with an environment free from recognized hazards, such as exposure to toxic chemicals, excessive noise levels, mechanical dangers, heat or cold stress, or unsanitary conditions. The Act created the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
Construction work is hazardous Land-Based job. Some construction site jobs include: building houses, roads, tree forts, workplaces and repair and maintain infrastructures. This work includes many hazardous task and conditions such as working with height, excavation, noise, dust, power tools and equipment. The most common fatalities are caused by the fatal four: falls, being struck by an object, electrocutions, and being caught in between two objects. Construction work has been increasing in developing and undeveloped countries over the past few years. With an increase in this type of work occupational fatalities have increased. Occupational fatalities are individuals who die while on the job or performing work related tasks. Within the field of construction it is important to have safe construction sites.
The permissible exposure limit is a legal limit in the United States for exposure of an employee to a chemical substance or physical agent such as high level noise. Permissible exposure limits are established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Most of OSHA’s PELs were issued shortly after adoption of the Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Act in 1970.
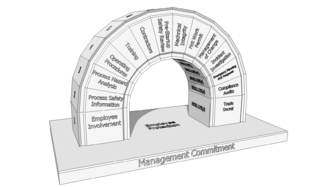
Process safety management system is a regulation promulgated by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). A process is any activity or combination of activities including any use, storage, manufacturing, handling or the on-site movement of highly hazardous chemicals (HHCs) as defined by OSHA and the Environmental Protection Agency.

Chloroprene is the common name for 2-chlorobuta-1,3-diene (IUPAC name) with the chemical formula CH2=CCl−CH=CH2. Chloroprene is a colorless volatile liquid, almost exclusively used as a monomer for the production of the polymer polychloroprene, a type of synthetic rubber. Polychloroprene is better known as Neoprene, the trade name given by DuPont.

Lockout-tagout (LOTO) or lock and tag is a safety procedure used in industry and research settings to ensure that dangerous machines are properly shut off and not able to be started up again prior to the completion of maintenance or repair work. It requires that hazardous energy sources be "isolated and rendered inoperative" before work is started on the equipment in question. The isolated power sources are then locked and a tag is placed on the lock identifying the worker who placed it. The worker then holds the key for the lock, ensuring that only he or she can remove the lock and start the machine. This prevents accidental startup of a machine while it is in a hazardous state or while a worker is in direct contact with it.
Environment (E), health (H) and safety (S) is a discipline and specialty that studies and implements practical aspects of environmental protection and safety at work. In simple terms it is what organizations must do to make sure that their activities do not cause harm to anyone. Commonly, quality - quality assurance & quality control - is adjoined to form the company division known as HSQE.

An occupational hazard is a hazard experienced in the workplace. Occupational hazards can encompass many types of hazards, including chemical hazards, biological hazards (biohazards), psychosocial hazards, and physical hazards. In the United States, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) conduct workplace investigations and research addressing workplace health and safety hazards resulting in guidelines. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes enforceable standards to prevent workplace injuries and illnesses. In the EU a similar role is taken by EU-OSHA.
The Division of Occupational Safety and Health of California is an agency of the Government of California established by the California Occupational Safety & Health Act of 1973. Administered by the California Department of Industrial Relations, Cal/OSHA's mission is to protect public health and safety through research and regulation related to hazards on the job in California workplaces as well as on elevators, amusement rides, and ski lifts, and related to the use of pressure vessels such as boilers and tanks. Cal/OSHA requires that qualifying organizations create illness and injury prevention programs meant to help identify and eliminate dangers before accidents and illnesses occur.
A recommended exposure limit (REL) is an occupational exposure limit that has been recommended by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) for adoption as a permissible exposure limit. The REL is a level that NIOSH believes would be protective of worker safety and health over a working lifetime if used in combination with engineering and work practice controls, exposure and medical monitoring, posting and labeling of hazards, worker training and personal protective equipment. No REL has ever been adopted by OSHA, but they have been used as guides by some industry and advocacy organizations. RELs for chemical exposures are usually expressed in parts per million (ppm), or sometimes in milligrams per cubic metre (mg/m3). Although not legally enforceable limits, NIOSH RELs are considered by OSHA during the promulgation of legally enforceable PELs.
The Oregon Occupational Safety and Health Division is a state government agency that regulates workplace safety and health in the U.S. state of Oregon. Oregon OSHA is a division of the Oregon Department of Consumer and Business Services and operates under a formal state-plan agreement with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Oregon OSHA's regulatory authority comes from the Oregon Safe Employment Act (OSEA); its jurisdiction covers most public and private sector workplaces in the state. Oregon OSHA's expressed mission is "to advance and improve workplace safety and health for all workers in Oregon."
Workplace health surveillance or occupational health surveillance (U.S.) is the ongoing systematic collection, analysis, and dissemination of exposure and health data on groups of workers. The Joint ILO/WHO Committee on Occupational Health at its 12th Session in 1995 defined an occupational health surveillance system as “a system which includes a functional capacity for data collection, analysis and dissemination linked to occupational health programmes”.
An occupational fatality is a death that occurs while a person is at work or performing work related tasks. Occupational fatalities are also commonly called “occupational deaths” or “work-related deaths/fatalities” and can occur in any industry or occupation.
The Washington State Department of Labor and Industries (L&I) is a department of the Washington state government that regulates and enforces labor standards. The agency administers the state's workers' compensation system, conducts workplace inspections, licenses and certifies trade workers, and issues permits for heavy machinery.