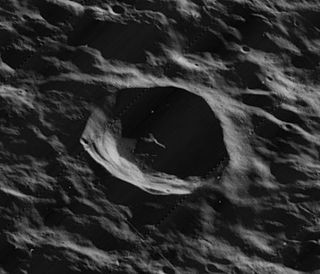
Lunar Orbiter 4 image | |
| Coordinates | 32°00′S85°12′W / 32.0°S 85.2°W Coordinates: 32°00′S85°12′W / 32.0°S 85.2°W |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 48 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 86° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Nathaniel S. Shaler |
Shaler is a lunar impact crater that lies on the southeast interior edge of the Montes Cordillera mountain ring that surrounds the immense Mare Orientale formation. It is located near the southwest limb of the Moon on the near side, and so is viewed nearly from on edge from the Earth. Just to the northwest of the crater is the slightly smaller crater Wright.

Lunar craters are impact craters on Earth's Moon. The Moon's surface has many craters, almost all of which were formed by impacts.

An impact crater is an approximately circular depression in the surface of a planet, moon, or other solid body in the Solar System or elsewhere, formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller body. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters range from small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth.

Montes Cordillera is a mountain range on the Moon. This feature forms the outer wall of peaks that surround the Mare Orientale impact basin, the inner ring being formed by the Montes Rook. The center of the range is located at selenographic coordinates 17.5° S, 81.6° W, and the diameter is 574 km (357 mi).
The long, irregular Vallis Bouvard valley begins at the southern rim of Shaler, and winds its way to the south-southeast towards the crater Baade. This is one of several such valleys that radiate away from the southeast edge of the Mare Orientale impact basin, the other two being Vallis Inghirami and Vallis Baade.
Vallis Bouvard is a 284-km-long valley on the Moon, centered at 38.3°S 83.1°W. It begins at the southern rim of the crater Shaler, and winds its way to the south-southeast towards Baade. This is one of several such valleys that radiate away from the southeast edge of the Mare Orientale circular impact basin, the other two being Vallis Inghirami and Vallis Baade. It was formed by a secondary crater chain. The valley was named after Alexis Bouvard.

Baade is a lunar impact crater that is located near the southwest limb of the Moon on the near side, to the southwest of the enormous Mare Orientale impact basin. The area to the east of this crater forms the junction between the 280-km-long Vallis Bouvard to the north and the narrower, 160-km-long Vallis Baade to the south-southeast. Both valleys radiate away from the impact basin to the north.

Vallis Inghirami is a valley on far side of the Moon which is a natural satellite of planet Earth. Diameter of the valley is about 145 km. Lunar co-ordinates of the valley are 43.8°S 72.2°W. Valley is named after Giovanni Inghirami. Valley was approved by IAU in 1964.
Shaler has been affected by its location on the southern edge of the Montes Cordillera, as the floor is rough and irregular, particularly toward the southwest where several small, parallel clefts appear in the surface. The rim is nearly circular, although slightly flattened along the south edge, and the edge remains sharply defined with little appearance of erosion.