
Deep-sea fish are fish that live in the darkness below the sunlit surface waters, that is below the epipelagic or photic zone of the sea. The lanternfish is, by far, the most common deep-sea fish. Other deep-sea fishes include the flashlight fish, cookiecutter shark, bristlemouths, anglerfish, viperfish, and some species of eelpout.
Ophidiiformes is an order of ray-finned fish that includes the cusk-eels, pearlfishes, viviparous brotulas, and others. Members of this order have small heads and long slender bodies. They have either smooth scales or no scales, a long dorsal fin and an anal fin that typically runs into the caudal fin. They mostly come from the tropics and subtropics, and live in both freshwater and marine habitats, including abyssal depths. They have adopted a range of feeding methods and lifestyles, including parasitism. The majority are egg-laying, but some are viviparous.
The abyssal zone or abyssopelagic zone is a layer of the pelagic zone of the ocean. The word abyss comes from the Greek word ἄβυσσος (ábussos), meaning "bottomless". At depths of 4,000–6,000 m (13,000–20,000 ft), this zone remains in perpetual darkness. It covers 83% of the total area of the ocean and 60% of Earth's surface. The abyssal zone has temperatures around 2–3 °C (36–37 °F) through the large majority of its mass. The water pressure can reach up to 76 MPa.

Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes. They occupy the sea floors and lake beds, which usually consist of mud, sand, gravel or rocks. In coastal waters, they are found on or near the continental shelf, and in deep waters, they are found on or near the continental slope or along the continental rise. They are not generally found in the deepest waters, such as abyssal depths or on the abyssal plain, but they can be found around seamounts and islands. The word demersal comes from the Latin demergere, which means to sink.

The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ophis meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses and others.
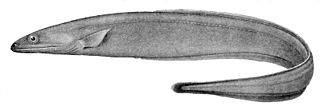
The grey cutthroat eel, Synaphobranchus affinis, is a cutthroat eel. It was originally described by Albert Günther in 1877. It lives a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope and global deep waters including near Portugal, Canary Islands, Morocco, Japan, Australia, and others. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which has been found at depths ranging from 300 to 2300 meters and at temperatures ranging from 3.3 - 11.3 °C. Males can grow to a length of up to 110 centimeters. It is primarily a scavenger, however it also actively hunts small fish and crustaceans.

Double anglers are a family, Diceratiidae, of anglerfishes. They are found in deep, lightless waters of the Atlantic, Indian and western Pacific Oceans.

Fish are very diverse animals and can be categorised in many ways. Although most fish species have probably been discovered and described, about 250 new ones are still discovered every year. According to FishBase about 34,800 species of fish had been described as of February 2022, which is more than the combined total of all other vertebrate species: mammals, amphibians, reptiles and birds.

Spectrunculus grandis is a species of Rhizopharyngia ray-finned fish in the cusk-eel family known by the common names pudgy cusk-eel and giant cusk-eel. It is one of two species in the formerly monotypic genus Spectrunculus, the other species, S. crassus, having been differentiated in 2008.
Coralliophila aedonia is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Muricidae, the murex snails or rock snails.

Pandalosia ephamilla is a species of minute sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Zebinidae.
Paraliparis membranaceus is a species of snailfish only known from a single specimen of 57 mm standard length collected in Sarmiento Channel in the fjordlands of southern Chile.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fish:
Bassozetus is a genus of cusk-eels found in Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

Tauredophidium hextii is a species of cusk-eel found in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans. It occurs at depths of from 1,500 to 2,660 metres. This species grows to a length of 10.5 centimetres (4.1 in) SL. It is the only known member of its genus. The specific name honours Rear-Admiral John Hext (1842-1924) who was commander of the Royal Indian Marine who supported the expedition in board the R.I.M.S. Investigator in the Arabian Sea which collected the type specimen. Only one larval specimen has been identified and was similar in overall form to the related bony-eared assfish and gargoyle cusk, with multiple elongate pectoral-fin rays
The faceless cusk is a genus of cusk-eel found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans at depths from 3,935 to 5,100 m. This species grows to 46.5 cm (18.3 in) in standard length.
The gargoyle cusk is a species of cusk-eel from the subfamily Neobythitinae of the family Ophidiidae. This species grows to a length of 57 centimetres (22 in) TL. It is the only known member of its genus, although research suggests the species should be classified in the genus Acanthonus. The specific name honours George S. Myers (1905-1985) of Stanford University who taught the describer, Daniel Cohen, ichthyology. It is a rare benthopelagic fish which occurs at depths of 984–2,500 metres (3,228–8,202 ft) around the world, other than the eastern Pacific, in tropical and subtropical latitudes. The larvae are similar in overall form to the related bony-eared assfish, but have the 1–4 and 15–20 pectoral-fin rays elongated.
The Pacific shortfinned eel, also known as the Pacific shortfinned freshwater eel, the short-finned eel, and the South Pacific eel, is an eel in the family Anguillidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1871. It is a tropical, freshwater eel which is known from western New Guinea, Queensland, Australia, the Society Islands, and possibly South Africa. The eels spend most of their lives in freshwater, but migrate to the Pacific Ocean to breed. Males can reach a maximum total length of 110 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of around 60 cm. The Pacific shortfinned eel is most similar to Anguilla australis, and Anguilla bicolor, but can be distinguished by the number of vertebrae.

Serrivomer sector, known commonly as the sawtooth eel, the saw-tooth snipe or the deep-sea eel, is an eel in the family Serrivomeridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern and western Pacific Ocean, including Japan, Chile, and California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 3,243 metres, most often around 305 metres (1,001 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 76 centimetres (30 in).

Ipnops meadi, also known as the grideye fish, is a highly specialized species of Placodithyran abyssal fish found in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone of the Indo-Pacific Ocean. The species was named after Giles W. Mead of the Harvard Museum of Comparative Zoology, a biology professor at Harvard, deep sea explorer, and ichthyologist.













