
Temnospondyli or temnospondyls is a diverse ancient order of small to giant tetrapods — often considered primitive amphibians — that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian and Triassic periods, with fossils being found on every continent. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods, but all had gone extinct by the Late Cretaceous. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are amphibians, many had characteristics such as scales and armour-like bony plates that distinguish them from the modern soft-bodied lissamphibians.

In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between 251.2 Ma and 247.2 Ma. The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian.
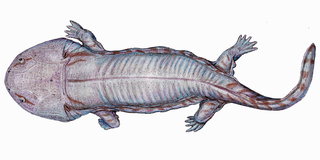
The Stereospondyli are a group of extinct temnospondyl amphibians that existed primarily during the Mesozoic period. They are known from all seven continents and were common components of many Triassic ecosystems, likely filling a similar ecological niche to modern crocodilians prior to the diversification of pseudosuchian archosaurs.

Trematosaurus is an extinct genus of trematosaurid temnospondyl amphibian found in Germany and Russia. It was first named by Hermann Burmeister in 1849 and the type species is Trematosaurus brauni.
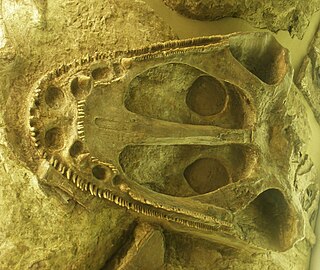
Mastodonsauridae is a family of capitosauroid temnospondyls. Fossils belonging to this family have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia. The family Capitosauridae is synonymous with Mastodonsauridae.

Microposaurus is an extinct genus of trematosaurid temnospondyl. Fossils are known from the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in South Africa and the Rouse Hill Siltstone of Australia that date back to the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic. These aquatic creatures were the short snouted lineage from Trematosaurinae.

Trematosauridae is a family of large marine temnospondyl amphibians with several included genera.
Wantzosaurus was a genus of temnospondyl amphibian of the Trematosauridae family. Fossils have been found in the Early Triassic Middle Sakamena Formation of what is now Madagascar. It showed adaptations for an almost completely aquatic lifestyle, having the ability to swim by lateral undulation. A pelagic lifestyle for this animal has been proposed.

Trematosaurinae is a subfamily of temnospondyl amphibians within the family Trematosauridae. Like all trematosaurids, they were marine piscivores, resembling crocodiles in their general build. Unlike the long, almost gharial-like snouts of the Lonchorhynchinae, the Trematosaurinae had more "normal" crocodile-like skulls.
Almasaurus is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Latiscopidae. It is known from several skulls and some postcranial material found from the Argana Formation in Morocco, which dates back to the Late Triassic.
Hyperokynodon is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. Fossils have been found in Germany. While most trematosaurids existed during the Early Triassic, Hyperokynodon has been found in Late Triassic deposits, making it the youngest known trematosaurid. Hyperokynodon was known since 1852, but it was not identified as a trematosaurid until 1987. The type and only species is H. keuperinus.
Cosgriffius is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. It was described in 1993 by Samuel P. Welles based on a single partial skull from the well-known Meteor Crater Quarry in Arizona that also produced more abundant remains of the capitosaur Wellesaurus peabodyi. The skull was long and slender, features typically associated with the trematosaurid subfamily Lonchorhynchinae. This is the only trematosaurid known from western North America.

Lapillopsis is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl within the family Lapillopsidae. Fossils belonging to the genus have been found in the Arcadia Formation of Queensland, Australia.

Thoosuchus is an extinct genus of basal trematosauroid trematosaurian temnospondyl. Fossils have been found from Russia and date back to the Early Triassic. It is the type genus of the family Thoosuchidae, formerly called the subfamily Thoosuchinae and placed within Benthosuchidae. The benthosuchids were originally composed of the majority of basal trematosaurian forms regarded as the ancestors of the trematosaurids. Although the genus was first named in 1940, material from one species, E. yakovlevi, was originally tentatively referred to Trematosuchus in 1926.

Tertrema is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. It is known from skull material from the Vikinghøgda Formation on Spitsbergen Island in Svalbard. Relative to most trematosaurids, Tertrema has a proportionally short snout and widely spaced occipital condyles. While typically placed in the subfamily Trematosaurinae, a 2021 phylogenetic analysis suggested that it was actually nested among the long-snouted lonchorhynchine trematosaurids.

Anaschisma is an extinct genus of large temnospondyl amphibians. These animals were part of the family called Metoposauridae, which filled the crocodile-like predatory niches in the late Triassic. It had large skull about 62 centimetres (24 in) long, and possibly reached 3 metres (9.8 ft) long. It was an ambush hunter, snapping up anything small enough to fit in its huge jaws. It was very common during the Late Triassic in what is now the American Southwest.

The Erfurt Formation, also known as the Lower Keuper, is a stratigraphic formation of the Keuper group and the Germanic Trias supergroup. It was deposited during the Ladinian stage of the Triassic period. It lies above the Upper Muschelkalk and below the Middle Keuper.

Warrenisuchus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Triassic of Queensland, Australia. It belongs to a diverse group of Triassic temnospondyls called Capitosauria. The type species Warrenisuchus aliciae was erected in 2009. W. aliciae was originally described as a species of Parotosuchus in 1988, which is known from other species that have been found in Europe, Africa, and Antarctica. In 2000 it was then assigned to a new genus called Rewanobatrachus along with the newly named species R. gunganj, which was declared the type species of the genus. However, R. gunganj was later reclassified as a species of Watsonisuchus, invalidating the name Rewanobatrachus and requiring that R. aliciae be placed in its own genus, which was named Warrenisuchus. However, several studies suggest that Warrenisuchus aliciae may be a species of Watsonisuchus as well. Unlike most capitosaurs, Warrenisuchus is known from many juvenile skulls less than 4 centimetres (1.6 in) in length.
The Vikinghøgda Formation is a geologic formation in Svalbard, Norway. It preserves fossils dating back to the Early Triassic (Griesbachian-Spathian) period. It is split into three members, from oldest to youngest: the Deltadalen Member (Induan), Lusitaniadalen Member (Smithian), and Vendomdalen Member (Spathian). The formation can be found in central and southern Spitsbergen, as well as the smaller islands of Barentsøya and Edgeøya. The type locality is positioned in the vicinity of Vikinghøgda and Sticky Keep, two low peaks along the southeast edge of the Sassendalen valley in Spitsbergen. The two upper members of the Vikinghøgda Formation were previously grouped together as the Sticky Keep Formation.

Manubrantlia was a genus of lapillopsid from the Early Triassic Panchet Formation of India. This genus is only known from a single holotype left jaw, given the designation ISI A 57. Despite the paucity of remains, the jaw is still identifiable as belonging to a relative of Lapillopsis. For example, all three of its coronoid bones possessed teeth, the articular bone is partially visible in lateral (outer) view, and its postsplenial does not contact the posterior meckelian foramen. However, the jaw also possesses certain unique features which justify the erection of a new genus separate from Lapillopsis. For example, the mandible is twice the size of any jaws referred to other lapillopsids. The most notable unique feature is an enlarged "pump-handle" shaped arcadian process at the back of the jaw. This structure is responsible for the generic name of this genus, as "Manubrantlia" translates from Latin to the English expression "pump-handle". The type and only known species of this genus is Manubrantlia khaki. The specific name refers to the greenish-brown mudstones of the Panchet Formation, with a color that had been described as "khaki" by the first British geologists who studied the formation.






























