A codex, plural codices, is a book constructed of a number of sheets of paper, vellum, papyrus, or similar materials. The term is now usually only used of manuscript books, with hand-written contents, but describes the format that is now near-universal for printed books in the Western world. The book is usually bound by stacking the pages and fixing one edge to a spine, which may just be thicker paper, or with stiff boards, called a hardback, or in elaborate historical examples a treasure binding.

In cryptography, a scytale is a tool used to perform a transposition cipher, consisting of a cylinder with a strip of parchment wound around it on which is written a message. The ancient Greeks, and the Spartans in particular, are said to have used this cipher to communicate during military campaigns.

The nictitating membrane is a transparent or translucent third eyelid present in some animals that can be drawn across the eye from the medial canthus for protection and to moisten it while maintaining vision. Some reptiles, birds, and sharks have full nictitating membranes; in many mammals, a small, vestigial portion of the membrane remains in the corner of the eye. Some mammals, such as camels, polar bears, seals and aardvarks, have full nictitating membranes. Often called a third eyelid or haw, it may be referred to in scientific terminology as the plica semilunaris, membrana nictitans, or palpebra tertia.

The nasolacrimal duct carries tears from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity. The duct begins in the eye socket between the maxillary and lacrimal bones, from where it passes downwards and backwards. The opening of the nasolacrimal duct into the inferior nasal meatus of the nasal cavity is partially covered by a mucosal fold. Excess tears flow through nasolacrimal duct which drains into the inferior nasal meatus.

In medieval music, the rhythmic modes were set patterns of long and short durations. The value of each note is not determined by the form of the written note, but rather by its position within a group of notes written as a single figure called a "ligature", and by the position of the ligature relative to other ligatures. Modal notation was developed by the composers of the Notre Dame school from 1170 to 1250, replacing the even and unmeasured rhythm of early polyphony and plainchant with patterns based on the metric feet of classical poetry, and was the first step towards the development of modern mensural notation. The rhythmic modes of Notre Dame Polyphony were the first coherent system of rhythmic notation developed in Western music since antiquity.

The fimbriated fold of tongue, also plica fimbriata is a slight fold of the mucous membrane on the underside of the tongue which runs laterally on either side of the frenulum. The free edge of the fimbriated fold occasionally exhibits a series of fringe-like processes..
Pompano en Papillote is a dish created by Jules Alciatore at Antoine's Restaurant in New Orleans for a banquet honoring the Brazilian balloonist Alberto Santos-Dumont. The dish was based in turn on a dish that Jules's father Antoine Alciatore had created—Pompano Montgolfier--honoring the brothers who had created the first balloons. A filet of pompano is baked in a sealed parchment paper envelope with a white sauce of wine, shrimp, and crabmeat. With a bit of luck the steam will puff up the parchment a bit, suggesting a hot air balloon.

The plica semilunaris is a small fold of bulbar conjunctiva on the medial canthus of the eye. It functions during movement of the eye, to help maintain tear drainage via the lacrimal lake, and to permit greater rotation of the globe, for without the plica the conjunctiva would attach directly to the eyeball, restricting movement. It is the vestigial remnant of the nictitating membrane which is drawn across the eye for protection, and is present in other animals such as birds, reptiles, and fish, but is rare in mammals, mainly found in monotremes and marsupials. Its associated muscles are also vestigial. It is loose, thus eye movements are not restricted by it. Only one species of primate, the Calabar angwantibo, is known to have a functioning nictitating membrane.

The peritoneum of the anterior pelvic wall covers the superior surface of the bladder, and on either side of this viscus forms a depression, termed the paravesical fossa, which is limited laterally by the fold of peritoneum covering the ductus deferens.

The term Charters of Freedom is used to describe the three documents in early American history which are considered instrumental to its founding and philosophy. These documents are the United States Declaration of Independence, the Constitution, and the Bill of Rights. While the term has not entered particularly common usage, the room at the National Archives Building in Washington, D.C. that houses the three documents is called the Rotunda for the Charters of Freedom.
Plica syndrome is a condition that occurs when a plica becomes irritated, enlarged, or inflamed.
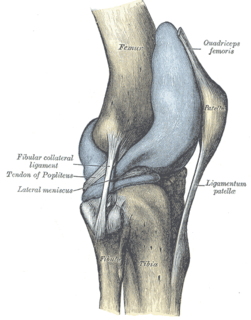
The articular capsule of the knee joint is wide and lax; thin in front and at the side; and contains the patella, ligaments, menisci, and bursae. The capsule consists of a synovial and a fibrous membrane separated by fatty deposits anteriorly and posteriorly.
The plica semilunaris is the thin upper part of the fold of mucous membrane in the supratonsillar fossa that reaches across between the two arches. A separate fold is called the plica triangularis which runs inferoposteriorly from the posterior surface of the palatoglossal arch to cover the inferior portion of the tonsil.

The tonsillar fossa is a space delineated by the triangular fold of the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches within the lateral wall of the oral cavity..

En papillote, or al cartoccio in Italian, is a method of cooking in which the food is put into a folded pouch or parcel and then baked. The parcel is typically made from folded parchment paper, but other material, such as a paper bag or aluminium foil, may be used. The parcel holds in moisture to steam the food. The pocket is created by overlapping circles of aluminum foil and parchment paper and then folding them tightly around the food to create a seal. A papillote should be opened at the table to allow people to smell the aroma when it opens.

The conservation and restoration of parchment constitutes the care and treatment of parchment materials which have cultural and historical significance. Typically undertaken by professional book and document conservators, this process can include preventative measures which protect against future deterioration as well as specific treatments to alleviate changes already caused by agents of deterioration.

Insulating glass (IG), more commonly known as double glazing, consists of two or three glass window panes separated by a vacuum or gas filled space to reduce heat transfer across a part of the building envelope.
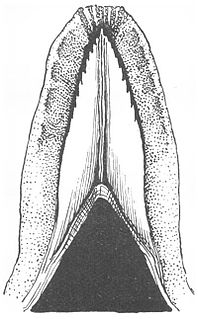
The sublingua ("under-tongue") is a muscular secondary tongue found below the primary tongue in tarsiers and living strepsirrhine primates, which includes lemurs and lorisoids. Although it is most fully developed in these primates, similar structures can be found in some other mammals, such as marsupials, treeshrews, and colugos. This "second tongue" lacks taste buds, and in lemuriforms, it is thought to be used to remove hair and other debris from the toothcomb, a specialized dental structure used to comb the fur during oral grooming.