Julian Jaynes was an American psychologist, best known for his book The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind (1976), in which he argued that ancient peoples were not conscious.
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties or other groups. The term, originally denoting a parley during battle in the Late Middle Ages, is derived from the Latin congressus.

A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate, so-called as an assembly of the senior and therefore allegedly wiser and more experienced members of the society or ruling class. Thus, the literal meaning of the word "senate" is Assembly of Elders.
A legislature is a deliberative assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. Legislatures form important parts of most governments; in the separation of powers model, they are often contrasted with the executive and judicial branches of government.
In government, unicameralism is the practice of having one legislative or parliamentary chamber. Thus, a unicameral parliament or unicameral legislature is a legislature which consists of one chamber or house.
A city council, town council, town board, or board of aldermen is the legislative body that governs a city, town, municipality, or local government area.
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house. The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restricted power than the lower house. Examples of upper houses in countries include the Australian Senate, Brazil's Senado Federal, France's Sénat, Germany's Bundesrat, India's Rajya Sabha, Ireland's Seanad, Malaysia's Dewan Negara, the Netherlands' Eerste Kamer, Pakistan's Senate of Pakistan, Russia's Federation Council, Switzerland's Council of States, United Kingdom's House of Lords and the United States Senate.
A lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.

The Parliaments of the Australian states and territories are legislative bodies within the federal framework of the Commonwealth of Australia.

The Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island, along with the Queen of Canada in Right of Prince Edward Island, represented by the Lieutenant-Governor of Prince Edward Island, forms the parliament of the province. The General Assembly meets at Province House, which is located at the intersection of Richmond and Great George Streets in Charlottetown.
The Vidhan Sabha or the State Legislative Assembly is the lower house of a state legislature in the States and Union Territories of India. In the 29 states and 2 union territories with unicameral state legislature it is the sole legislative house. In 7 states it is the lower house of their bicameral state legislatures with the upper house being Vidhan Parishad or the State Legislative Council. 5 Union Territories are governed directly by the Union Government and have no legislative body. Members of a Vidhan Sabha are referred to as MLAs and are directly elected to serve 5 year terms by single-member constituencies. In 14 states the Governor of a state may appoint one Anglo-Indian MLA to their respective states Vidhan Sabha in accordance with the 23rd Amendment of the Constitution of India. The Constitution of India states that a Vidhan Sabha must have no less than 60 and no more than 500 members however an exception may be granted via an Act of Parliament as is the case in the states of Goa, Sikkim, Mizoram and the union territory of Puducherry which have fewer than 60 members. A Vidhan Sabha may be dissolved in a state of emergency, by the Governor on request of the Chief Minister, or if a motion of no confidence is passed against the majority coalition.

The Legislature of American Samoa or Fono is the territorial legislature of American Samoa. Like most state and territorial legislatures of the United States, it is a bicameral legislature with a House of Representatives and a Senate. The legislature is located in Fagatogo along Pago Pago harbor.

The Slovenian Parliament is the informal designation of the general representative body of the Slovenian nation and the legislative body of the Republic of Slovenia.

The Parliament of Cameroon is the legislature of Cameroon. A bicameral body, it consists of the Senate and the National Assembly.

The Philippine Legislature was the legislature of the Philippines from 1907 to 1935, during the American colonial period, and predecessor of the current Congress of the Philippines. It was bicameral and the legislative branch of the Insular Government.

The Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly is the lower house of the Andhra Pradesh Legislature. As of 2014 the Legislative Assembly of Andhra Pradesh consists of 175 MLA's with a term of 5 years. The structure of the assembly is Bicameral and holds three sessions annually: the Budget, Monsoon and Winter sessions. The Legislative Assembly took up residence in the interim Legislative Assembly Building in Amaravati beginning in the 2016 Budget session. The new building has systems for automatic speech translation and an automatic vote recording system.
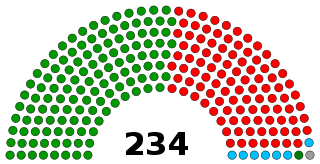
The Tamil Nadu Legislature is the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. The Legislature is composed of Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly and the Governor of Tamil Nadu
The Canal de Televisión del Congreso de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos, shortened to Canal del Congreso, is a television channel in Mexico that broadcasts the sessions of both houses of the Congress of the Union. It is available on all Mexican cable and satellite systems, as well as over-the-air in Mexico City on digital television station XHHCU-TDT channel 45.









