Pomerania is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland.

The geography of Ukraine varies greatly from one region of the country to another, with the majority of the country lying within the East European Plain. Ukraine is the second-largest country by area in Europe. Its various regions have diverse geographic features ranging from highlands to lowlands, as well as climatic range and a wide variety in hydrography.

Europe is traditionally defined as one of seven continents. Physiographically, it is the northwestern peninsula of the larger landmass known as Eurasia ; Asia occupies the eastern bulk of this continuous landmass and all share a common continental shelf. Europe's eastern frontier is delineated by the Ural Mountains in Russia. The southeast boundary with Asia is not universally defined, but the modern definition is generally the Ural River or, less commonly, the Emba River. The boundary continues to the Caspian Sea, the crest of the Caucasus Mountains, and on to the Black Sea. The Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles conclude the Asian boundary. The Mediterranean Sea to the south separates Europe from Africa. The western boundary is the Atlantic Ocean. Iceland, though on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and nearer to Greenland than mainland Europe, is generally included in Europe for cultural reasons and because it is over twice as close to mainland Europe as mainland North America. There is ongoing debate on where the geographical centre of Europe falls.

The North European Plain is a geomorphological region in Europe, mostly in Poland, Denmark, Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, with small parts of northern France and Czech republic.

The Wiehen Hills are a hill range in North Rhine-Westphalia and Lower Saxony in Germany. The hills run from west to east like a long finger away from the main upland area of the Lower Saxon Hills, beginning at the Weser River near Minden and terminating in the vicinity of Osnabrück. It is the northernmost of the German Central Upland ranges extending into the Northern Lowlands. Their highest hill is the Heidbrink near Lübbecke with an altitude of 320 metres (1,050 ft).
The Belarusian Ridge is a line of terminal moraines in the northwest of Belarus. The feature is part of the East European Plain.
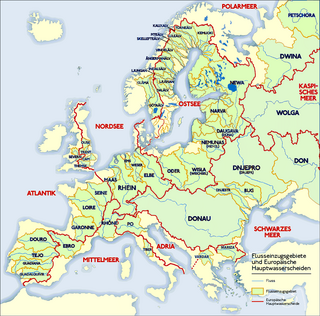
The main European watershed is the drainage divide ("watershed") which separates the basins of the rivers that empty into the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea and the Baltic Sea from those that feed the Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea and the Black Sea. It stretches from the tip of the Iberian Peninsula at Gibraltar in the southwest to the endorheic basin of the Caspian Sea in Russia in the northeast.

The European Plain or Great European Plain is a plain in Europe and is a major feature of one of four major topographical units of Europe - the Central and Interior Lowlands. It is the largest mountain-free landform in Europe, although a number of highlands are identified within it.
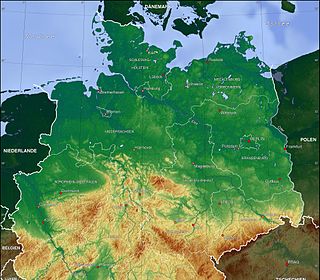
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north and Germany's Central Uplands to the south.
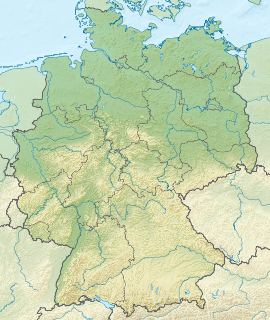
Germany is a country in west-central Europe, that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Germany has the second largest population in Europe and is seventh largest in area. The territory of Germany covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of waters.

