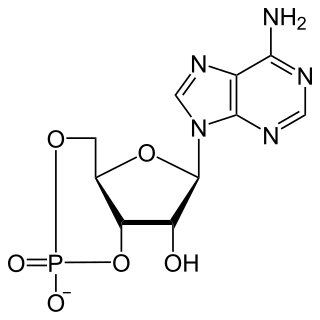
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway.

Bonnie Lynn Bassler is an American molecular biologist; the Squibb Professor in Molecular Biology and chair of the Department of Molecular Biology at Princeton University; and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. She has researched cell-to-cell chemical communication in bacteria and discovered key insights into the mechanism by which bacteria communicate, known as quorum sensing. She has contributed to the idea that disruption of chemical signaling can be used as an antimicrobial therapy.
In biology, quorum sensing or quorum signaling (QS) is the ability to detect and respond to cell population density by gene regulation. Quorum sensing is a type of cellular signaling, and more specifically can be considered a type of paracrine signaling. However, it also contains traits of both autocrine signaling: a cell produces both the autoinducer molecule and the receptor for the autoinducer. As one example, QS enables bacteria to restrict the expression of specific genes to the high cell densities at which the resulting phenotypes will be most beneficial, especially for phenotypes that would be ineffective at low cell densities and therefore too energetically costly to express. Many species of bacteria use quorum sensing to coordinate gene expression according to the density of their local population. In a similar fashion, some social insects use quorum sensing to determine where to nest. Quorum sensing in pathogenic bacteria activates host immune signaling and prolongs host survival, by limiting the bacterial intake of nutrients, such as tryptophan, which further is converted to serotonin. As such, quorum sensing allows a commensal interaction between host and pathogenic bacteria. Quorum sensing may also be useful for cancer cell communications.

The lactose operon is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in E. coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most enteric bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of beta-galactosidase. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes for this reason. This lactose metabolism system was used by François Jacob and Jacques Monod to determine how a biological cell knows which enzyme to synthesize. Their work on the lac operon won them the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 1965.

Aliivibrio fischeri is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a single polar flagella. Free-living A. fischeri cells survive on decaying organic matter. The bacterium is a key research organism for examination of microbial bioluminescence, quorum sensing, and bacterial-animal symbiosis. It is named after Bernhard Fischer, a German microbiologist.

Vibrio harveyi is a Gram-negative, bioluminescent, marine bacterium in the genus Vibrio. V. harveyi is rod-shaped, motile, facultatively anaerobic, halophilic, and competent for both fermentative and respiratory metabolism. It does not grow below 4 °C. V. harveyi can be found free-swimming in tropical marine waters, commensally in the gut microflora of marine animals, and as both a primary and opportunistic pathogen of marine animals, including Gorgonian corals, oysters, prawns, lobsters, the common snook, barramundi, turbot, milkfish, and seahorses. It is responsible for luminous vibriosis, a disease that affects commercially farmed penaeid prawns. Additionally, based on samples taken by ocean-going ships, V. harveyi is thought to be the cause of the milky seas effect, in which, during the night, a uniform blue glow is emitted from the seawater. Some glows can cover nearly 6,000 sq mi (16,000 km2).

N-Acyl homoserine lactones are a class of signaling molecules involved in bacterial quorum sensing, a means of communication between bacteria enabling behaviors based on population density.

Catabolite activator protein is a trans-acting transcriptional activator that exists as a homodimer in solution. Each subunit of CAP is composed of a ligand-binding domain at the N-terminus and a DNA-binding domain at the C-terminus. Two cAMP molecules bind dimeric CAP with negative cooperativity. Cyclic AMP functions as an allosteric effector by increasing CAP's affinity for DNA. CAP binds a DNA region upstream from the DNA binding site of RNA Polymerase. CAP activates transcription through protein-protein interactions with the α-subunit of RNA Polymerase. This protein-protein interaction is responsible for (i) catalyzing the formation of the RNAP-promoter closed complex; and (ii) isomerization of the RNAP-promoter complex to the open conformation. CAP's interaction with RNA polymerase causes bending of the DNA near the transcription start site, thus effectively catalyzing the transcription initiation process. CAP's name is derived from its ability to affect transcription of genes involved in many catabolic pathways. For example, when the amount of glucose transported into the cell is low, a cascade of events results in the increase of cytosolic cAMP levels. This increase in cAMP levels is sensed by CAP, which goes on to activate the transcription of many other catabolic genes.
Luminescent bacteria emit light as the result of a chemical reaction during which chemical energy is converted to light energy. Luminescent bacteria exist as symbiotic organisms carried within a larger organism, such as many deep sea organisms, including the Lantern Fish, the Angler fish, certain jellyfish, certain clams and the Gulper eel. The light is generated by an enzyme-catalyzed chemoluminescence reaction, wherein the pigment luciferin is oxidised by the enzyme luciferase. The expression of genes related to bioluminescence is controlled by an operon called the lux operon.

