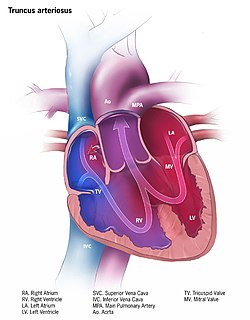
Persistent truncus arteriosus, is a rare form of congenital heart disease that presents at birth. In this condition, the embryological structure known as the truncus arteriosus fails to properly divide into the pulmonary trunk and aorta. This results in one arterial trunk arising from the heart and providing mixed blood to the coronary arteries, pulmonary arteries, and systemic circulation.
Bruit, also called vascular murmur, is the abnormal sound generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery due to either an area of partial obstruction or a localized high rate of blood flow through an unobstructed artery.
Cardiac nursing is a nursing specialty that works with patients who suffer from various conditions of the cardiovascular system. Cardiac nurses help treat conditions such as unstable angina, cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction and cardiac dysrhythmia under the direction of a cardiologist.
The cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high density single structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves and influences the forces exerted through them. The cardiac skeleton separates and partitions the atria from the ventricles.
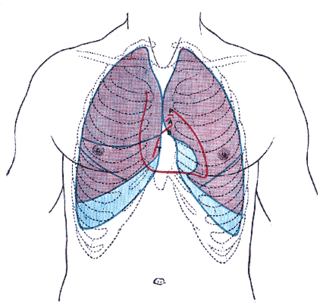
Commotio cordis is an often lethal disruption of heart rhythm that occurs as a result of a blow to the area directly over the heart, at a critical time during the cycle of a heart beat causing cardiac arrest. It is a form of ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib), not mechanical damage to the heart muscle or surrounding organs, and not the result of heart disease. The fatality rate is about 65% even with prompt CPR and defibrillation, and more than 80% without.
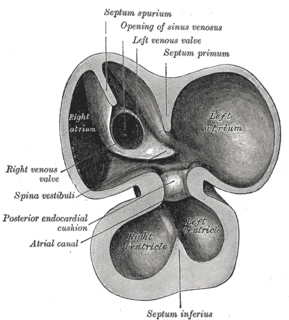
Endocardial cushions, or atrioventricular cushions, refer to a subset of cells in the development of the heart that play a vital role in the proper formation of the heart septa.
Pentalogy of Cantrell is a rare syndrome that causes defects involving the diaphragm, abdominal wall, pericardium, heart and lower sternum.
Ectopia cordis is a congenital malformation in which the heart is abnormally located either partially or totally outside of the thorax. The ectopic heart can be found along a spectrum of anatomical locations, including the neck, chest, or abdomen. In most cases, the heart protrudes outside the chest through a split sternum.
Cardiovascular technologists are health professionals that deal with the circulatory system.

The Hamilton General Hospital (HGH) is a major teaching hospital in Downtown Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, located at the intersection of Barton Street East and Victoria Avenue North. It is operated by Hamilton Health Sciences and is formally affiliated with the Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine at McMaster University.

William P. Murphy Jr. is a medical doctor and inventor of medical devices including collaborating on a flexible sealed blood bag used for blood transfusions. He is the son of the American physician William Parry Murphy who shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology for Medicine in 1934, and Harriett Adams, the first licensed female dentist in Massachusetts.

Adam Christian Thebesius was a German anatomist who was a native of Sandenwalde, Silesia.

The smallest cardiac veins are minute valveless veins in the walls of all four heart chambers. The veins are sometimes accurately referred to as vessels, but they are frequently confused with a distinct set of artery connections eponymously referred to as the "vessels of Wearn". In his 1928 publication, Wearn himself referred to the arterio-cameral connections as thebesian. However, Wearn's 1933 and 1941 publications emphatically described the thebesian veins as distinct from arterio-cameral vessels.
Cardiothoracic anesthesiology is a subspeciality of the medical practice of anesthesiology devoted to the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care of adult and pediatric patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery and related invasive procedures.

Bare-metal stent is a stent without a coating or covering. It is a mesh-like tube of thin wire. The first stents licensed for use in cardiac arteries were bare metal – often 316L stainless steel. More recent stents use cobalt chromium alloy. The first stents used in gastrointestinal conditions of the esophagus, gastroduodenum, biliary ducts, and colon were plastic; bare metal stents were first brought into the clinic in the 1990s.

The Richard M. Ross Heart Hospital is located at The Ohio State University in Columbus, Ohio. The hospital specializes in cardiology, and is ranked number 20 in the United States for its heart program. Care is provided for patients with cardiovascular disease or peripheral vascular disease. The hospital was the first in the country to perform robotic surgery.

Adventist HealthCare Washington Adventist Hospital is a 204-licensed bed acute care facility located in Takoma Park, Maryland, United States. Washington Adventist Hospital provides a range of health services such as cardiac and vascular care, maternity services, cancer care, surgical services including robotic surgery and orthopedics and emergency services.

Levamlodipine (INN), also known as levoamlodipine or S-amlodipine is a pharmacologically active enantiomer of amlodipine. Amlodipine belongs to the dihydropyridine group of calcium channel blocker used as an antihypertensive and antianginal agent. Levamlodipine is currently marketed in Russia under the brand name EsCordi Cor, in Brazil under the brand name Novanlo and in India under the trade names Eslo, Asomex, and Espin.
Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital, also known as the Perambur railway hospital, is a 500-bed hospital of the Southern Railway located in Ayanavaram, Chennai. It is spread across a land measuring 15 acres (6.1 ha) and was established during the British rule. The hospital has specialized in 15 basic disciplines and super-specialized in 3 disciplines. The National Board of Examination (NBE) has accredited the hospital for recognition in postgraduate training. The hospital has also been accredited by international institutions such as Royal College of Surgeons for imparting training in PG courses. It is also an approved institution for training nurses.












