An appurtenance is something subordinate to or belonging to another larger, principal entity, that is, an adjunct, satellite, or accessory that generally accompanies something else. [1] The word derives from the Latin appertinere, "to appertain".
An appurtenance is something subordinate to or belonging to another larger, principal entity, that is, an adjunct, satellite, or accessory that generally accompanies something else. [1] The word derives from the Latin appertinere, "to appertain".
In a legal context, an appurtenance refers to a right, privilege, or improvement belonging to or that accompanies a principal property. [1] For example, the Supreme Court of Minnesota has defined appurtenance as "That which belongs to something else. Something annexed to another thing more worthy." [2] Applying this definition, an empty portion of land behind an adjoining house that is regarded as that house's backyard may be an appurtenance to the house. The idea being expressed is that the backyard "belongs" to the house, which is the more significant of the two properties.
In Gestalt theory, appurtenance (or "belongingness") is the relation between two things seen which exert influence on each other. For example, fields of color exert influence on each other. "A field part x is determined in its appearance by its 'appurtenance' to other field parts. The more x belongs to the field part y, the more will its whiteness be determined by the gradient xy, and the less it belongs to the part z, the less will its whiteness depend on the gradient xz." [3]
In lexicology, an appurtenance is a modifier that is appended or prepended to another word to coin a new word that expresses "belongingness". In the English language, appurtenances are most commonly found in toponyms and demonyms, for example, 'Israeli', 'Bengali' etc. have an -i suffix of appurtenance.[ citation needed ]
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an object to change its velocity, i.e., to accelerate, unless counterbalanced by other forces. The concept of force makes the everyday notion of pushing or pulling mathematically precise. Because the magnitude and direction of a force are both important, force is a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newton (N) and often represented by the symbol F.
In law, possession is the control a person intentionally exercises toward a thing. Like ownership, the possession of anything is commonly regulated by country under property law. In all cases, to possess something, a person must have an intention to possess it. A person may be in possession of some property.

The tidal force is a gravitational effect that stretches a body along the line towards the center of mass of another body due to a gradient in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenomena, including tides, tidal locking, breaking apart of celestial bodies and formation of ring systems within the Roche limit, and in extreme cases, spaghettification of objects. It arises because the gravitational field exerted on one body by another is not constant across its parts: the nearest side is attracted more strongly than the farthest side. It is this difference that causes a body to get stretched. Thus, the tidal force is also known as the differential force, as well as a secondary effect of the gravitational field.

A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words begin, start, commence, and initiate are all synonyms of one another: they are synonymous. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words are considered synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, long and extended in the context long time or extended time are synonymous, but long cannot be used in the phrase extended family. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms.

A yard is an area of land immediately adjacent to one or more buildings. It may be either enclosed or open. The word may come from the same linguistic root as the word garden and has many of the same meanings.
Norms are concepts (sentences) of practical import, oriented to affecting an action, rather than conceptual abstractions that describe, explain, and express. Normative sentences imply "ought-to" types of statements and assertions, in distinction to sentences that provide "is" types of statements and assertions. Common normative sentences include commands, permissions, and prohibitions; common normative abstract concepts include sincerity, justification, and honesty. A popular account of norms describes them as reasons to take action, to believe, and to feel.
Advowson or patronage is the right in English law of a patron (avowee) to present to the diocesan bishop a nominee for appointment to a vacant ecclesiastical benefice or church living, a process known as presentation.
In logic, the law of identity states that each thing is identical with itself. It is the first of the historical three laws of thought, along with the law of noncontradiction, and the law of excluded middle. However, few systems of logic are built on just these laws.
In common law, the curtilage of a house or dwelling is the land immediately surrounding it, including any closely associated buildings and structures, but excluding any associated "open fields beyond". In feudal times every castle with its dependent buildings was protected by a surrounding wall, and all the land within the wall was termed the curtilage. The term excludes any closely associated buildings, structures, or divisions that contain the separate intimate activities of their own respective occupants, with those occupying residents being persons other than those residents of the house or dwelling of which the building is associated.
An idiosyncrasy is an unusual feature of a person, though there are also other uses. It usually means unique habits. The term is often used to express peculiarity. A synonym may be distinctive.

Representation is the use of signs that stand in for and take the place of something else. It is through representation that people organize the world and reality through the act of naming its elements. Signs are arranged in order to form semantic constructions and express relations.

Accessio is a concept from Roman property law for acquiring ownership of property which is merged, or acceded to, another piece of property. Generally, the owner of the principal, whatever it may be, also became the owner of the accessory. Its usage continues in modern times in legal systems around the world incorporating Roman property law, primarily civilian legal systems.

Kannauji is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Kannauj region of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Kannauji is closely related to Hindustani, with a lexical similarity of 83–94% with Hindi. Some consider it to be a dialect of Hindustani, whereas others consider it a separate Western Hindi language. Kannauji has at least 9.5 million native speakers as of 2001.
In real estate, a lot or plot is a tract or parcel of land owned or meant to be owned by some owner(s). A plot is essentially considered a parcel of real property in some countries or immovable property in other countries. Possible owner(s) of a plot can be one or more person(s) or another legal entity, such as a company/corporation, organization, government, or trust. A common form of ownership of a plot is called fee simple in some countries.
Ugandan English is the variety of English spoken in Uganda. The term Uglish is first recorded in 2012. Other colloquial portmanteau words are Uglish, Uganglish and Ugandlish (2010).
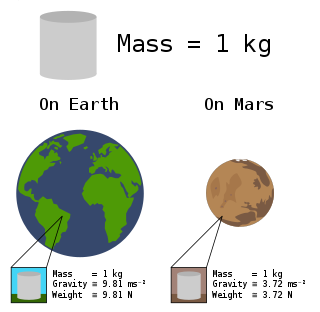
In common usage, the mass of an object is often referred to as its weight, though these are in fact different concepts and quantities. Nevertheless, one object will always weigh more than another with less mass if both are subject to the same gravity.
Belongingness is the human emotional need to be an accepted member of a group. Whether it is family, friends, co-workers, a religion, or something else, some people tend to have an 'inherent' desire to belong and be an important part of something greater than themselves. This implies a relationship that is greater than simple acquaintance or familiarity.
An easement is a nonpossessory right to use and/or enter onto the real property of another without possessing it. It is "best typified in the right of way which one landowner, A, may enjoy over the land of another, B". An easement is a property right and type of incorporeal property in itself at common law in most jurisdictions.
In mathematics and physics, vector is a term that refers colloquially to some quantities that cannot be expressed by a single number, or to elements of some vector spaces.

In physics, a field is a physical quantity, represented by a scalar, vector, or tensor, that has a value for each point in space and time. For example, on a weather map, the surface temperature is described by assigning a number to each point on the map; the temperature can be considered at a certain point in time or over some interval of time, to study the dynamics of temperature change. A surface wind map, assigning an arrow to each point on a map that describes the wind speed and direction at that point, is an example of a vector field, i.e. a 1-dimensional (rank-1) tensor field. Field theories, mathematical descriptions of how field values change in space and time, are ubiquitous in physics. For instance, the electric field is another rank-1 tensor field, while electrodynamics can be formulated in terms of two interacting vector fields at each point in spacetime, or as a single-rank 2-tensor field.