
USS Mississippi (BB-41/AG-128), the second of three members of the New Mexico class, was the third ship of the United States Navy named in honor of the 20th state. The ship was built at the Newport News Shipbuilding Company of Newport News, Virginia, from her keel laying in April 1915, her launching in January 1917, and her commissioning in December that year. She was armed with a battery of twelve 14-inch (356 mm) guns in four three-gun turrets, and was protected by heavy armor plate, with her main belt armor being 13.5 inches (343 mm) thick.

The Fletcher class was a class of destroyers built by the United States during World War II. The class was designed in 1939, as a result of dissatisfaction with the earlier destroyer leader types of the Porter and Somers classes. Some went on to serve during the Korean War and into the Vietnam War.

The Benham class of ten destroyers was built for the United States Navy (USN). They were part of a series of USN destroyers limited to 1,500 tons standard displacement by the London Naval Treaty and built in the 1930s. The class was laid down in 1936-1937 and all were commissioned in 1939. Much of their design was based on the immediately preceding Gridley and Bagley-class destroyers. Like these classes, the Benhams were notable for including sixteen 21-inch (533 mm) torpedo tubes, the heaviest torpedo armament ever on US destroyers. They introduced a new high-pressure boiler that saved space and weight, as only three of the new boilers were required compared to four of the older designs. The class served extensively in World War II in the Atlantic, Mediterranean, and Pacific theaters, including Neutrality Patrols in the Atlantic 1940-1941. Sterett received the United States Presidential Unit Citation for the Battle of Guadalcanal and the Battle of Vella Gulf, and the Philippine Republic Presidential Unit Citation for her World War II service. Two of the class were lost during World War II, three would be scrapped in 1947, while the remaining five ships would be scuttled after being contaminated from the Operation Crossroads atomic bomb tests at Bikini Atoll in the Pacific.

The Clemson class was a series of 156 destroyers which served with the United States Navy from after World War I through World War II.

The Allen M. Sumner class was a group of 58 destroyers built by the United States during World War II. Another twelve ships were completed as destroyer minelayers. Often referred to as simply the Sumner class, this class was characterized by their twin 5-inch/38 caliber gun mounts, dual rudders, additional anti-aircraft weapons, and many other advancements over the previous Fletcher class. The Allen M. Sumner design was extended 14 feet (4.3 m) amidships to become the Gearing class, which was produced in larger numbers.

The Porter-class destroyers were a class of eight 1,850-ton large destroyers in the United States Navy. Like the preceding Farragut-class, their construction was authorized by Congress on 26 April 1916, but funding was delayed considerably. They were designed based on a 1,850-ton standard displacement limit imposed by the London Naval Treaty; the treaty's tonnage limit allowed 13 ships of this size, and the similar Somers class was built later to meet the limit. The first four Porters were laid down in 1933 by New York Shipbuilding in Camden, New Jersey, and the next four in 1934 at Bethlehem Steel Corporation in Quincy, Massachusetts. All were commissioned in 1936 except Winslow, which was commissioned in 1937. They were built in response to the large Fubuki-class destroyers that the Imperial Japanese Navy was building at the time and were initially designated as flotilla leaders. They served extensively in World War II, in the Pacific War, the Atlantic, and in the Americas. Porter was the class' only loss, in the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands on 26 October 1942.

The Somers-class destroyer was a class of five 1850-ton United States Navy destroyers based on the Porter class. They were answers to the large destroyers that the Japanese navy was building at the time, and were initially intended to be flotilla leaders. They were laid down 1935-1936 and commissioned 1937-1939. They were built to round out the thirteen destroyers of 1,850 tons standard displacement allowed by the tonnage limits of the London Naval Treaty, and were originally intended to be repeat Porters. However, new high-pressure, high-temperature boilers became available, allowing the use of a single stack. This combined with weight savings allowed an increase from two quadruple centerline torpedo tube mounts to three. However, the Somers class were still over-weight and top-heavy. This was the first US destroyer class to use 600 psi (4,100 kPa) steam superheated to 850 °F (454 °C), which became standard for US warships built in the late 1930s and World War II.

