This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The Farther Adventures of Robinson Crusoe is a novel by Daniel Defoe, first published in 1719. Just as in its significantly more popular predecessor, Robinson Crusoe (1719), the first edition credits the work's fictional protagonist Robinson Crusoe as its author. It was published under the considerably longer original title: The Farther Adventures of Robinson Crusoe; Being the Second and Last Part of His Life, And of the Strange Surprising Accounts of his Travels Round three Parts of the Globe. Although intended to be the last Crusoe tale, the novel is followed by non-fiction book involving Crusoe by Defoe entitled Serious Reflections During the Life and Surprising Adventures of Robinson Crusoe: With his Vision of the Angelick World (1720).

The Terek River, a major river in the Northern Caucasus, flows through South Ossetia and Russia into the Caspian Sea. It rises in South Ossetia near the juncture of the Greater Caucasus Mountain Range and the Khokh Range, to the southwest of Mount Kazbek, winding north in a white torrent between the town of Stepantsminda and the village of Gergeti toward the Russian region North Ossetia and the city of Vladikavkaz. It turns east to flow through Chechnya and Dagestan before dividing into two branches which empty into the Caspian Sea. Below the city of Kizlyar it forms a swampy river delta around 100 kilometres (62 mi) wide. The river is a key natural asset in the region, providing irrigation and hydroelectric power in its upper reaches.

The Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 was the first treaty between Russia and China. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River and Lake Baikal. This border along the Argun River and Stanovoy Range lasted until the Amur Annexation in 1860. For background see History of Sino-Russian relations.
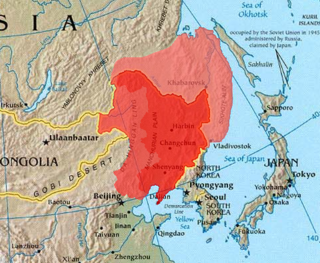
Outer Manchuria is an unofficial term for a territory in Northeast Asia that was formerly controlled by the Qing dynasty and now belongs to Russia. It is considered part of Manchuria by some definitions. Russia officially received this territory by way of the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Treaty of Peking in 1860. The northern part of the area was also in dispute between 1643 and 1689.

Abdul-Halim Salamovich Sadulayev was the fourth President of the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria. Sadulayev served little more than a full year as President before being killed in a gun battle with FSB and pro-Russian Chechen forces.
The Treaty of Kyakhta (or Kiakhta) (Russian: Кяхтинский договор, Kjahtinskij dogovor; Chinese: 布連斯奇條約/恰克圖條約; pinyin: Bùliánsīqí / Qiàkètú tiáoyuē, Wade-Giles: Pu4lien2ssŭ1ch‘i2 / Ch‘ia4k‘o4tu2 t‘iao2yüeh1, Xiao'erjing: بُلِيًاصِٿِ / ٿِاكْتُ تِيَوْيُؤ; Mongolian: Хиагтын гэрээ, Xiagtın gerê; Manchu: ᠵᡠᠸᠠᠨ
ᡝᠮᡠ
ᡥᠠᠴᡳᠨ ᡳ
ᠪᡳᡨᡥᡝ, Wylie: chuwan emu hatsin-i pitghe, Möllendorff: juwan emu hacin-i bithe), along with the Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689), regulated the relations between Imperial Russia and the Qing Empire of China until the mid-19th century. It was signed by Tulišen and Count Sava Lukich Raguzinskii-Vladislavich at the border city of Kyakhta on 23 August 1727.

Argun, also known as Ustrada is a town in the Chechen Republic, Russia, located on the Argun River. Population: 29,525 (2010 Census); 25,698 (2002 Census); 25,491 (1989 Census); 22,000 (1968).

Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia, or Dauria is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" (trans-) Lake Baikal in Russia.

Hulun Lake or Dalai Lake, is a large lake in the Inner Mongolia region of northern China.
The Battle of Khankala was a failed attempt by the Chechen separatists to counterattack at the strategic position at Khankala from Grozny and Argun using armoured vehicles.

The Sunzha is a river in North Ossetia, Ingushetia and Chechnya, Russia, a tributary of the Terek River. It flows northeast inside the great northwest bend of the Terek River and catches most of the rivers that flow north from the mountains before they reach the Terek. It is 278 kilometres (173 mi) long. The Sunzha rises on the Northern slope of the Caucasus Major. Its major tributaries are the Assa River and Argun River. With a turbidity of 3,800 grams per cubic metre (6.4 lb/cu yd), it carries 12.2 million tons of alluvium per year. It is used for irrigation. Cities that lie on the Sunzha include Nazran, Karabulak, Grozny, and Gudermes. During the First and Second Chechen Wars, the destruction of petroleum reservoirs caused the Sunzha to become polluted with petroleum.

Kanti Abdurakhmanov — ethnic Chechen, Master Sergeant of artillery battery during World War II. For heroic deeds during the war he was awarded the title Hero of the Russian Federation in May 1996.
Argun is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia.

Adlan Abuevich Varayev was a Russian-Chechen welterweight freestyle wrestler who won a silver medal at the 1988 Olympics. He won the 1987 World Championships, beating Dave Schultz in the final, and placed second in 1986. Varayev held the European welterweight title in 1986–1988. After retiring from competitions worked as a wrestling coach and administrator. He trained the Russian national freestyle team and served as vice-president of the Russian Wrestling Federation. He accidentally drowned after a bad fall into the Argun River.

The wildlife of Chechnya includes a range of flora and fauna as reflected by its varying topographic and climatic conditions, with the Greater Caucasus to the south, the foreland zone the Terek and Sunza river valleys in the west and east, and the rolling plains of Nogai steppe in the north. Lake Kezenoyam in Chechnya is near the border with Dagestan and can sustain plankton growth. Salmo ezenami, a rare species of trout now critically endangered due to introduction of the invasive species European chub, is native only to this lake and is therefore endemic to Lake Kezenoyam.
Vladimir Beslanovich Argun is a Russian football player. He currently plays for Abkhazian club Nart Sukhum.













