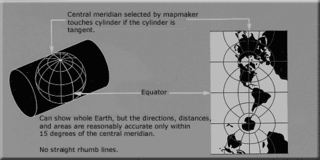
A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.
A world file is a six line plain text sidecar file used by geographic information systems (GIS) to georeference raster map images. The file specification was introduced by Esri, and consists of six coefficients of an affine transformation that describes the location, scale and rotation of a raster on a map.

Grid references define locations in maps using Cartesian coordinates. Grid lines on maps define the coordinate system, and are numbered to provide a unique reference to features. This reference is normally based on projected easting and northings

The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude. It is often called British National Grid (BNG).
In cartography, the term Gauss–Krüger, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss and Johann Heinrich Louis Krüger, is used in three slightly different ways.

The Irish grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used for paper mapping in Ireland. The Irish grid partially overlaps the British grid, and uses a similar co-ordinate system but with a meridian more suited to its westerly location.

The Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) is the geocoordinate standard used by NATO militaries for locating points on the earth. The MGRS is derived from the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) grid system and the universal polar stereographic (UPS) grid system, but uses a different labeling convention. The MGRS is used for the entire earth.

The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) conformal projection uses a 2-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system to give locations on the surface of the Earth. Like the traditional method of latitude and longitude, it is a horizontal position representation, i.e. it is used to identify locations on the Earth independently of altitude. However, it differs from that method in several respects.

The universal polar stereographic (UPS) coordinate system is used in conjunction with the universal transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate system to locate positions on the surface of the earth. Like the UTM coordinate system, the UPS coordinate system uses a metric-based cartesian grid laid out on a conformally projected surface. UPS covers the Earth's polar regions, specifically the areas north of 84°N and south of 80°S, which are not covered by the UTM grids, plus an additional 30 minutes of latitude extending into UTM grid to provide some overlap between the two systems.

A spatial reference system (SRS) or coordinate reference system (CRS) is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems. Spatial reference systems are defined by the OGC's Simple feature access using well-known text representation of coordinate reference systems, and support has been implemented by several standards-based geographic information systems. Spatial reference systems can be referred to using a SRID integer, including EPSG codes defined by the International Association of Oil and Gas Producers. It is specified in ISO 19111:2007 Geographic information—Spatial referencing by coordinates, prepared by ISO/TC 211, also published as OGC Abstract Specification, Topic 2: Spatial referencing by coordinate.

The terms easting and northing are geographic Cartesian coordinates for a point. Easting refers to the eastward-measured distance, while northing refers to the northward-measured distance. When using common projections such as the transverse Mercator projection, these are distances projected on an imaginary surface similar to a bent sheet of paper, and are not the same as distances measured on the curved surface of the Earth.

Jordan Transverse Mercator (JTM) is a grid system created by the Royal Jordan Geographic Center (RJGC). This system is based on 6° belts with a Central Meridian of 37° East and a Scale Factor at Origin (mo) = 0.9998. The JTM is based on the Hayford ellipsoid adopted by the IUGG in 1924. No transformation parameters are presently offered by the government. However, Prof. Stephen H. Savage of Arizona State University provides the following parameters for the projection:

Irish Transverse Mercator (ITM) is the geographic coordinate system for Ireland. It was implemented jointly by the Ordnance Survey Ireland (OSi) and the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland (OSNI) in 2001. The name is derived from the Transverse Mercator projection it uses and the fact that it is optimised for the island of Ireland.

Israeli Transverse Mercator is the new geographic coordinate system for Israel. The name is derived from the Transverse Mercator projection it uses and the fact that it is optimized for Israel. ITM has replaced the old coordinate system ICS. This coordinate system is sometimes also referred as the "New Israeli Grid". It has been use since January 1, 1994.
The article Transverse Mercator projection restricts itself to general features of the projection. This article describes in detail one of the (two) implementations developed by Louis Krüger in 1912; that expressed as a power series in the longitude difference from the central meridian. These series were recalculated by Lee in 1946, by Redfearn in 1948, and by Thomas in 1952. They are often referred to as the Redfearn series, or the Thomas series. This implementation is of great importance since it is widely used in the U.S. State Plane Coordinate System, in national and also international mapping systems, including the Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system (UTM). They are also incorporated into the Geotrans coordinate converter made available by the United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. When paired with a suitable geodetic datum, the series deliver high accuracy in zones less than a few degrees in east-west extent.
In 1989 Bernard Russel Bowring gave formulas for the Transverse Mercator that are simpler to program but retain millimeter accuracy. Bowring rewrote the fourth order Redfearn series in a more compact notation by replacing the spherical terms, i.e. those independent of ellipticity, by the exact expressions used in the spherical transverse Mercator projection. There was no gain in accuracy since the elliptic terms were still truncated at the 1mm level. Such modifications were of possible use when computing resources were minimal.
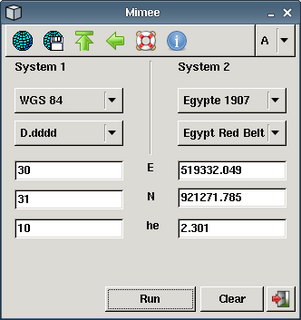
Mimee is a program which can convert geographical coordinates between various datums and formats.
The Gauss–Boaga projection is a map projection used in Italy that uses a Hayford ellipsoid.