
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying passengers or goods, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Historically, a "ship" was a sailing vessel with at least three square-rigged masts and a full bowsprit. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and tradition.

Merchant raiders are armed commerce raiding ships that disguise themselves as non-combatant merchant vessels.

A merchant ship, merchant vessel, trading vessel, or merchantman is a watercraft that transports cargo or carries passengers for hire. This is in contrast to pleasure craft, which are used for personal recreation, and naval ships, which are used for military purposes.

"East Indiaman" was a general name for any sailing ship operating under charter or licence to any of the East India Companies of the major European trading powers of the 17th through the 19th centuries. The term is therefore used to refer to vessels belonging to the Danish, Dutch (Oostindiëvaarder), English, French, Portuguese, or Swedish (ostindiefarare) East India companies.

The Japanese raiders in the Indian Ocean were those vessels used by the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Second World War to pursue its war on Allied commerce in that theatre.
Possessing a powerful fleet of warships, prior to the start of World War II, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had strategically planned to fight a war of fleet actions, and as a consequence delegated few resources to raiding merchant vessels. Nevertheless, in 1940, two passenger-cargo vessels – Aikoku Maru and Hōkoku Maru – of the Osaka Shipping Line were requisitioned for conversion to Armed Merchant Cruisers (AMC)s, in anticipation of the likely thrust southward by the Japanese. These vessels were subsequently used as merchant raiders attacking Allied commercial shipping along vital sea lanes of communication between Australia and the Middle East. Using their comprehensive armament and speed to their advantage, the raiders experienced a brief period of success. Japanese raiding in the Indian Ocean largely ceased by the end of 1942 after an action with a Dutch vessel, the Ondina and a Royal Indian Navy corvette, the Bengal in which the Hokoku Maru was sunk.

SM U-35 was a German U 31-class U-boat which operated in the Mediterranean Sea during World War I. It ended up being the most successful U-boat participating in the war, sinking 224 ships for a total of 539,741 gross register tons (GRT).

Length overall is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth.

Launched on October 4, 1853 Great Republic is noteworthy as the largest wooden clipper ship ever constructed.

HMS Torbay (N79) was a T-class submarine of the Royal Navy. She was laid down at Chatham Dockyard and launched on 9 April 1940.
German submarine U-81 was a Type VIIC U-boat of the navy (Kriegsmarine) of Nazi Germany during World War II, famous for sinking the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal.

A baghlah, bagala or baggala is a large deep-sea dhow, a traditional Arabic sailing vessel. The name "baghla" means "mule" in the Arabic language.
HMS Sophie was an 18-gun Cruizer class brig-sloop of the Royal Navy. She served during the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812. During the War of 1812 Sophie participated in the economic war against American trade, capturing or destroying numerous small merchant vessels, and in an unsuccessful attack on Fort Bowyer, Alabama. Later, she moved to the East Indies where she served in the First Anglo-Burmese War. The Admiralty sold Sophie in 1825.

Badger's Island is located in the Piscataqua River at Kittery, Maine, directly opposite Portsmouth, New Hampshire. It carries U.S. Route 1 between the states, connecting to the Kittery mainland by the Badger's Island Bridge, and to New Hampshire by the Memorial Bridge. Now largely a suburb of Portsmouth, the island features houses, condominiums, restaurants and marinas.
German submarine U-652 was a Type VIIC U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The submarine was laid down on 5 February 1940 at the Howaldtswerke yard at Hamburg, launched on 7 February 1941, and commissioned on 3 April 1941 under the command of Oberleutnant zur See Georg-Werner Fraatz.

HMS Merlin was one of the two original Merlin-class sloops that served the Royal Navy during the French Revolutionary Wars. She was launched in 1796 and was broken up in 1803. Her greatest accomplishment was her role as the leading vessel in a motley flotilla of local vessels that defeated a Spanish attack on the British colonists in Honduras at the Battle of St. George's Caye. She later captured a number of small merchant vessels in the West Indies before returning to Britain, where she was broken up.
A number of sailing vessels were named Alexander:
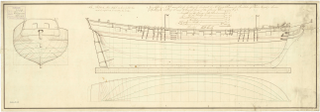
HMS Diligence was the name ship of her class of brig-sloops of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1795 and lost in 1800. She spent her career on the Jamaica station where she captured four armed vessels, one of them after a short engagement, and many small Spanish and French merchant vessels in the Caribbean inter-island and coastal trade.
Earl of Mornington, was a merchant vessel of 500 tons burthen (bm) built at Bombay Dockyard of teak and launched in 1766 or 1768. She made three voyages under charter to the British East India Company (EIC) under the command of captain Benjamin Ferguson. She does not appear in Lloyd's Register until 1804 and no longer appears in either Lloyd's Register or in the Register of Shipping in 1810.

A grab was a type of ship common on the Malabar Coast in the 18th and 19th Centuries. The name comes from "ghurāb" or "ghorāb", Arabic for raven, which word came into Marathi and Konkani as "gurab". The ghurāb was originally a galley, but the type evolved.
Weather-induced crop failures in Britain in 1799 and 1800 forced the British Government to import rice from Bengal to counter popular unrest. The wheat harvests of 1799 and 1800 were about one-half and three-quarters of the average, respectively. The price of bread rose sharply, leading to bread riots; some of rioters invoked the French Revolution.













