Related Research Articles

Cyprus, officially called the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. It is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean and is located south of Turkey; west of Syria; northwest of the Gaza Strip, Israel, and Lebanon; north of Egypt; and southeast of Greece. The country's capital and largest city is Nicosia.

The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution of 1821 or Greek Revolution, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by the British Empire, France, and Russia, while the Ottomans were aided by their North African vassals, particularly the eyalet of Egypt. The war led to the formation of modern Greece. The revolution is celebrated by Greeks around the world as independence day on 25 March.

The Church of Cyprus is one of the autocephalous Greek Orthodox churches that together with other Eastern Orthodox churches form the communion of the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is one of the oldest Eastern Orthodox autocephalous churches; it claims to have always been independent, although it may have been subject to the Church of Antioch before its autocephaly was recognized in 431 at the Council of Ephesus. The bishop of the ancient capital, Salamis was constituted metropolitan by Emperor Zeno, with the title archbishop.

Enosis is the movement of various Greek communities that live outside Greece for incorporation of the regions that they inhabit into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea, an irredentist concept of a Greek state that dominated Greek politics following the creation of modern Greece in 1830. The Megali Idea called for the annexation of all ethnic Greek lands, parts of which had participated in the Greek War of Independence in the 1820s but were unsuccessful and so remained under foreign rule.

The Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922 was fought between Greece and the Turkish National Movement during the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire in the aftermath of World War I, between May 1919 and October 1922.
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks are mostly ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,000 Turkish settlers were given land once they arrived in Cyprus. Additionally, many of the island's local Christians converted to Islam during the early years of Ottoman rule. Nonetheless, the influx of mainly Muslim settlers to Cyprus continued intermittently until the end of the Ottoman period. Today, while Northern Cyprus is home to a significant part of the Turkish Cypriot population, the majority of Turkish Cypriots live abroad, forming the Turkish Cypriot diaspora. This diaspora came into existence after the Ottoman Empire transferred the control of the island to the British Empire, as many Turkish Cypriots emigrated primarily to Turkey and the United Kingdom for political and economic reasons.

The Eyalet of Cyprus was an eyalet (province) of the Ottoman Empire made up of the island of Cyprus, which was annexed into the Empire in 1571. The Ottomans changed the way they administered Cyprus multiple times. It was a sanjak (sub-province) of the Eyalet of the Archipelago from 1670 to 1703, and again from 1784 onwards; a fief of the Grand Vizier ; and again an eyalet for the short period from 1745 to 1748.

This article is about the history of Cyprus from 1878 to the present.

The Turkish invasion of Cyprus was launched on 20 July 1974, following the Cypriot coup d'état on 15 July 1974.

Archbishop Kyprianos of Cyprus was the head of the Cypriot Orthodox Church in the early 19th century at the time that the Greek War of Independence broke out.

Gregory V was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 1797 to 1798, from 1806 to 1808 and from 1818 to 1821. He was an ethnic Greek. He was responsible for much restoration work to the Patriarchal Cathedral of St George, which had been badly damaged by fire in 1738.
This is a timeline of modern Greek history.
Several distinct periods of Cypriot intercommunal violence involving the two main ethnic communities, Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots, marked mid-20th century Cyprus. These included the Cyprus Emergency of 1955–59 during British rule, the post-independence Cyprus crisis of 1963–64, and the Cyprus crisis of 1967. Hostilities culminated in the 1974 de facto division of the island along the Green Line following the Turkish invasion of Cyprus. The region has been relatively peaceful since then, but the Cyprus dispute has continued, with various attempts to solve it diplomatically having been generally unsuccessful.

There were numerous massacres during the Greek War of Independence (1821-1829) perpetrated by both the Ottoman forces and the Greek revolutionaries. The war was characterized by a lack of respect for civilian life, and prisoners of war on both sides of the conflict. Massacres of Greeks took place especially in Ionia, Crete, Constantinople, Macedonia and the Aegean islands. Turkish, Albanian, Greeks, and Jewish populations, who were identified with the Ottomans inhabiting the Peloponnese, suffered massacres, particularly where Greek forces were dominant. Settled Greek communities in the Aegean Sea, Crete, Central and Southern Greece were wiped out, and settled Turkish, Albanian, Greeks, and smaller Jewish communities in the Peloponnese were destroyed.
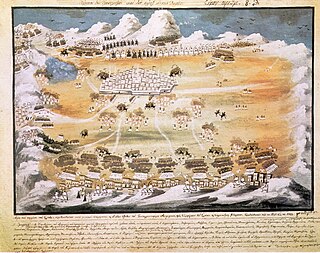
The siege of Tripolitsa, also known as the fall of Tripolitsa and in Turkish sources as the Tripolitsa massacre, was an early victory of the revolutionary Greek forces in the summer of 1821 during the Greek War of Independence, which had begun earlier that year, against the Ottoman Empire. Tripolitsa was an important target, because it was the administrative center of the Ottomans in the Peloponnese.
Marathovounos is a village in the Famagusta District of central Cyprus. It is under the de facto control of Northern Cyprus.
The Constantinople massacre of 1821 was orchestrated by the authorities of the Ottoman Empire against the Greek community of Constantinople in retaliation for the outbreak of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1830). As soon as the first news of the Greek uprising reached the Ottoman capital, there occurred mass executions, pogrom-type attacks, destruction of churches, and looting of the properties of the city's Greek population. The events culminated with the hanging of the Ecumenical Patriarch, Gregory V and the beheading of the Grand Dragoman, Konstantinos Mourouzis.
This is a timeline of the presence of Eastern Orthodoxy in Greece from 1821 to 1924. The history of Greece traditionally encompasses the study of the Greek people, the areas they ruled historically, as well as the territory now composing the modern state of Greece.