 USC&GS Ogden conducting current surveys in Boston Harbor. | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Ogden |
| Namesake: | Herbert Gouverneur Ogden (1846-1906) |
| Builder: | Canton Lumber Company, Baltimore, Maryland |
| Cost: | $12,000 USD |
| Completed: | 1919 |
| In service: | 1919 |
| Out of service: | 1944 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Survey Launch |
| Length: | 60 ft (18 m) |
| Beam: | 14.8 ft (4.5 m) |
| Draft: | 4.6 ft (1.4 m) |
| Propulsion: | Two gasoline engines |
USC&GS Ogden was a launch that served as a survey ship in the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey from 1919 to 1944. She was the only Coast and Geodetic Survey ship to bear the name.

A launch is an open motorboat. The forward part of the launch may be covered. Prior to the era of engines on small craft, a launch was the largest boat carried on a sailing vessel, powered by sail or by oars. In competitive rowing, a launch is a motorized boat used by the coach during training.
Ogden was built by the Canton Lumber Company at Baltimore, Maryland, in 1919. She entered Coast and Geodetic Survey service that year.

Maryland is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east. The state's largest city is Baltimore, and its capital is Annapolis. Among its occasional nicknames are Old Line State, the Free State, and the Chesapeake Bay State. It is named after the English queen Henrietta Maria, known in England as Queen Mary.
Ogden spent her career on the United States East Coast. She worked as a wire-drag hydrographic survey vessel with the Coast and Geodetic Survey launch USC&GS Marindin.

Hydrographic survey is the science of measurement and description of features which affect maritime navigation, marine construction, dredging, offshore oil exploration/offshore oil drilling and related activities. Strong emphasis is placed on soundings, shorelines, tides, currents, seabed and submerged obstructions that relate to the previously mentioned activities. The term hydrography is used synonymously to describe maritime cartography, which in the final stages of the hydrographic process uses the raw data collected through hydrographic survey into information usable by the end user.
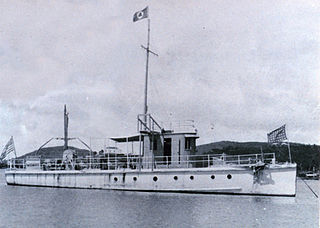
USC&GS Marindin was a launch that served as a survey ship in the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey from 1919 to 1944. She was the only Coast and Geodetic Survey ship to bear the name.
Ogden was retired from Coast and Geodetic Survey service in 1944.

















