This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Corona Australis is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means "southern crown", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.

Terra Australis was a hypothetical continent first posited in antiquity and which appeared on maps between the 15th and 18th centuries. The existence of Terra Australis was not based on any survey or direct observation, but rather on the idea that continental land in the Northern Hemisphere should be balanced by land in the Southern Hemisphere. This theory of balancing land has been documented as early as the 5th century on maps by Macrobius, who uses the term Australis on his maps.
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of the Environment. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. It conducts and supports collaborative research programs with other Australian and international organisations, such as the Bureau of Meteorology and Geoscience Australia, as well as administering and maintaining a presence in Australian Antarctic and sub-Antarctic territories.
Southern lights may refer to

Aurora Leigh (1856) is an epic novel/poem by Elizabeth Barrett Browning. The poem is written in blank verse and encompasses nine books. It is a first person narration, from the point of view of Aurora; its other heroine, Marian Erle, is an abused self-taught child of itinerant parents. The poem is set in Florence, Malvern, London and Paris. The author uses her knowledge of Hebrew and Greek, while also playing off modern novels, such as Corinne ou l'Italie by Anne Louise Germaine de Staël and the novels by George Sand. As far as Book 5, Aurora narrates her past, from her childhood to the age of about 27; in Books 6–9, the narrative has caught up with her, and she reports events in diary form. Elizabeth Barrett Browning styled the poem "a novel in verse", and referred to it as "the most mature of my works, and the one into which my highest convictions upon Life and Art have entered." Scholar Deirdre David asserts that Barrett Browning's work in Aurora Leigh has made her into "a major figure in any consideration of the nineteenth-century woman writer and of Victorian poetry in general." John Ruskin called it the greatest long poem of the nineteenth century.
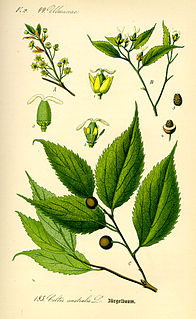
Celtis australis, commonly known as the European nettle tree, Mediterranean hackberry, lote tree, or honeyberry, is a deciduous tree native to southern Europe, North Africa, and Asia Minor. The tree was introduced to England in 1796.

Houghton Bay and Valley is one of the southern suburbs of Wellington, New Zealand.

The D'Entrecasteaux Channel is a body of water located between Bruny Island and the south-east of the mainland of Tasmania, Australia. The channel is the mouth for the estuaries of the Derwent and the Huon Rivers and empties into the Tasman Sea of the South Pacific Ocean. It was sighted by Abel Tasman in 1642 and surveyed in 1792 by Bruni d'Entrecasteaux.

Citrus australis, the Dooja, round lime, Australian lime or Australian round lime, is a large shrub or small tree producing an edible fruit. It grows in forest margins in the Beenleigh area and northwards, in Queensland, Australia.

Painting on Glass is the second studio album by The 3rd and the Mortal.

MV Akademik Shokalskiy is an Akademik Shuleykin-class ice-strengthened ship, built in Finland in 1982 and originally used for oceanographic research. In 1998 she was fully refurbished to serve as a research ship for Arctic and Antarctic work; she is used also for expedition cruising. She is named after the Russian oceanographer Yuly Shokalsky.

Illuminate Light & Laser Spectacular is a seasonal evening show at the Dreamworld theme park on the Gold Coast, Australia.
The Olympic Australis Opal is the largest and most valuable opal yet found, valued at A$2,500,000. It was found in 1956 at the 'Eight Mile' opal field in the outback opal gemstone mining town of Coober Pedy in South Australia. South Australia is the largest producer of white opal and crystal opal gemstones in the world.

The Coronet cluster, also known as the R CrA cluster after its best-known member, is a small open cluster located about 170 parsecs away in the southern constellation Corona Australis, isolated at the edge of the Gould Belt. The Coronet cluster is 3.5 times closer to the Earth than the Orion Nebula Cluster. The cluster center is composed of mostly young stars. The variable T Coronae Australis is also a member, only one arc minute from R CrA.

Aurora Melbourne Central is a topped out residential skyscraper in Melbourne, Australia. It is Melbourne's second-tallest building and the third tallest building in Australia, equal in height to Brisbane Skytower.

George Edward Marston was an English artist who twice accompanied Sir Ernest Shackleton on expeditions to Antarctic, first from 1907–09 on the Nimrod expedition, and then later from 1914–17 on the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition, which ended with the crew being marooned on Elephant Island.