Holstein Switzerland is a hilly area with a patchwork of lakes and forest in Schleswig Holstein, Germany, reminiscent of Swiss landscape. Its highest point is the Bungsberg. It is a designated nature park as well as an important tourist destination in Northern Germany situated between the cities of Kiel and Lübeck.
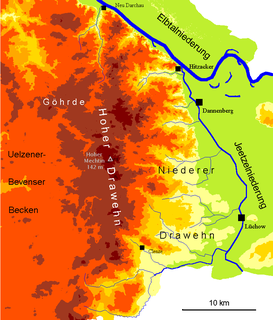
The Drawehn is a partly wooded and partly agricultural region of hills in the northeastern part of the German state of Lower Saxony, lying between the districts of Lüneburg and Uelzen in the west and Lüchow-Dannenberg in the east.

This division of Germany into major natural regions takes account primarily of geomorphological, geological, hydrological, and pedological criteria in order to divide the country into large, physical units with a common geographical basis. Political boundaries play no part in this, apart from defining the national border.

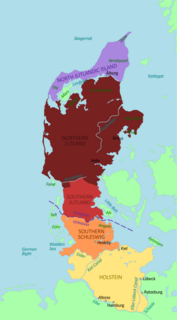
The Schleswig-Holstein Uplands or Schleswig-Holstein Morainic Uplands is one of the three landscapes of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein; the others being the marsch and the geest. In addition, the gently rolling hills or Hügelland of the Baltic Uplands, the many small lakes and the long, deep embayments (Förde) formed by the moraines of the Weichselian Ice Age are characteristic features of the area. Its best-known towns are Kiel, Lübeck and Flensburg. The highest elevation in the area is the Bungsberg in the region known as Holstein Switzerland. On the Bungsberg is the only ski lift in the state.

The Lauenburg Lakes Nature Park was founded in 1961 and lies in the district of Lauenburg in the southeastern part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is right on the border with the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in the Schleswig-Holstein Uplands, a Young Drift moraine landscape that formed during the Weichselian glaciation of the last ice age.
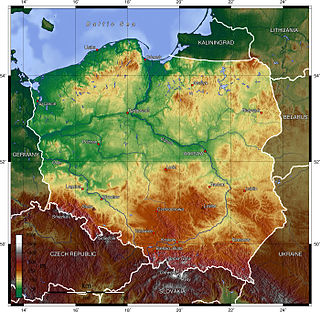
Poland is a country in Central Europe with an area of 312,679 square kilometres, and mostly temperate climate. Generally speaking, Poland is an almost unbroken plain reaching from the Baltic Sea in the north, to the Carpathian Mountains in the south. Within that plain, terrain variations run in bands east to west. The Baltic coast has two natural harbors, the larger one in the Gdańsk-Gdynia region, and a smaller one near Szczecin in the far northwest. The northeastern region, also known as the Masurian Lake District with more than 2,000 lakes, is densely wooded and sparsely populated. To the south of the lake district, and across central Poland a vast region of plains extends all the way to the Sudetes on the Czech and Slovak borders southwest, and to the Carpathians on the Czech, Slovak and Ukrainian borders southeast. The central lowlands had been formed by glacial erosion in the Pleistocene ice age. The neighboring countries are Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and Lithuania and the Russian exclave of Kaliningrad to the northeast.
The Smolensk–Moscow Upland is located in the Yaroslavl, Vladimir, Moscow and Smolensk regions of Russia, as well as the Vitebsk region of Belarus.
Hügelland is a type of landscape consisting of low, rolling hills whose topography or surface structure lies between that of a lowland region and that of a more rugged hill range or low mountain range. The term is German and has no exact equivalent in English, but is often translated as "hill country", "hilly terrain", "upland(s)" or "gently undulating" or "rolling country", or "rolling countryside". It is derived from Hügel, a low hill or hillock and appears frequently as a proper name for this type of terrain.

The North Brandenburg Plateaux and Upland is a natural region in the northwest of Brandenburg and, to a lesser extent, the southwest of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and northeast of Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. It is major unit group no. 77 in the natural regional divisions of Germany. The Brandenburg portion of the North Brandenburg Plateaux and Upland is largely coextensive with the natural region of Prignitz and Ruppin Land in the structural atlas of the state of Brandenburg.