Spot 42 (spf) RNA is a regulatory non-coding bacterial small RNA encoded by the spf gene. Spf is found in gammaproteobacteria and the majority of experimental work on Spot42 has been performed in Escherichia coli and recently in Aliivibrio salmonicida. In the cell Spot42 plays essential roles as a regulator in carbohydrate metabolism and uptake, and its expression is activated by glucose, and inhibited by the cAMP-CRP complex.

The enzyme S-ribosylhomocysteine lyase catalyzes the reaction
Autoinducers are signaling molecules that are produced in response to changes in cell-population density. As the density of quorum sensing bacterial cells increases so does the concentration of the autoinducer. Detection of signal molecules by bacteria acts as stimulation which leads to altered gene expression once the minimal threshold is reached. Quorum sensing is a phenomenon that allows both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria to sense one another and to regulate a wide variety of physiological activities. Such activities include symbiosis, virulence, motility, antibiotic production, and biofilm formation. Autoinducers come in a number of different forms depending on the species, but the effect that they have is similar in many cases. Autoinducers allow bacteria to communicate both within and between different species. This communication alters gene expression and allows bacteria to mount coordinated responses to their environments, in a manner that is comparable to behavior and signaling in higher organisms. Not surprisingly, it has been suggested that quorum sensing may have been an important evolutionary milestone that ultimately gave rise to multicellular life forms.

In molecular biology, the LuxR-type DNA-binding HTH domain is a DNA-binding, helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain of about 65 amino acids. It is present in transcription regulators of the LuxR/FixJ family of response regulators. The domain is named after Vibrio fischeri luxR, a transcriptional activator for quorum-sensing control of luminescence. LuxR-type HTH domain proteins occur in a variety of organisms. The DNA-binding HTH domain is usually located in the C-terminal region of the protein; the N-terminal region often containing an autoinducer-binding domain or a response regulatory domain. Most luxR-type regulators act as transcription activators, but some can be repressors or have a dual role for different sites. LuxR-type HTH regulators control a wide variety of activities in various biological processes.
Interspecies quorum sensing is a type of quorum sensing in which bacteria send and receive signals to other species besides their own. This is accomplished by the secretion of signaling molecules which trigger a response in nearby bacteria at high enough concentrations. Once the molecule hits a certain concentration it triggers the transcription of certain genes such as virulence factors. It has been discovered that bacteria can not only interact via quorum sensing with members of their own species but that there is a kind of universal molecule that allows them to gather information about other species as well. This universal molecule is called autoinducer 2 or AI-2.
Vibrio campbellii is a Gram-negative, curved rod-shaped, marine bacterium closely related to its sister species, Vibrio harveyi. It is an emerging pathogen in aquatic organisms.
Acyl-homoserine-lactone synthase is an enzyme with systematic name acyl-(acyl-carrier protein):S-adenosyl-L-methionine acyltranserase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Bioluminescent bacteria are light-producing bacteria that are predominantly present in sea water, marine sediments, the surface of decomposing fish and in the gut of marine animals. While not as common, bacterial bioluminescence is also found in terrestrial and freshwater bacteria. These bacteria may be free living or in symbiosis with animals such as the Hawaiian Bobtail squid or terrestrial nematodes. The host organisms provide these bacteria a safe home and sufficient nutrition. In exchange, the hosts use the light produced by the bacteria for camouflage, prey and/or mate attraction. Bioluminescent bacteria have evolved symbiotic relationships with other organisms in which both participants benefit close to equally. Another possible reason bacteria use luminescence reaction is for quorum sensing, an ability to regulate gene expression in response to bacterial cell density.
Everett Peter Greenberg is an American microbiologist. He is the inaugural Eugene and Martha Nester Professor of Microbiology at the Department of Microbiology of the University of Washington School of Medicine. He is best known for his research on quorum sensing, and has received multiple awards for his work.

4,5-Dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione (DPD) is an organic compound that occurs naturally but exists as several related structures. The idealized formula for this species is CH3C(O)C(O)CH(OH)CH2OH, but it is known to exist as several other forms resulting from cyclization. It is not stable at room temperature as a pure material, which has further complicated its analysis. The (S)-stereoisomer occurs naturally. It is typically hydrated, i.e., one keto group has added water to give the geminal diol.












