Butyrolactone may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Butyrolactone may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure, or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring.

1,4-Butanediol, colloquially known as BD, is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2CH2CH2CH2OH. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is one of four stable isomers of butanediol.
GBL may refer to:

γ-Butyrolactone (GBL) is a hygroscopic colorless, water-miscible liquid with a weak characteristic odor. It is the simplest 4-carbon lactone. It is mainly used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, e.g. methyl-2-pyrrolidone. In humans GBL acts as a prodrug for γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), and it is used as a recreational intoxicant with effects similar to barbiturates.

Glutaric acid is the organic compound with the formula C3H6(COOH)2. Although the related "linear" dicarboxylic acids adipic and succinic acids are water-soluble only to a few percent at room temperature, the water-solubility of glutaric acid is over 50% (w/w).

Thomas James Gugliotta is a former American professional basketball player who played thirteen seasons in the National Basketball Association (NBA).
2-Pyrrolidone is an organic compound consisting of a 5-membered lactam, making it the simplest γ-lactam. It is a colorless liquid that is miscible with water and most common organic solvents.
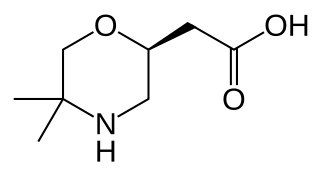
SCH-50911 is a selective GABAB antagonist. Its main applications are in pharmacology research.
The molecular formula C4H6O2 may refer to:

A GABA receptor agonist is a drug that is an agonist for one or more of the GABA receptors, producing typically sedative effects, and may also cause other effects such as anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant effects. There are three receptors of the gamma-aminobutyric acid. The two receptors GABA-α and GABA-ρ are ion channels that are permeable to chloride ions which reduces neuronal excitability. The GABA-β receptor belongs to the class of G-Protein coupled receptors that inhibit adenylyl cyclase, therefore leading to decreased cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). GABA-α and GABA-ρ receptors produce sedative and hypnotic effects and have anti-convulsion properties. GABA-β receptors also produce sedative effects. Furthermore, they lead to changes in gene transcription.

Manganese(III) acetate describes a family of coordination complexes with the approximate formula Mn(O2CCH3)3. All are brown solids, which are soluble in acetic acid and water. These compounds are used in organic synthesis as oxidizing agents.

Aceburic acid (INN), also known as 4-acetoxybutanoic acid or 4-hydroxybutyric acid acetate, is drug described as an analgesic which was never marketed. It is the acetyl ester of gamma-hydroxybutyrate, and based on its structural relation to GHB, is likely to behave as a prodrug to it.

γ-Hydroxyvaleric acid (GHV), also known as 4-methyl-GHB, is a designer drug related to γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). It is sometimes seen on the grey market as a legal alternative to GHB, but with lower potency and higher toxicity, properties which have tended to limit its recreational use.

SKF-97,541 is a compound used in scientific research which acts primarily as a selective GABAB receptor agonist. It has sedative effects in animal studies and is widely used in research into potential treatment of various types of drug addiction.

CGP-35348 is a compound used in scientific research which acts as an antagonist at GABAB receptors.

HA-966 or (±) 3-Amino-1-hydroxy-pyrrolidin-2-one is a molecule used in scientific research as a glycine receptor and NMDA receptor antagonist / low efficacy partial agonist. It has neuroprotective and anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, antinociceptive and sedative / hypnotic effects in animal models. Pilot human clinical trials in the early 1960s showed that HA-966 appeared to benefit patients with tremors of extrapyramidal origin.
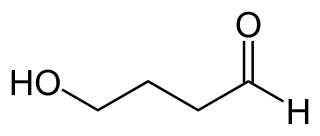
γ-Hydroxybutyraldehyde, also referred to as GHBAL, γ-hydroxybutaldehyde or γ-hydroxybutanal, is a chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) from 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD). Like 1,4-BD, it also behaves as a prodrug to GHB when taken exogenously. However, as with all aliphatic aldehydes, γ-hydroxybutaldehyde is caustic and is strong-smelling and foul-tasting; thus, actual ingestion of this compound is likely to be unpleasant and result in severe nausea and vomiting.

Tetronic acid is a chemical compound, classified as a γ-lactone, with the molecular formula C4H4O3.

2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a cyclic orthoester which can be reacted with diols to biodegradable polyorthoesters.

β-Butyrolactone is the intramolecular carboxylic acid ester (lactone) of the optically active 3-hydroxybutanoic acid. It is produced during chemical synthesis as a racemate. β-Butyrolactone is suitable as a monomer for the production of the biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB). Polymerisation of racemic (RS)-β-Butyrolactone provides (RS)-polyhydroxybutyric acid, which, however, is inferior in essential properties to the (R)-poly-3-hydroxybutyrate originating from natural sources.