
Aluminium is a chemical element; it has symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than that of other common metals; about one-third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, forming a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, nonmagnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope: 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the twelfth-most common element in the universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiometric dating.

An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, opacity, and luster, but may have properties that differ from those of the pure metals, such as increased strength or hardness. In some cases, an alloy may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the mixture imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength.

A metal is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile and malleable. These properties are the result of the metallic bond between the atoms or molecules of the metal.

Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.

Scandium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanides. It was discovered in 1879 by spectral analysis of the minerals euxenite and gadolinite from Scandinavia.

Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron, copper, silver, tin, lead and zinc. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil fuel source of carbon, such as carbon monoxide from incomplete combustion of coke—or, in earlier times, of charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures as the chemical potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide is lower than that of the bonds in the ore.

An alum is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double sulfate salt of aluminium with the general formula XAl(SO
4)
2·12 H
2O, such that X is a monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the formula KAl(SO
4)
2·12 H
2O. Other alums are named after the monovalent ion, such as sodium alum and ammonium alum.
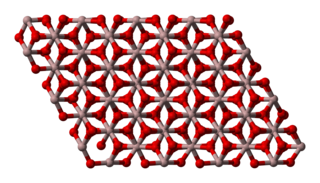
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula Al2O3. It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, or alundum in various forms and applications. It occurs naturally in its crystalline polymorphic phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire. Al2O3 is significant in its use to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point.

The boron group are the chemical elements in group 13 of the periodic table, consisting of boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl) and nihonium (Nh). This group lies in the p-block of the periodic table. The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three valence electrons. These elements have also been referred to as the triels.
A period 5 element is one of the chemical elements in the fifth row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fifth period contains 18 elements, beginning with rubidium and ending with xenon. As a rule, period 5 elements fill their 5s shells first, then their 4d, and 5p shells, in that order; however, there are exceptions, such as rhodium.

Slag is a by-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and recycled metals. Slag is mainly a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous, ferroalloy or non-ferrous/base metals. Within these general categories, slags can be further categorized by their precursor and processing conditions.

Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges down to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry.
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflective surface, the process can also involve roughening as in satin, matte or beaded finishes. In short, the ceramics which are used to cut, grind and polish other softer materials are known as abrasives.

Potassium alum, potash alum, or potassium aluminium sulfate is a chemical compound: the double sulfate of potassium and aluminium, with chemical formula KAl(SO4)2. It is commonly encountered as the dodecahydrate, KAl(SO4)2·12H2O. It crystallizes in an octahedral structure in neutral solution and cubic structure in an alkali solution with space group P a −3 and lattice parameter of 12.18 Å. The compound is the most important member of the generic class of compounds called alums, and is often called simply alum.

Cupellation is a refining process in metallurgy in which ores or alloyed metals are treated under very high temperatures and subjected to controlled operations to separate noble metals, like gold and silver, from base metals, like lead, copper, zinc, arsenic, antimony, or bismuth, present in the ore. The process is based on the principle that precious metals typically oxidise or react chemically at much higher temperatures than base metals. When they are heated at high temperatures, the precious metals remain apart, and the others react, forming slags or other compounds.

Antimony(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb2O3. It is the most important commercial compound of antimony. It is found in nature as the minerals valentinite and senarmontite. Like most polymeric oxides, Sb2O3 dissolves in aqueous solutions with hydrolysis. A mixed arsenic-antimony oxide occurs in nature as the very rare mineral stibioclaudetite.
In metallurgy, non-ferrous metals are metals or alloys that do not contain iron in appreciable amounts.
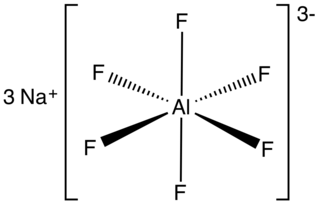
Sodium hexafluoroaluminate is an inorganic compound with formula Na3AlF6. This white solid, discovered in 1799 by Peder Christian Abildgaard (1740–1801), occurs naturally as the mineral cryolite and is used extensively in the industrial production of aluminium metal. The compound is the sodium (Na+) salt of the hexafluoroaluminate (AlF63−) ion.

Colored gold is the name given to any gold that has been treated using techniques to change its natural color. Pure gold is slightly reddish yellow in color, but colored gold can come in a variety of different colors by alloying it with different elements.

Aluminium metal is very rare in native form, and the process to refine it from ores is complex, so for most of human history it was unknown. However, the compound alum has been known since the 5th century BCE and was used extensively by the ancients for dyeing. During the Middle Ages, its use for dyeing made it a commodity of international commerce. Renaissance scientists believed that alum was a salt of a new earth; during the Age of Enlightenment, it was established that this earth, alumina, was an oxide of a new metal. Discovery of this metal was announced in 1825 by Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted, whose work was extended by German chemist Friedrich Wöhler.

















