International Tropical Timber Agreement, 1994 was drafted to ensure that by the year 2000 exports of tropical timber originated from sustainably managed sources and to establish a fund to assist tropical timber producers in obtaining the resources necessary to reach this objective.
It defined the mandate of the International Tropical Timber Organization.
Liberia is one of the poorest countries in the world, and its economy is extremely underdeveloped, largely due to the First Liberian Civil War in 1989-96. The civil war destroyed much of Liberia's economy, especially the infrastructure in and around Monrovia. The war also caused a brain drain and the loss of capital, as the civil war involved overthrowing the Americo-Liberian minority that ruled the country. Some returned during 1997, but many have not.
The economy of Samoa is dependent on agricultural exports, development aid and private financing from overseas. The country is vulnerable to devastating storms. Agriculture employs two-thirds of the labor force, and furnishes 9% of exports, featuring coconut cream, coconut oil and copra. Outside a large automotive wire harness factory, the manufacturing sector mainly processes agricultural products. Tourism is an expanding sector; more than 70,000 tourists visited the islands in 1996 and 120,000 in 2014. The Samoan Government has called for deregulation of the financial sector, encouragement of investment, and continued fiscal discipline. Observers point to the flexibility of the labor market as a basic strength factor for future economic advances.

Mahogany is a kind of wood—the straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus Swietenia, indigenous to the Americas and part of the pantropical chinaberry family, Meliaceae.
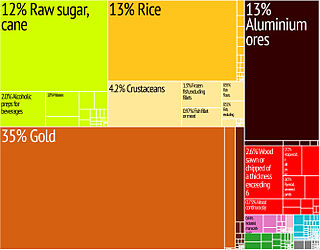
With a per capita gross domestic product of $8,300 in 2016 and an average GDP growth of 4.2% over the last decade. Guyana is one of the fastest developing countries in the Western Hemisphere. This is evident from the contrast between poor slum areas and elite residential areas with imperious mansions, often built within a few kilometers of one another.

A per capita GDP of $3,200 ranks Solomon Islands as a lesser developed nation. Over 75% of its labour force is engaged in subsistence farming and fishing.
Canadian historians until the 1980s tended to focus on economic history, including labour history. In part this is because Canada has had far fewer political or military conflicts than other societies. This was especially true in the first half of the twentieth century when economic history was overwhelmingly dominant. Many of the most prominent English Canadian historians from this period were economic historians, such as Harold Innis, Donald Creighton and Arthur R. M. Lower.
Scholars of Canadian history were heirs to the traditions that developed in Europe and the United States, but frameworks that worked well elsewhere often failed in Canada. The heavily Marxist influenced economic history that dominates Europe has little relevance to most of Canadian history. A focus on class, urban areas, and industry fails to address Canada's rural and resource based economy. Similarly, the monetarist school that is dominant in the United States also has been difficult to transfer north of the border.
Muscogee, is a ghost town located twenty miles northwest of Pensacola, Florida, United States, in Escambia County, along the Perdido River. Named after the Muscogee Lumber Company, formed by Georgia lumber men, the European-American town was founded in 1857 by a group of lumbermen to harvest timber from the surrounding pine forests. They and the following company clearcut the timber, and once the forests were gone, lumbering ended in this area.
The timber industry is a significant contributor to the economy of Russia, worth around 20 billion dollars per year.
Russian Forest Industry - a set of Russian industries related to wood harvesting and processing. One of the oldest sectors of the economy.

Lweje is a town in Kachin State in north-eastern Burma near the border with Longchuan County, Yunnan Province, China. It is one of the 10 border trade points with 4 neighbouring countries opened in 2002 by the military regime.
The trade relationship of the United States with Canada was the second largest in the world after China and the United States. In 2016, the goods and services trade between the two countries totaled $627.8 billion. U.S. exports were $320.1 billion, while imports were $307.6 billion. The United States had a $12.5 billion trade surplus with Canada in 2016. Canada has historically held a trade deficit with the United States in every year since 1985 in net trade of goods, excluding services. The trade relationship between the two countries crosses all industries and is vitally important to both nations' success as each country is one of the largest trade partners of the other.

Deforestation in Laos is a major environmental concern, with Laos losing forest area to legal and illegal logging.

The economy of the U.S. state of Oregon is made up of a number of sectors. During the 1990s and 2000s, Oregon has attempted to transition its economy from one based on natural resources to one based on a mix of manufacturing, services, and high technology.

Forestry in New Zealand has a history starting with European settlement in the 19th century and is now an industry worth seven percent of annual revenue. Much of the original native forest cover was burnt off and logged, however forests have been extensively planted, predominantly with fast-growing cultivars of the Monterey Pine. Wood chips, whole logs, lumber and paper products are exported from New Zealand.
Vanport Manufacturing is a Boring, Oregon based logging company that exports lumber from the United States to foreign countries. Started in 1967, the company originally exported timber to Japan before expanding markets to China, Taiwan, and Russia. Vanport took over operations of the sawmill on the Warm Springs Indian Reservation in 2008. As of 2012 the company had 208 employees.
A resource-based economy or natural-resource-based economy is the economy of a country whose gross national product or gross domestic product to a large extent comes from natural resources.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1819 was unanimously adopted on 18 June 2008.

The Ministry of Primary Industries, abbreviated MPI, is a ministry of the Government of Malaysia that is responsible for plantation and commodities: palm oil, rubber, timber, furniture, cocoa, pepper, kenaf, tobacco.
Ekin is an unincorporated community in Hamilton and Tipton counties, in the U.S. state of Indiana.











