
East Anglia is a geographical area in the East of England. The area included has varied but the legally defined NUTS 2 statistical unit comprises the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, including the City of Peterborough unitary authority area. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a tribe whose name originated in Anglia, northern Germany.

Edmund the Martyr was king of East Anglia from about 855 until his death.
Æthelred, also Ethelred, is an Old English personal name and may refer to:

ITV Anglia, previously known as Anglia Television or Anglia, is the ITV franchise holder for the East of England. The station is based at Anglia House in Norwich, with regional news bureaux in Cambridge and Northampton. ITV Anglia is owned and operated by ITV plc under the licence name of ITV Broadcasting Limited.
Æthelwold was a common Anglo Saxon name. It may refer to:

Æthelberht, also called Saint Ethelbert the King, was an eighth-century saint and a king of East Anglia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom which today includes the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. Little is known of his reign, which may have begun in 779, according to later sources, and very few of the coins issued during his reign have been discovered. It is known from the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle that he was killed on the orders of Offa of Mercia in 794.

Wihtburh was an East Anglia saint, princess and abbess who was possibly a daughter of Anna of East Anglia, located in present-day England. She founded a monastery at Dereham in Norfolk. A traditional story says that the Virgin Mary sent a pair of female deer to provide milk for her workers during the monastery's construction. Withburga's body is supposed to have been uncorrupted when discovered half a century after her death: it was later stolen on the orders of the abbot of Ely. A spring appeared at the site of the saint's empty tomb at Dereham.

Felix of Burgundy, also known as Felix of Dunwich, was a saint and the first bishop of the East Angles. He is widely credited as the man who introduced Christianity to the kingdom of East Anglia. Almost all that is known about the saint originates from The Ecclesiastical History of the English People, completed by Bede in about 731, and the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle. Bede praised Felix for delivering "all the province of East Anglia from long-standing unrighteousness and unhappiness".
Sigeberht of East Anglia, was a saint and a king of East Anglia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom which today includes the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. He was the first English king to receive a Christian baptism and education before his succession and the first to abdicate in order to enter the monastic life. The principal source for Sigeberht is Bede's Ecclesiastical History of the English People, which was completed in the 730s.

Sidwell was a virgin saint from the English county of Devon, possibly of British origin. Her historical existence is not well established.

BBC East is the BBC English Region serving Norfolk, Suffolk, Essex, Cambridgeshire, most of Northamptonshire, Bedfordshire, Hertfordshire and northern Buckinghamshire.

Saint Foillan is an Irish saint of the seventh century.
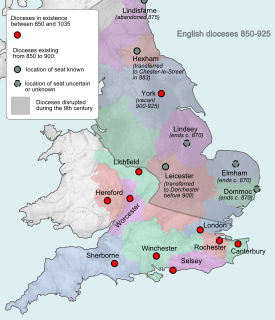
Dommoc, a place not certainly identified but probably within the modern county of Suffolk, was the original seat of the Anglo-Saxon bishops of the Kingdom of East Anglia. It was established by Sigeberht of East Anglia for Saint Felix in c. 629–31. It remained the bishopric of all East Anglia until c. 673, when Theodore of Tarsus, Archbishop of Canterbury, divided the see and created a second bishopric at either North Elmham, Norfolk, or South Elmham, Suffolk. The see of Dommoc continued to exist until the time of the Viking Wars of the 860s, after which it lapsed.

Alberht was an eighth century king of East Anglia. He shared the kingdom with Beonna and he is believed to have also shared rule with a supposed ruler named Hun. He may still have been king in around 760. He is recorded by the Fitzwilliam Museum and Simon Keynes as Æthelberht I.
Beonna was a medieval Bishop of Hereford. He was consecrated in 824 and died between 825 and 832.

Greater Anglia is a train operating company in Great Britain owned as a joint venture by Abellio, the international arm of the state-owned Dutch national rail operator Nederlandse Spoorwegen, and the Japanese company Mitsui. It operates the East Anglia franchise, providing the majority of commuter/regional services from its Central London terminus at London Liverpool Street to Essex, Suffolk, Norfolk and parts of Hertfordshire and Cambridgeshire as well as many regional services throughout the East of England.

Eadwold of Cerne was a 9th-century hermit, Anglian Prince and patron saint of Cerne, Dorset, who lived as a hermit on a hill about four miles from Cerne. His feast day is 29 August.













