
Compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was co-developed by Philips and Sony and released in 1982. The format was originally developed to store and play only sound recordings (CD-DA) but was later adapted for storage of data (CD-ROM). Several other formats were further derived from these, including write-once audio and data storage (CD-R), rewritable media (CD-RW), Video Compact Disc (VCD), Super Video Compact Disc (SVCD), Photo CD, PictureCD, CD-i, and Enhanced Music CD. The first commercially available audio CD player, the Sony CDP-101, was released October 1982 in Japan.

CD-R is a digital optical disc storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can be written once and read arbitrarily many times.
The International Federation of the Phonographic Industry (IFPI) is the organisation that represents the interests of the recording industry worldwide. It is a non-profit members' organisation registered in Switzerland and founded in Italy in 1933. It operates a Secretariat based in London, with regional offices in Brussels, Hong Kong and Miami.
Replication may refer to:

Mastering, a form of audio post production, is the process of preparing and transferring recorded audio from a source containing the final mix to a data storage device, the source from which all copies will be produced. In recent years digital masters have become usual, although analog masters, such as audio tapes, are still being used by the manufacturing industry, notably by a few engineers who have chosen to specialize in analog mastering.

In computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read and record, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives. Optical disc drives that are no longer in production include CD-ROM drive, CD writer drive, combo (CD-RW/DVD-ROM) drive, and DVD writer drive supporting certain recordable and rewritable DVD formats. As of 2015, DVD writer drive supporting all existing recordable and rewritable DVD formats is the most common for desktop PCs and laptops. There are also the DVD-ROM drive, BD-ROM drive, Blu-ray Disc combo (BD-ROM/DVD±RW/CD-RW) drive, and Blu-ray Disc writer drive.
An ISO image is a disk image of an optical disc. In other words, it is an archive file that contains everything that would be written to an optical disc, sector by sector, including the optical disc file system. ISO image files bear the .iso filename extension. The name ISO is taken from the ISO 9660 file system used with CD-ROM media, but what is known as an ISO image might also contain a UDF file system.

Extended Resolution Compact Disc (XRCD) is a mastering and manufacture process patented by JVC for producing Red Book compact discs. It was first introduced in 1995.
In computing, external storage comprises devices that store information outside a computer. Such devices may be permanently attached to the computer, may be removable or may use removable media.
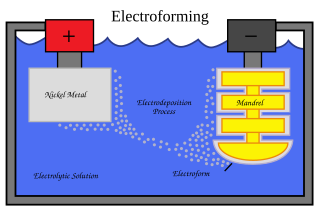
Electroforming is a metal forming process that forms parts through electrodeposition on a model, known in the industry as a mandrel. Conductive (metallic) mandrels are passivated (chemically) to preclude 'plating' and thereby to allow subsequent separation of the finished electroform. Non-conductive mandrels require the deposition of a conductive layer prior to electrodeposition. Conductive layers can be deposited chemically, or using vacuum deposition techniques. The outer surface of the mandrel forms the inner surface of the form.
DiscoVision is the name of several things related to the video LaserDisc format.
Disc rot is the tendency of CD or DVD or other optical discs to become unreadable because of physical or chemical deterioration. The causes of this effect vary from oxidation of the reflective layer, to physical scuffing and abrasion of disc surfaces or edges, including visible scratches, to other kinds of reactions with contaminants, to ultra-violet light damage and de-bonding of the adhesive used to adhere the layers of the disc together.

Compact disc manufacturing is the process by which commercial compact discs (CDs) are replicated in mass quantities using a master version created from a source recording. This may be either in audio form (CD-Audio) or data form (CD-ROM). This process is used in the mastering of read-only compact discs; CD-Rs, CD-RWs, and DVDs are made somewhat differently, though the methods are broadly similar.
CD publishing is the use of CD duplication systems to create a large number of unique discs. For instance, storing a unique serial number on each copy of a software application disc would be considered CD publishing.

Established in Taiwan in 1988, RITEK Corporation manufactures compact disk products such as CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-R, DVD-RW, DVD+R, DVD+RW, DVD-RAM, HD DVD, Blu-ray Disc and Blu-ray M-Disc, storage cards such as CF (CompactFlash) cards, SD cards and MMC cards (MultiMediaCard), memory stick and consumer electronics. Over recent years, RITEK also made inroads to green energy by manufacturing solar models and offering installation services for solar systems. Meanwhile, RITEK also produces solar cells and touch panel products such as PMOLED and ITO glass. RITEK has also developed and launched a few products in nano and biotechnology. The company's English name is a portmanteau of the words “right” and “technology”.
The preservation of optical media is essential because it is a resource in libraries, and stores audio, video, and computer data to be accessed by patrons. While optical discs are generally more reliable and durable than older media types, environmental conditions and/or poor handling can result in lost information. This article will introduce the different types of optical media discs and offer a discussion of strategies for preservation of these materials.
The Image Mastering Application Programming Interface, or IMAPI, is a component of Microsoft Windows operating system used for CD and DVD authoring and recording.

A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data. Computers can read—but not write to or erase—CD-ROMs, i.e. it is a type of read-only memory.
Blu-spec CD describes a Red Book CD manufactured by a process introduced by Sony Music Entertainment Japan in late 2008. Its name derives from the similar manufacturing process to that used to create Blu-ray Discs. Instead of a traditional infra-red laser, a blue laser is used for recording the pits on the CD master that is needed for disc replication. The blue laser purportedly creates more precise pits, which Sony claims reduces distortion in the optical read-out process.










