
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a winter sport in which teams of two or four teammates make timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. The timed runs are combined to calculate the final score.

An exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton (endoskeleton) of, for example, a human. In usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of animals with exoskeletons include insects such as grasshoppers and cockroaches, and crustaceans such as crabs and lobsters. The shells of certain sponges and the various groups of shelled molluscs, including those of snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons and nautilus, are also exoskeletons. Some animals, such as the tortoise, have both an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton.

Skeleton is a winter sliding sport in which a person rides a small sled, known as a skeleton bobsled, down a frozen track while lying face down and head-first. The sport and the sled may have been named from the bony appearance of the sled.
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the body. It is composed of around 270 bones at birth – this total decreases to around 206 bones by adulthood after some bones get fused together. The bone mass in the skeleton reaches maximum density around age 21. The human skeleton can be divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton is formed by the vertebral column, the rib cage, the skull and other associated bones. The appendicular skeleton, which is attached to the axial skeleton, is formed by the shoulder girdle, the pelvic girdle and the bones of the upper and lower limbs.

A skeleton is a type of physically manifested undead often found in fantasy, gothic and horror fiction, and mythical art. Most are human skeletons, but they can also be from any creature or race found on Earth or in the fantasy world.
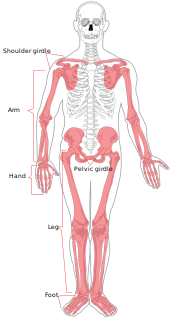
The appendicular skeleton is the portion of the skeleton of vertebrates consisting of the bones that support the appendages. The appendicular skeleton includes the skeletal elements within the limbs, as well as supporting pectoral and pelvic girdle. The word appendicular is the adjective of the noun appendage, which itself means a part that is joined to something larger.

The axial skeleton is the part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk of a vertebrate. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of six parts; the skull bones, the ossicles of the middle ear, the hyoid bone, the rib cage, sternum and the vertebral column. The axial skeleton together with the appendicular skeleton form the complete skeleton. Another definition of axial skeleton is the bones including the vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, ribs, and sternum.

{{Roopkund-trekking-guide|date=December 2018}}

The Skeleton Dance is a 1929 Silly Symphony animated short subject produced and directed by Walt Disney and animated by Ub Iwerks. In the film, four human skeletons dance and make music around a spooky graveyard—a modern film example of medieval European "danse macabre" imagery. It is the first entry in the Silly Symphony series.

Skeleton is a winter sport featured in the Winter Olympics where the competitor rides head-first and prone on a flat sled. It is normally run on an ice track that allows the sled to gain speed by gravity. It was first contested at the 1928 Winter Olympics in St. Moritz and again in 1948 Winter Olympics, after which it was discontinued as an Olympic sport. Skeleton was reintroduced at the 2002 Winter Olympics, with both men's and women's events, and has been held in each Winter Olympic competition since. Skeleton is so-named as the first metal sleds introduced in 1892 were said to resemble a human skeleton.

Gashadokuro are mythical creatures in Japanese mythology.
The International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Federation (IBSF), originally known by the French name Fédération Internationale de Bobsleigh et de Tobogganing (FIBT), is the international sports federation for bobsleigh and skeleton. It acts as an umbrella organization for 14 national bobsleigh and skeleton associations as of 2007. It was founded on 23 November 1923 by the delegates of Great Britain, France, Switzerland, Canada and the United States at the meeting of their first International Congress in Paris, France. In June 2015, it announced a name change from FIBT to IBSF. The federation's headquarters are in Lausanne, Switzerland.
The IBSF World Championships, part of the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Federation, have taken place on an annual basis in non-Winter Olympic years since 1930. A two-man event was included in 1931 with a combined championship occurring in 1947. Men's skeleton was introduced as a championship of its own in 1982 while women's bobsleigh and skeleton events were introduced in 2000. Both the women's bobsleigh and skeleton events were merged with the men's bobsleigh events at the 2004 championships. A mixed team event, consisting of one run each of men's skeleton, women's skeleton, 2-man bobsleigh, and 2-women bobsleigh debuted in 2007.

The Skeleton Crew is a fictional organization appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics.

The facial skeleton comprises the facial bones that may attach to build a portion of the skull. The remainder of the skull is the braincase.
The Skeleton World Cup season is a yearly competition first organized by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Federation since 1986–87. The women's version of this event debuted in 1996–97.

The Museum of Osteology, located in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States, North America, is a private museum devoted to the study of bones and skeletons (osteology). This museum displays over 350 skeletons from animal species from animals all over the world. With another 7000 specimens as part of the collection, but not on display, this is the largest privately held collection of osteological specimens in the world.

Harimau or Tiger Cave is a limestone cavern in the Indonesian island of Sumatra where the island's first known rock art has been discovered. The cave also held 66 skeletons of farmers from 3,000 years ago.















