This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The Faboideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Fabaceae or Leguminosae. An acceptable alternative name for the subfamily is Papilionoideae, or Papilionaceae when this group of plants is treated as a family.

Templetonia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. They are native to Australia. The genus is named in honour of John Templeton, an Irish naturalist and botanist.

Walliserops is a genus of spinose phacopid trilobite, of the family Acastidae, found in Lower to Middle Devonian age rocks from the Anti-Atlas Mountains of Morocco. All species of Walliserops possess a three-pronged "trident" that protrudes from the glabella. Walliserops is most closely related to the genus Comura.
Poecilanthe is a genus of legume in the Fabaceae family.

Platerodrilus is a genus of beetles of the family Lycidae. They commonly appear in the literature under the name Duliticola, which is an obsolete junior synonym. The females stay in the larval form and are about 40–80 mm in length. They have a flat dark body with large scales over the head, resembling trilobites, hence the informal names Trilobite beetle, Trilobite larva or "Sumatran Trilobite larva". The males are much smaller, 8–9 mm, with a beetle-like appearance. Most are found in tropical rainforests, notably in India and South-east Asia.
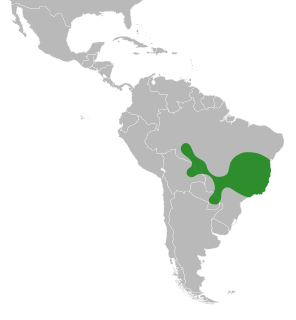
Cyclolobium brasiliense is a species of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It is native to Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay and is the only member of the genus Cyclolobium.

Plagiocarpus is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae.

Bumastus is an extinct genus of corynexochid trilobites which existed from the Early Ordovician period to the Late Silurian period. They were relatively large trilobites, reaching a length of 6 in (15 cm). They were distinctive for their highly globular, smooth-surfaced exoskeleton. They possessed well-developed, large compound eyes and were believed to have dwelled in shallow-water sediments in life.
Ceratocephala may refer to :

Taklamakania is a genus of asaphid trilobites of the family Raphiophoridae that lived during the late Caradoc of Inner Mongolia, China. Like all raphiophorids it is blind, with a headshield that is subsemicircular, carrying genal spines and a forward directed spine on the central raised area, with the front of the glabella inflated and the natural fracture lines of the cephalon coinciding with its margin. It is easily distinguished from most other raphiophorids by the 3 thorax segments. Pseudampyxina, Nanshanaspis, and Kongqiangheia also have only 3 such segments, but all three lack the frontal spine that emanates from the glabellum of Taklamakania species. All other raphiophorid genera have at least 5 thorax segments. Three species, T. tarimensis, T. tarimheensis, and T. xinjiangensis, have been assigned to this genus sofar.
A trilobite is a type of extinct marine arthropod.

Bulbaspis is a late Ordovician genus of asaphid trilobites of the family Raphiophoridae found primarily in upper Ordovician-aged deepwater marine strata of Kazakhstan, China, and possibly Tasmania. Species of Bulbaspis are similar to other raphiophorids such as Ampyx and Raphiophorus, save that the long spine that emanates from the glabella of the latter two genera has been modified into a knob-like or bulb-like structure in Bulbaspis that developed incrementally in the animal's growth. The function of the bulb is as yet unknown: one hypothesis suggests sexual selection may have had a role in its evolution in the genus.

Limadendron is a genus of small trees in the Fabaceae family that was recently separated from the genus Poecilanthe.
The Olenidae were a family of trilobites. They are thought to have evolved a symbiotic relationship with sulfur-eating bacteria from which they derived food.









