This article does not cite any sources .(April 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
 2004 English Editions | |
| Author | Herman Kinder |
|---|---|
| Original title | Atlas zur Weltgeschichte |
| Illustrator | Werner Hilgemann |
| Country | United States |
| Language | English |
| Genre | Historical atlas |
| Publisher | Penguin Books |
Publication date | 1964 (German), 1974, 2004 |
| Media type | Paperback |
| ISBN | 978-0-14-101263-6 |
The Penguin Atlas of World History is a two-volume, paperback-sized historical atlas first published by Penguin Books in 1974, with the latest edition published in 2004. It was translated from a German atlas, Atlas zur Weltgeschichte by Hermann Kinder and Werner Hilgemann, originally published by Deutsche Taschenbuch Verlag ten years prior to the first English edition, in 1964.

A historical atlas is an atlas that includes historical maps and charts depicting the evolving geopolitical landscape. They are helpful in understanding historical context, the scope and scale of historical events and historical subjects, and macro-history. Some historical atlases try to present the entire history of the world, such as the Historical Atlas of the World, while others are more specialised, for only one time period or location, such as the Historical Atlas of the American West or The Historical Atlas of China. They may also include historical photographs and explanatory text or essays.

Penguin Books is a British publishing house. It was co-founded in 1935 by Sir Allen Lane, his brothers Richard and John, as a line of the publishers The Bodley Head, only becoming a separate company the following year. Penguin revolutionised publishing in the 1930s through its inexpensive paperbacks, sold through Woolworths and other high street stores for sixpence, bringing high-quality paperback fiction and non-fiction to the mass market. Penguin's success demonstrated that large audiences existed for serious books. Penguin also had a significant impact on public debate in Britain, through its books on British culture, politics, the arts, and science.

German is a West Germanic language that is mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, South Tyrol (Italy), the German-speaking Community of Belgium, and Liechtenstein. It is also one of the three official languages of Luxembourg and a co-official language in the Opole Voivodeship in Poland. The languages which are most similar to German are the other members of the West Germanic language branch: Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German/Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, and Yiddish. There are also strong similarities in vocabulary with Danish, Norwegian and Swedish, although those belong to the North Germanic group. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language, after English.
Volume 1 encompasses pre-history to the eve of the French Revolution, and Volume 2 includes the Revolution itself and extends to the Iraq War. The book is formatted such that maps appear on the left-hand page with accompanying textual notations on the right, as opposed to most larger-format atlases that feature irregular and mixed formatting of text and maps. However, time lines, such as one tracing the development of life, and organizational charts, such as a graphic depicting the workings of the United Nations according to its charter, are occasionally featured as well.

The French Revolution was a period of far-reaching social and political upheaval in France and its colonies beginning in 1789. The Revolution overthrew the monarchy, established a republic, catalyzed violent periods of political turmoil, and finally culminated in a dictatorship under Napoleon who brought many of its principles to areas he conquered in Western Europe and beyond. Inspired by liberal and radical ideas, the Revolution profoundly altered the course of modern history, triggering the global decline of absolute monarchies while replacing them with republics and liberal democracies. Through the Revolutionary Wars, it unleashed a wave of global conflicts that extended from the Caribbean to the Middle East. Historians widely regard the Revolution as one of the most important events in human history.

The Iraq War was a protracted armed conflict that began in 2003 with the invasion of Iraq by a United States-led coalition that overthrew the government of Saddam Hussein, in breach of international law. The conflict continued for much of the next decade as an insurgency emerged to oppose the occupying forces and the post-invasion Iraqi government. An estimated 151,000 to 600,000 or more Iraqis were killed in the first three to four years of conflict. The U.S. became re-involved in 2014 at the head of a new coalition; the insurgency and many dimensions of the civil armed conflict continue. The invasion occurred as part of a declared war against international terrorism and its sponsors under the administration of U.S. President George W. Bush following the September 11 terrorist attacks.
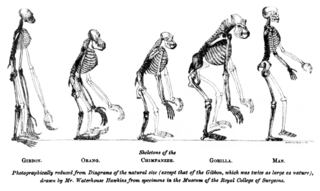
The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to the present. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years (Ga) ago and evidence suggests life emerged prior to 3.7 Ga. The similarities among all known present-day species indicate that they have diverged through the process of evolution from a common ancestor. Approximately 1 trillion species currently live on Earth of which only 1.75–1.8 million have been named and 1.6 million documented in a central database. These represent less than one percent of the species that have ever lived on earth.
The Atlas is also notable for Werner Hilgemann's unique cartographical style, which treats city and state names on maps as political/governing entities, allowing them to be graphically linked with other labels to show alliances and treaties, thereby adding an extra informational dimension.