Related Research Articles

The C38 class was a class of steam locomotive built for the New South Wales Government Railways in Australia.

The National Rail Corporation was an Australian rail operator established by the Federal, New South Wales and Victorian governments in February 1992. In February 2002, National Rail was sold to a Patrick Corporation and Toll Holdings consortium and rebranded Pacific National.

The 80 class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Comeng for the Public Transport Commission between 1978 and 1983.

The DL class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Clyde Engineering, Kelso for Australian National between 1988 and 1990. Five remain in service with Pacific National.

Commonwealth Engineering was an Australian engineering company that designed and built railway locomotives, rolling stock and trams.
The New South Wales 85 class were a class of 10 electric locomotives built by Comeng, Granville between May 1979 and July 1980 for the Public Transport Commission.

Clyde Engineering was an Australian manufacturer of locomotives, rolling stock, and other industrial products.

The GM class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Clyde Engineering, Granville for the Commonwealth Railways in several batches between 1951 and 1967. As at January 2014, some remain in service with Aurizon and Southern Shorthaul Railroad.

The 79 class is a diesel-electric locomotive built by General Electric, Erie, United States for the Department of Railways New South Wales in 1943.

The 70 class were a class of diesel-hydraulic locomotives built by Commonwealth Engineering, Granville for the New South Wales Department of Railways in 1960–61. They were ordered to replace steam locomotives at Port Kembla.

The Goldsworthy railway, owned and operated by BHP, is a private rail network in the Pilbara region of Western Australia built to carry iron ore. It is one of two railway lines BHP operates in the Pilbara, the other being the Mount Newman railway.
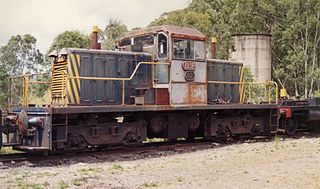
The BHP Newcastle 37 class were a class of diesel locomotives built by A Goninan & Co, Broadmeadow for the BHP, Newcastle steelworks between 1960 and 1983.

The Trans-Australian was an Australian passenger train operated by the Commonwealth Railways initially between Port Augusta and Kalgoorlie on the Trans-Australian Railway line, and later extended west to Perth, and east to Port Pirie and Adelaide.
The D9 class were a class of diesel locomotives built by English Electric, Rocklea for Australian Iron & Steel's, Port Kembla steelworks between 1956 and 1960.
The D16 class are a class of diesel locomotives built by English Electric, Rocklea for Australian Iron & Steel's, Port Kembla steelworks between 1959 and 1964.
D34 was a diesel locomotive built by English Electric, Rocklea for Australian Iron & Steel's, Port Kembla steelworks in 1969.
The D35 class are a class of diesel locomotives built by English Electric, Rocklea for Australian Iron & Steel's, Port Kembla steelworks between 1971 and 1975.

Charles Henry Hoskins (1851-1926) was an Australian industrialist, who was significant in the development of the iron and steel industry in Australia.

The Cadia Mine railway line is a closed and dismantled railway line in New South Wales, Australia. The 18.5 km long branch line started where it branched from the Main Western Railway line at Spring Hill.and ended at Cadia. Its main role was to carry iron ore from the quarry at Cadia and for much of its life was privately operated.

Sir Cecil Harold Hoskins (1889–1971) was an Australian industrialist associated with the iron and steel industry. He is notable mainly for the establishment of the steel industry at Port Kembla, the company Australian Iron & Steel, and its subsequent merger with BHP in 1935. He was also on the board of the Australian Mutual Provident Society for many years and was its chairman from 1947 to 1962. He is less well known for his involvement in centre-right political organisations and the scouting movement, and his interest in landscape gardens.
References
- ↑ Oberg, Leon (1984). Locomotives of Australia 1850s-1980s. Frenchs Forest: Reed Books. pp. 186–187. ISBN 0-730100-05-7.
- ↑ "Australian Iron & Steel" Railway Digest October 1986 pages 299-303
- ↑ 750 Class (Port Kembla) Archived 2014-02-02 at the Wayback Machine Railpage
- ↑ Dunn, John (2006). Comeng: A History of Commonwealth Engineering Volume 1: 1921-1955. Kenthurst: Rosenberg Publishing. p. 166. ISBN 1877058424.
- ↑ Port Kembla - Diesel Locomotive Fleetlisting Light Rail Research Society of Australia
Railway Transportation, November 1951, 'D-E locos and 60-ton cars boost operations for AI&S'