| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Antarctica |
| Coordinates | 64°19′19″S62°56′06″W / 64.322°S 62.935°W |
| Archipelago | Melchior Islands, Palmer Archipelago |
| Area | 1 km2 (0.39 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
| Administered under the Antarctic Treaty System | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | Uninhabited |
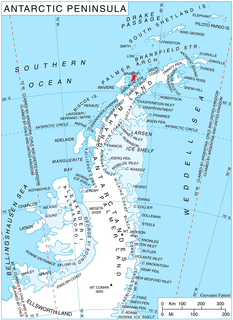
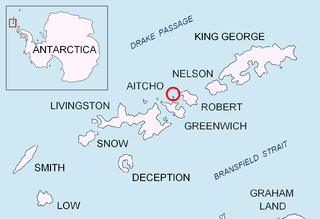
Bremen Island (German : Bremeninsel) is a 1 km2 (0.39 sq mi) or 100 ha (247 acres) uninhabited island, part of the Melchior Islands in the Southern Ocean along the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula.

German is a West Germanic language that is mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, South Tyrol (Italy), the German-speaking Community of Belgium, and Liechtenstein. It is also one of the three official languages of Luxembourg and a co-official language in the Opole Voivodeship in Poland. The languages which are most similar to German are the other members of the West Germanic language branch: Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German/Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, and Yiddish. There are also strong similarities in vocabulary with Danish, Norwegian and Swedish, although those belong to the North Germanic group. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language, after English.

The Melchior Islands are a group of many low, ice-covered islands lying near the center of Dallmann Bay in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. They were first seen but left unnamed by a German expedition under Eduard Dallmann, 1873–74. The islands were resighted and roughly charted by the Third French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, 1903–05. Charcot named what he believed to be the large easternmost island in the group "Île Melchior" after Vice Admiral Jules Melchior of the French Navy, but later surveys proved Charcot's Île Melchior to be two islands, now called Eta Island and Omega Island. The name Melchior Islands has since become established for the whole island group now described, of which Eta Island and Omega Island form the eastern part, while the Sigma Islands mark the northern limit of the islands. The group was roughly surveyed in 1927 by Discovery Investigations personnel in the RRS Discovery, and was resurveyed by Argentine expeditions in 1942 and 1943, and again in 1948.

The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean or the Austral Ocean, and the "Southern Icy Ocean".</ref> comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the fourth largest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. This ocean zone is where cold, northward flowing waters from the Antarctic mix with warmer subantarctic waters.
Contents
A 1 km (0.62 mi) long channel ( Bremenkanal ) separates Omega Island and Bremen Island. The existence of the channel was discovered during a zodiac excursion on 2 February 2003 by the German cruise ship MS Bremen , [1] named after the German city of Bremen. The name "Bremen Island" was proposed by Bärbel Krämer of Hapag-Lloyd.

Omega Island is an island 3.7 kilometres (2 nmi) long, which lies immediately south of Eta Island in the Melchior Islands, Palmer Archipelago. This island, the largest feature in the southeast part of the Melchior Islands, is part of what was called Île Melchior by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, 1903–05, but the name Melchior now applies for the whole island group. Omega Island was roughly surveyed by DI personnel in 1927. The name Omega, derived from the last letter of the Greek alphabet, appears to have been first used on a 1946 Argentine government chart following surveys of the Melchior Islands by Argentine expeditions in 1942 and 1943.

Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central and Western Europe, lying between the Baltic and North Seas to the north, and the Alps to the south. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France to the southwest, and Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands to the west.

A cruise ship is a passenger ship used for pleasure voyages when the voyage itself, the ship's amenities, and sometimes the different destinations along the way, form part of the passengers' experience. Transportation is not the only purpose of cruising, particularly on cruises that return passengers to their originating port. On "cruises to nowhere" or "nowhere voyages", cruise ships make 2-to-3 night round trips without any ports of call.
Coordinates: 64°19′19″S62°56′06″W / 64.322°S 62.935°W

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.