
The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the United States. The Constitution, originally comprising seven articles, delineates the national frame of government. Its first three articles embody the doctrine of the separation of powers, whereby the federal government is divided into three branches: the legislative, consisting of the bicameral Congress ; the executive, consisting of the President ; and the judicial, consisting of the Supreme Court and other federal courts. Articles Four, Five and Six embody concepts of federalism, describing the rights and responsibilities of state governments, the states in relationship to the federal government, and the shared process of constitutional amendment. Article Seven establishes the procedure subsequently used by the thirteen States to ratify it. It is regarded as the oldest written and codified national constitution in force.

The Constitution Party, previously known as the U.S. Taxpayers' Party, is a national political party in the United States. The idea that the principles and intents of the U.S. Constitution remain relevant in human relations was the origin of the 1991 founding. Founding members included 2016 presidential candidate Darrell Castle and former acting Office of Economic Opportunity Director Howard Phillips. The party platform is based on originalist interpretations of the Constitution and shaped by principles it finds set forth in the Declaration of Independence, Bill of Rights, Constitution and the Bible.

USS Constitution, also known as Old Ironsides, is a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy named by President George Washington after the United States Constitution. She is the world's oldest commissioned naval vessel still afloat. She was launched in 1797, one of six original frigates authorized for construction by the Naval Act of 1794 and the third constructed. Joshua Humphreys designed the frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so Constitution and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. She was built at Edmund Hartt's shipyard in the North End of Boston, Massachusetts. Her first duties were to provide protection for American merchant shipping during the Quasi-War with France and to defeat the Barbary pirates in the First Barbary War.

The President of India is the ceremonial head of state of India and the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces.

The Federal Government of the United States is the national government of the United States, a federal republic in North America, composed of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and several island possessions. The federal government is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the President, and the federal courts, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court.

A commander-in-chief, sometimes also called supreme commander, is the person that exercises supreme command and control over an armed forces or a military branch. As a technical term, it refers to military competencies that reside in a country's executive leadership – a head of state or a head of government.
A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions (codicils), thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document.
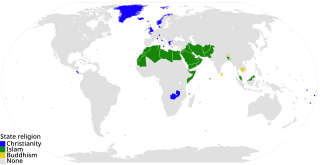
A state religion is a religious body or creed officially endorsed by the state. A state with an official religion, while not secular, is not necessarily a theocracy, a country whose rulers have both secular and spiritual authority. State religions are official or government-sanctioned establishments of a religion, but the state does not need be under the control of the religion nor is the state-sanctioned religion necessarily under the control of the state.

The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework demarcating fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens. It is the longest written constitution of any country on earth. B. R. Ambedkar, chairman of the drafting committee, is widely considered to be its chief architect.

The President of Pakistan, is the head of state of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the civilian Commander-in-Chief of the Pakistan Armed Forces, per the Constitution of Pakistan. The office-holder represents the "unity of the Republic". The current President of Pakistan is Arif Alvi.

The Prime Minister of Pakistan is the head of government of Pakistan and designated as the "chief executive of the Republic".
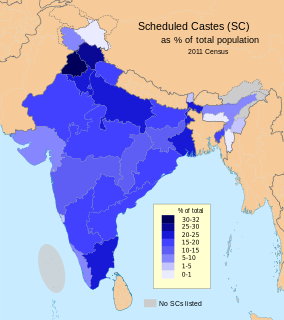
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of historically disadvantaged people in India. The terms are recognised in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes. The people in scheduled castes are essentially the lowest part of Hindu society.
Article 370 of the Indian constitution is an article that gives autonomous status to the state of Jammu and Kashmir. The article is drafted in Part XXI of the Constitution: Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions. The Constituent Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir, after its establishment, was empowered to recommend the articles of the Indian constitution that should be applied to the state or to abrogate the Article 370 altogether. After the J&K Constituent Assembly later created the state's constitution and dissolved itself without recommending the abrogation of Article 370, the article was deemed to have become a permanent feature of the Indian Constitution.

The United States Bill of Rights comprises the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. Proposed following the often bitter 1787–88 debate over ratification of Constitution, and written to address the objections raised by Anti-Federalists, the Bill of Rights amendments add to the Constitution specific guarantees of personal freedoms and rights, clear limitations on the government's power in judicial and other proceedings, and explicit declarations that all powers not specifically granted to the U.S. Congress by the Constitution are reserved for the states or the people. The concepts codified in these amendments are built upon those found in earlier documents, especially the Virginia Declaration of Rights (1776), as well as the English Bill of Rights (1689) and the Magna Carta (1215).

In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are currently 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory and shares its sovereignty with the federal government. Due to this shared sovereignty, Americans are citizens both of the federal republic and of the state in which they reside. State citizenship and residency are flexible, and no government approval is required to move between states, except for persons restricted by certain types of court orders. Four states use the term commonwealth rather than state in their full official names.
A union territory is a type of administrative division in the Republic of India. Unlike the states of India, which have their own governments, union territories are federal territories ruled directly by the union government, hence the name "union territory"














