
Dungeons & Dragons is a fantasy tabletop role-playing game (RPG) originally designed by Gary Gygax and Dave Arneson. The game was first published in 1974 by Tactical Studies Rules, Inc. (TSR). It has been published by Wizards of the Coast since 1997. The game was derived from miniature wargames, with a variation of the 1971 game Chainmail serving as the initial rule system. D&D's publication is commonly recognized as the beginning of modern role-playing games and the role-playing game industry, and also deeply influenced video games, especially the role-playing video game genre.

In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus, and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others.
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a cryptographically broken but still widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. Although MD5 was initially designed to be used as a cryptographic hash function, it has been found to suffer from extensive vulnerabilities. It can still be used as a checksum to verify data integrity, but only against unintentional corruption; collision attacks are possible when malice is introduced. It remains suitable for other non-cryptographic purposes, for example for determining the partition for a particular key in a partitioned database, and may be preferred due to lower computational requirements than more recent Secure Hash Algorithms.

In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages.

Paris is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km², making it the 34th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world.

The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. It is a graphic formulation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit an approximate periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. The rows of the table are called periods, and the columns are called groups. Elements from the same column group of the periodic table show similar chemical characteristics. Trends run through the periodic table, with nonmetallic character increasing from left to right across a period, and from down to up across a group, and metallic character increasing in the opposite direction. The underlying reason for these trends is electron configurations of atoms. The periodic table exclusively lists electrically neutral atoms that have an equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons and puts isotopes at the same place. Other atoms, like nuclides and isotopes, are graphically collected in other tables like the tables of nuclides.

In mathematics, the Taylor series of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series, when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the mid-18th century.
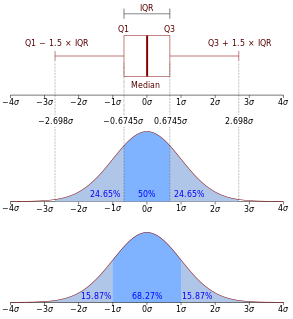
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample in the sample space can be interpreted as providing a relative likelihood that the value of the random variable would be close to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the absolute likelihood for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0, the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample.

Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia, also known as just Washington or simply D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. It is located on the east bank of the Potomac River, which forms its southwestern and southern border with the U.S. state of Virginia, and it shares a land border with the U.S. state of Maryland on its remaining sides. The city was named for George Washington, a Founding Father and the first president of the United States, and the federal district is named after Columbia, a female personification of the nation. As the seat of the U.S. federal government and several international organizations, the city is an important world political capital. It is one of the most visited cities in the U.S. with over 20 million visitors as of 2016.

Sterling is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling.

The Douglas C-47 Skytrain or Dakota is a military transport aircraft developed from the civilian Douglas DC-3 airliner. It was used extensively by the Allies during World War II and remained in front-line service with various military operators for many years.
House is an American medical drama television series that originally ran on the Fox network for eight seasons, from November 16, 2004, to May 21, 2012. The series' main character is Dr. Gregory House, an unconventional, misanthropic medical genius who, despite his dependence on pain medication, leads a team of diagnosticians at the fictional Princeton–Plainsboro Teaching Hospital (PPTH) in New Jersey. The series' premise originated with Paul Attanasio, while David Shore, who is credited as creator, was primarily responsible for the conception of the title character.
SHA-2 is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001. They are built using the Merkle–Damgård construction, from a one-way compression function itself built using the Davies–Meyer structure from a specialized block cipher.

Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The D-isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring agent in food manufacturing. It is also used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewables-based solvent in cleaning products. The less common L-isomer has a piny, turpentine-like odor, and is found in the edible parts of such plants as caraway, dill, and bergamot orange plants.

Avatar is a 2009 American epic science fiction film directed, written, produced, and co-edited by James Cameron and starring Sam Worthington, Zoe Saldana, Stephen Lang, Michelle Rodriguez and Sigourney Weaver. It is set in the mid-22nd century when humans are colonizing Pandora, a lush habitable moon of a gas giant in the Alpha Centauri star system, in order to mine the valuable mineral unobtanium. The expansion of the mining colony threatens the continued existence of a local tribe of Na'vi – a humanoid species indigenous to Pandora. The film's title refers to a genetically engineered Na'vi body operated from the brain of a remotely located human that is used to interact with the natives of Pandora.

In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its impacts on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming.

A Doctor of Philosophy is the most common degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Because it is an earned research degree, those studying for a PhD are required to produce original research that expands the boundaries of knowledge, normally in the form of a dissertation, and defend their work before a panel of other experts in the field. The completion of a PhD is often a requirement for employment as a university professor, researcher, or scientist in many fields. Individuals who have earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree may, in many jurisdictions, use the title Doctor with their name, although the proper etiquette associated with this usage may also be subject to the professional ethics of their own scholarly field, culture, or society. Those who teach at universities or work in academic, educational, or research fields are usually addressed by this title "professionally and socially in a salutation or conversation." Alternatively, holders may use post-nominal letters such as "Ph.D.", "PhD", or "DPhil". It is, however, considered incorrect to use both the title and post-nominals at the same time.
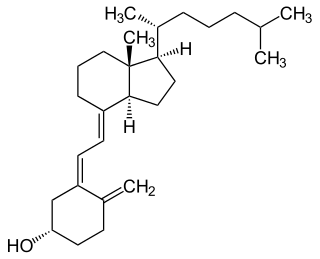
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).













