This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a precursor polypeptide with 241 amino acid residues. POMC is synthesized in the pituitary from the 285-amino-acid-long polypeptide precursor pre-pro-opiomelanocortin (pre-POMC), by the removal of a 44-amino-acid-long signal peptide sequence during translation.

The complement system is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promotes inflammation, and attacks the pathogen's cell membrane. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. The complement system can, however, be recruited and brought into action by antibodies generated by the adaptive immune system.

The alternative pathway of the complement system is an innate component of the immune system's natural defense against infections.

Proprotein convertase 1, also known as prohormone convertase, prohormone convertase 3, or neuroendocrine convertase 1 and often abbreviated as PC1/3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK1 gene. PCSK1 and PCSK2 differentially cleave proopiomelanocortin and they act together to process proinsulin and proglucagon in pancreatic islets.
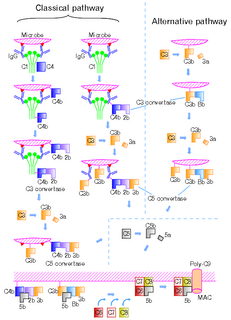
C5 convertase is an enzyme belonging to a family of serine proteases that play key role in the innate immunity. It participates in the complement system ending with cell death.

Furin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FURIN gene. Some proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, and must have sections removed in order to become active. Furin cleaves these sections and activates the proteins. It was named furin because it was in the upstream region of an oncogene known as FES. The gene was known as FUR and therefore the protein was named furin. Furin is also known as PACE.
Proprotein convertases are a family of proteins that activate other proteins. Many proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, because they contain chains of amino acids that block their activity. Proprotein convertases remove those chains and activate the protein. The prototypical proprotein convertase is furin. Proprotein convertases have medical significance, because they are involved in many important biological processes, such as cholesterol synthesis. Compounds called proprotein convertase inhibitors can block their action, and block the target proteins from becoming active. Many proprotein convertases, especially furin and PACE4, are involved in pathological processes such as viral infection, inflammation, hypercholesterolemia, and cancer, and have been postulated as therapeutic targets for some of these diseases.

Proprotein convertase 2 (PC2) also known as prohormone convertase 2 or neuroendocrine convertase 2 (NEC2) is a serine protease and proprotein convertase PC2, like proprotein convertase 1 (PC1), is an enzyme responsible for the first step in the maturation of many neuroendocrine peptides from their precursors, such as the conversion of proinsulin to insulin intermediates. To generate the bioactive form of insulin, a second step involving the removal of C-terminal basic residues is required; this step is mediated by carboxypeptidases E and/or D. PC2 plays only a minor role in the first step of insulin biosynthesis, but a greater role in the first step of glucagon biosynthesis compared to PC1. PC2 binds to the neuroendocrine protein named 7B2, and if this protein is not present, proPC2 cannot become enzymatically active. 7B2 accomplishes this by preventing the aggregation of proPC2 to inactivatable forms. The C-terminal domain of 7B2 also inhibits PC2 activity until it is cleaved into smaller inactive forms. Thus, 7B2 is both an activator and an inhibitor of PC2. PC2 has been identified in a number of animals, including C. elegans.

ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 (ADAM17), also called TACE, is a 70-kDa enzyme that belongs to the ADAM protein family of disintegrins and metalloproteases.

Met-enkephalin, also known as metenkefalin (INN), sometimes referred to as opioid growth factor (OGF), is a naturally occurring, endogenous opioid peptide that has opioid effects of a relatively short duration. It is one of the two forms of enkephalin, the other being leu-enkephalin. The enkephalins are considered to be the primary endogenous ligands of the δ-opioid receptor, due to their high potency and selectivity for the site over the other endogenous opioids.

C3b is the larger of two elements formed by the cleavage of complement component 3, and is considered an important part of the innate immune system. C3b is potent in opsonization: tagging pathogens, immune complexes (antigen-antibody), and apoptotic cells for phagocytosis. Additionally, C3b plays a role in forming a C3 convertase when bound to Factor B, or a C5 convertase when bound to C4b and C2b or when an additional C3b molecule binds to the C3bBb complex.

Carboxypeptidase E (CPE), also known as carboxypeptidase H (CPH) and enkephalin convertase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPE gene. This enzyme catalyzes the release of C-terminal arginine or lysine residues from polypeptides.

Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK5 gene, found in chromosome 9q21.3 Two alternatively spliced transcripts are described for this gene but only one has its full length nature known.

Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK7 gene.
Lysine carboxypeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Nardilysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Magnolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction










