Caesium or cesium is a chemical element with symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C (83.3 °F), which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. The most reactive of all metals, it is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at −116 °C (−177 °F). It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite, while the radioisotopes, especially caesium-137, a fission product, are extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors.

Gold is a chemical element with symbol Au and atomic number 79, making it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. In its purest form, it is a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native) form, as nuggets or grains, in rocks, in veins, and in alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver and also naturally alloyed with copper and palladium. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium.

Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most other chemicals. Russian-born scientist of Baltic-German ancestry Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element in 1844 at Kazan State University and named it after the Latin name of his homeland, Ruthenia. Ruthenium is usually found as a minor component of platinum ores; the annual production has risen from about 19 tonnes in 2009 to some 35.5 tonnes in 2017. Most ruthenium produced is used in wear-resistant electrical contacts and thick-film resistors. A minor application for ruthenium is in platinum alloys and as a chemistry catalyst. A new application of ruthenium is as the capping layer for extreme ultraviolet photomasks. Ruthenium is generally found in ores with the other platinum group metals in the Ural Mountains and in North and South America. Small but commercially important quantities are also found in pentlandite extracted from Sudbury, Ontario and in pyroxenite deposits in South Africa.

Acid mine drainage, acid and metalliferous drainage (AMD), or acid rock drainage (ARD) is the outflow of acidic water from metal mines or coal mines.

A minehunter is a naval vessel that seeks, detects, and destroys individual naval mines. Minesweepers, on the other hand, clear mined areas as a whole, without prior detection of mines. A vessel that combines both of these roles is known as a mine countermeasures vessel (MCMV).

Ammonal is an explosive made up of ammonium nitrate and aluminium powder, not to be confused with T-ammonal which contains trinitrotoluene as well to increase properties such as brisance.

The Dodge Power Wagon is a four wheel drive medium duty truck that was produced in various model series from 1945 to 1981 by Dodge, then as a nameplate for the Dodge Ram from 2005 to 2013, and, most recently ‘13-present, as an individual model marketed by Ram Trucks. It was developed as the WDX truck, and until about 1960 it was internally known by its engineering code T137 – a name still used for the original series by enthusiasts.

Gold mining is the resource extraction of gold by mining.

Tsumeb is a city of 15,000 inhabitants and the largest town in Oshikoto region in northern Namibia. Tsumeb is the "gateway to the north" of Namibia. It is the closest town to the Etosha National Park. Tsumeb used to be the regional capital of Oshikoto until 2008 when Omuthiya was proclaimed a town and the new capital. The area around Tsumeb forms its own electoral constituency and has a population of 44,113. The town is the site of a deep mine, that in its heyday was known simply as "The Tsumeb Mine" but has since been renamed the Ongopolo Mine.

Magnesium nitrate refers to inorganic compounds with the formula Mg(NO3)2(H2O)x, where x = 6, 2, and 0. All are white solids. The anhydrous material is hygroscopic, quickly forming the hexahydrate upon standing in air. All of the salts are very soluble in both water and ethanol.

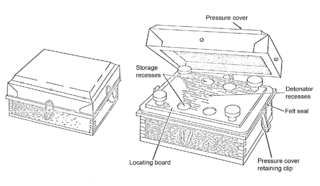
The Schu-mine 42 (Shoe-mine), also known as the Schützenmine 42, was a German anti-personnel mine used during the Second World War. It consisted of a simple wooden box with a hinged lid containing a 200-gram (7.1 oz) block of cast TNT and a ZZ-42 type detonator. A slot in the lid pressed down on the striker retaining pin, sufficient pressure on the lid caused the pin to move, releasing the striker which triggered the detonator.

The TM-38 was a rectangular, metal-cased Soviet anti-tank mine used during the Second World War. The mine had a large raised rectangular central pressure plate with four reinforcing creases. When enough pressure was applied to the plate it collapses pressing down on a bolt connected to an internal lever. The lever is pulls a retaining pin from the MUV fuze, which releases the striker, which impacts the MD-2 detonator.

Tiger is a former populated place in Pinal County in the U.S. state of Arizona. The town was settled as Schultz around 1881 in what was then the Arizona Territory, then later reestablished as Tiger after World War I.

The TS-50 is a 90 mm (3.5 in) diameter circular Italian blast resistant minimum metal anti-personnel mine designed and produced by Valsella Meccanotecnica.

The CC 48 is an Italian wooden cased minimum metal anti-tank mine that was used during the Second World War. The mine uses a shaped TNT explosive charge to produce a directional cutting effect. The mine uses two PMC/43 fuzes, but these can be replaced with PMC/42/2 anti-personnel fuzes, combined with weakening the lid this can make it sensitive enough to be detonated by the weight of a mine.

The ANDROS is a series of remote control military robots designed by REMOTEC, a subsidiary of Northrup Grumman. The ANDROS series is primarily designed for military, explosive ordnance disposal (EOD), and law enforcement or SWAT applications. The ANDROS gained notability in 2016 for being involved in the first instance of a robot being used to kill another person, Micah Xavier Johnson, the gunman involved in the 2016 shooting of Dallas police officers.

The environmental impact of mining can occur at local, regional, and global scales through direct and indirect processes, leading to erosion, sinkholes, biodiversity loss, and the contamination of soil, groundwater, and surface water by chemicals from mining processes. The process of mining directly emits carbon into the atmosphere which also has impact on biodiversity and human health. The contamination of watersheds resulting from the leakage of chemicals also has affect on the health of the local population. Some mining methods may have significant environmental and public health effects, therefore mining companies in some countries are required to follow environmental and rehabilitation codes, to ensure that the mined area is returned to its original state.

Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. Like nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.

Metal is a low-level, low-overhead hardware-accelerated 3D graphic and compute shader application programming interface (API) developed by Apple Inc., and which debuted in iOS 8. Metal combines functions similar to OpenGL and OpenCL under one API. It is intended to bring to iOS, macOS, and tvOS apps some of the performance benefits of similar APIs on other platforms, such as Vulkan and DirectX 12.