
In computing, multitasking is the concurrent execution of multiple tasks over a certain period of time. New tasks can interrupt already started ones before they finish, instead of waiting for them to end. As a result, a computer executes segments of multiple tasks in an interleaved manner, while the tasks share common processing resources such as central processing units (CPUs) and main memory. Multitasking automatically interrupts the running program, saving its state and loading the saved state of another program and transferring control to it. This "context switch" may be initiated at fixed time intervals, or the running program may be coded to signal to the supervisory software when it can be interrupted.
Microsoft Windows is a group of several graphical operating system families, all of which are developed, marketed, and sold by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Windows families include Windows NT and Windows Embedded; these may encompass subfamilies, e.g. Windows Embedded Compact or Windows Server. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile and Windows Phone.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is any operating system (OS) intended to serve real-time applications that process data as it comes in, typically without buffer delays. Processing time requirements are measured in tenths of seconds or shorter increments of time.
A real time system is a time bound system which has well defined fixed time constraints. Processing must be done within the defined constraints or the system will fail.
They either are event driven or time sharing. Event driven systems switch between tasks based on their priorities while time sharing systems switch the task based on clock interrupts. Most RTOS’s use a pre-emptive scheduling algorithm.
In computing, time-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many users by means of multiprogramming and multi-tasking at the same time.
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is an emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve specialized hardware, software, or a combination.
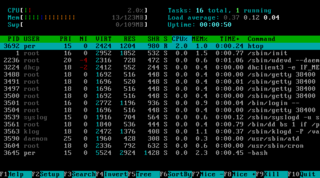
In computing, a process is the instance of a computer program that is being executed. It contains the program code and its activity. Depending on the operating system (OS), a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently.

Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) involves a multiprocessor computer hardware and software architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single, shared main memory, have full access to all input and output devices, and are controlled by a single operating system instance that treats all processors equally, reserving none for special purposes. Most multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture. In the case of multi-core processors, the SMP architecture applies to the cores, treating them as separate processors.
Multiprocessing is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There are many variations on this basic theme, and the definition of multiprocessing can vary with context, mostly as a function of how CPUs are defined.

In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often for software development. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets.

VM is a family of IBM virtual machine operating systems used on IBM mainframes System/370, System/390, zSeries, System z and compatible systems, including the Hercules emulator for personal computers.
A multiplayer video game is a video game in which more than one person can play in the same game environment at the same time, either locally or over the internet. During its early history, video games were often single-player-only activities, putting the player against preprogrammed challenges or AI-controlled opponents, which lack the flexibility of human thought. Multiplayer games allow players interaction with other individuals in partnership, competition or rivalry, providing them with social communication absent from single-player games. In multiplayer games, players may compete against one or more human contestants, work cooperatively with a human partner to achieve a common goal, supervise other players' activity, co-op. Multiplayer games usually require players to share the resources of a single game system or use networking technology to play together over a greater distance.

A bicycle-sharing system, public bicycle system, or bike-share scheme, is a service in which bicycles are made available for shared use to individuals on a short term basis for a price or free. Many bike share systems allow people to borrow a bike from a "dock" and return it at another dock belonging to the same system. Docks are special bike racks that lock the bike, and only release it by computer control. The user enters payment information, and the computer unlocks a bike. The user returns the bike by placing it in the dock, which locks it in place. Other systems are dockless. For many systems, smartphone mapping apps show nearby available bikes and open docks.
In computing, preemption is the act of temporarily interrupting a task being carried out by a computer system, without requiring its cooperation, and with the intention of resuming the task at a later time. Such changes of the executed task are known as context switches. It is normally carried out by a privileged task or part of the system known as a preemptive scheduler, which has the power to preempt, or interrupt, and later resume, other tasks in the system.
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed during overlapping time periods—concurrently—instead of sequentially. This is a property of a system—this may be an individual program, a computer, or a network—and there is a separate execution point or "thread of control" for each computation ("process"). A concurrent system is one where a computation can advance without waiting for all other computations to complete.
In computing, a shared resource, or network share, is a computer resource made available from one host to other hosts on a computer network. It is a device or piece of information on a computer that can be remotely accessed from another computer, typically via a local area network or an enterprise intranet, transparently as if it were a resource in the local machine.
Network sharing is made possible by inter-process communication over the network.
A clustered file system is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system. Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance.

The usage share of operating systems is the percentage of computing devices that run each operating system at any particular time. All such figures are necessarily estimates because data about operating system share is difficult to obtain; there are few reliable primary sources—and no agreed methodologies for its collection.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, development starting in the 1970s at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.

In computer science, shared memory is memory that may be simultaneously accessed by multiple programs with an intent to provide communication among them or avoid redundant copies. Shared memory is an efficient means of passing data between programs. Depending on context, programs may run on a single processor or on multiple separate processors.