A dual-purpose gun is a naval artillery mounting designed to engage both surface and air targets.
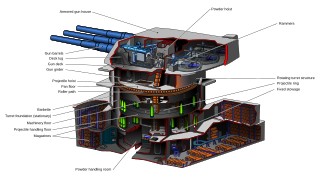
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a gun or group of guns, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted groups of similar large-caliber naval rifles. With the evolution of technology the term has come to encompass guided missiles as a vessel's principal offensive weapon, deployed both on surface ships and submarines.

The 3-inch gun M1918 was a United States 3-inch anti-aircraft gun that entered service in 1918 and served until it was largely superseded by the 3-inch anti-aircraft gun M3 in 1930, though the M1918 remained with some National Guard units until early in World War II. The M3 was subsequently replaced by the M1 90mm AA gun early in World War II, primarily during 1942. The M3 3" gun was later adapted for the anti-tank role, serving as the main armament of the M10 tank destroyer during World War II.

The Mark 12 5"/38 caliber gun was a United States naval gun. The gun was installed into Single Purpose and Dual Purpose mounts used primarily by the US Navy. On these 5" mounts, Single Purpose (SP) means that the mount is limited to 35° elevation with no provision for AA shell fuze setters, and is designed to fire at surface targets only. Dual Purpose (DP) means that it is designed to be effective against both surface and aircraft targets because it can elevate to 85° and has on mount AA shell fuze setters. The 38 caliber barrel was a mid-length compromise between the previous United States standard 5"/51 low-angle gun and 5"/25 anti-aircraft gun. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile 5 inches (127 mm) in diameter, and the barrel was 38 calibers long, making the 5"/38 dual purpose midway in barrel length between the 5"/51 surface-to-surface and the 5"/25 anti-aircraft guns. The increased barrel length provided greatly improved performance in both anti-aircraft and anti-surface roles compared to the 5"/25 gun. However, except for the barrel length and the use of semi-fixed ammunition, the 5"/38 gun was derived from the 5"/25 gun. Both weapons had power ramming, which enabled rapid fire at high angles against aircraft. The 5"/38 entered service on USS Farragut, commissioned in 1934. The base ring mount, which improved the effective rate of fire, entered service on USS Gridley, commissioned in 1937.
A 5-inch gun is a gun with a 5-inch bore. Examples include these naval weapons:

The 6"/47 caliber Mark 16 gun was used in the main batteries of several pre-war and World War II US Navy light cruisers. They were primarily mounted in triple turrets and used against surface targets. The 6"/47 caliber Mark 16DP gun was a dual purpose fitting of the Mark 16 for use against aircraft as well as surface ships. It was installed in the post-war Worcester-class light cruisers and the anti-aircraft gunnery training ship Mississippi.

The 4"/50 caliber gun was the standard low-angle, quick-firing gun for United States, first appearing on the monitor Arkansas and then used on "Flush Deck" destroyers through World War I and the 1920s. It was also the standard deck gun on S-class submarines, and was used to rearm numerous submarines built with 3-inch (76 mm) guns early in World War II. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile 4-inch (102 mm) in diameter, and the barrel was 50 calibers long.

The 5"/25 caliber gun entered service as the standard heavy anti-aircraft (AA) gun for United States Washington Naval Treaty cruisers commissioned in the 1920s and 1930s. The goal of the 5"/25 design was to produce a heavy AA gun that was light enough to be rapidly trained manually. The gun was also mounted on pre-World War II battleships and aircraft carriers until replaced by the standard dual-purpose 5"/38 caliber gun, which was derived from the 5"/25 and was similar except for the barrel length. Guns removed from battleships were probably converted for submarine use by late 1943, while a purpose-built variant for submarines was available in mid-1944, and was widely used by them. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile 5 inches (127 mm) in diameter, and the barrel was 25 calibers long.

A deck gun is a type of naval artillery mounted on the deck of a submarine. Most submarine deck guns were open; however, a few larger submarines placed these guns in a turret.

The QF 5.25-inch Mark I gun was the heaviest dual-purpose gun used by the Royal Navy during the Second World War. Although considered less than completely successful, it saw extensive service. 267 guns were built.

The 3"/23 caliber gun was the standard anti-aircraft gun for United States destroyers through World War I and the 1920s. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile 3 inches (76 mm) in diameter, and the barrel was 23 calibers long

The 12.7 cm SK C/34 was a German medium-caliber naval gun deployed on destroyers from 1934 through the Second World War. Some of these guns remained in service until 2003 in the coastal defense units of Norway.





















