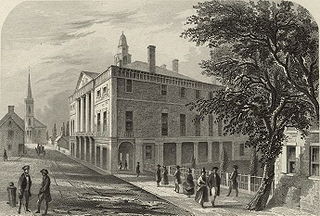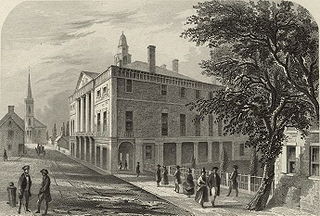
The 1st United States Congress, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met from March 4, 1789, to March 4, 1791, during the first two years of George Washington's presidency, first at Federal Hall in New York City and later at Congress Hall in Philadelphia. With the initial meeting of the First Congress, the United States federal government officially began operations under the new frame of government established by the 1787 Constitution. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 of the Constitution. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority. Twelve articles of amendment to the Constitution were passed by this Congress and sent to the states for ratification; the ten ratified as additions to the Constitution on December 15, 1791, are collectively known as the Bill of Rights, with an additional amendment ratified more than two centuries later to become the Twenty-seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution.

The 2nd United States Congress, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met at Congress Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from March 4, 1791, to March 4, 1793, during the third and fourth years of George Washington's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 of the United States Constitution. Additional House seats were assigned to the two new states of Vermont and Kentucky. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority.

The 28th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1843, to March 4, 1845, during the third and fourth years of John Tyler's presidency. The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the Sixth Census of the United States in 1840. The Senate had a Whig majority, and the House had a Democratic majority.

The 54th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1895, to March 4, 1897, during the last two years of Grover Cleveland's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Eleventh Census of the United States in 1890. The House had a Republican majority, and the Republicans were the largest party in the Senate.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 26th Congress were held during President Martin Van Buren's term at various dates in different states from July 1838 to November 1839.

In the United States House of Representatives elections in 1828 and 1829, the Jacksonians soundly took control of the presidency, with Andrew Jackson's victory, and greatly increased their majority in Congress. Outgoing President John Quincy Adams's unpopularity played a major role in the Jacksonian pick-up, as did the perception of the Anti-Jacksonian Party as urban and elitist. Major increases in suffrage also heightened Jacksonian wins, as newly enfranchised voters tended to associate with Jacksonian principles. The Anti-Masonic Party, a single issue faction based on distrust of Freemasonry, became the first third party in American history to garner seats in the House.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 17th Congress were held at various dates in different states between July 1820 and August 1821 as President James Monroe won reelection unopposed.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 3rd Congress were held in 1792 and 1793, coinciding with the re-election of George Washington as President. While Washington ran for president as an independent, his followers formed the nation's first organized political party, the Federalist Party, whose members and sympathizers are identified as pro-Administration on this page. In response, followers of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison created the opposition Democratic-Republican Party, who are identified as anti-Administration on this page. The Federalists promoted urbanization, industrialization, mercantilism, centralized government, and a broad interpretation of the United States Constitution. In contrast, Democratic-Republicans supported the ideal of an agrarian republic made up of self-sufficient farmers and small, localized governments with limited power.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 2nd Congress took place in 1790 and 1791, in the middle of President George Washington's first term. While formal political parties still did not exist, coalitions of pro-Washington (pro-Administration) representatives and anti-Administration representatives each gained two seats as a result of the addition of new states to the union.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 1st Congress were held in 1788 and 1789, coinciding with the election of George Washington as first President of the United States. The dates and methods of election were set by the states. Actual political parties did not yet exist, but new members of Congress were informally categorized as either "pro-Administration" or "anti-Administration".
The United States Senate elections of 1790 and 1791 were the second series of elections of senators in the United States. In these elections, terms were up for the nine senators in Class 1. As of these elections, formal organized political parties had yet to form in the United States, but two political factions were present: The coalition of senators who supported President George Washington's administration were known as the Pro-Administration Party, and the senators against him as the Anti-Administration Party.

The 1789 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held on March 3 and 4, 1789, to elect 6 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the 1st United States Congress.

The 1790 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 27 to 29, 1790, to elect six U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives.

The 1793 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held in January 1793, to elect 10 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives.

The 1798 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 24 to 26, 1798, to elect ten U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 6th United States Congress.

The 1814 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 26 to 28, 1814, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 14th United States Congress.

The 1816 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 23 to 25, 1816, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 15th United States Congress. At the same time, a vacancy was filled in the 14th United States Congress.

The 1821 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 24 to 26, 1821, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 17th United States Congress.
James Townsend was an American politician from New York.
Elections for the United States House of Representatives for the 2nd Congress were held in Massachusetts beginning October 4, 1790, with subsequent elections held in four districts due to a majority not being achieved on the first ballot.