
Euboea or Evia is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. The narrow Euripus Strait separates it from Boeotia in mainland Greece. In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about 180 kilometres (110 mi) long, and varies in breadth from 50 kilometres (31 mi) to 6 kilometres (3.7 mi). Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboea in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos.
Dion or Dio may refer to:

Styra is a village and a former municipality on the island Euboea, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Karystos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 188.583 km2. It is located in the southern part of Euboea, facing the eastern shore of Attica across the South Euboean Gulf. Nowadays it can be reached by ferryboat from the tiny harbor of Agia Marina, as well as by bridge from Chalcis. Above the port there is a hill where the church of Saints Kostantine and Helen is situated with a panoramic view of the coast and Stouronisi . Styra is a very popular destination for Athenians during the summer period. After the collapse of the Iron Curtain, Albanians migrated into the area. The town takes its name from the ancient town of Styra.

Greek National Road 44 is a single carriageway road in central Greece. It connects Thebes with Karystos on southern Euboea, via Chalcis and Eretria. The total length of the GR-44 is nearly 160 km. The highway lies in the regional units of Boeotia and Euboea.
Myloi may refer to places in Greece:
Apollodorus of Carystus in Euboea, was one of the most important writers of the Attic New Comedy, who flourished in Athens between 300 and 260 B.C. He is to be distinguished from the older Apollodorus of Gela (342—290), a contemporary of Menander who was also a writer of New Comedy. He wrote 47 comedies and obtained the prize five times. Terence's Hecyra and Phormio were adapted from the Hekyra and Epidikazomenos of Apollodorus.

Marmari is a village and a former municipality in Euboea, Greece, in the southeastern end of the island. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Karystos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 241.332 km2. The Greek National Road 44 runs through Marmari. There are ferry routes with the mainland port of Rafina. The mountains dominate the east. Its main economy are businesses and agriculture. Marmari is located SE of Chalkida, E of Rafina and west of Karystos.
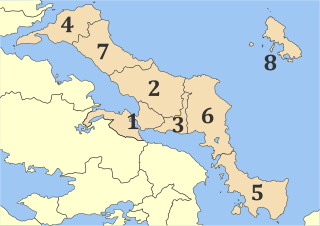
Euboea is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Central Greece. It consists of the islands of Euboea and Skyros, as well as a 395 km² area on the Greek mainland. Its land area is 4,167.449 km², whereas the total land area of the municipalities actually on the island Euboea is 3,684.848 km², which includes that of numerous small offshore islets near Euboea's southern tip.
Diocles of Carystus was a well regarded Greek physician, born in Carystus, a city on Euboea, Greece. Diocles lived not long after the time of Hippocrates, to whom Pliny says he was next in age and fame. Not much is known of his life, other that he lived and worked in Athens, where he wrote what may be the first medical treatise in Attic. His most important work was in practical medicine, especially diet and nutrition, but he also wrote the first systematic textbook on animal anatomy. According to a number of sources, he was the first to use the word "anatomy" to describe the study. He belonged to the medical sect of the Dogmatici, and wrote several medical works, of which only the titles and some fragments remain, preserved by Galen, Caelius Aurelianus, Oribasius, Athenaeus, and other ancient writers.

Amarynthos, is a coastal town and a former municipality in Euboea, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Eretria, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 109.909 km2. In 2011 its population was 3,672 for the town and 6,723 for the municipal unit. The Amarynthos is 8 km east of Eretria, 27 km southeast of Chalcis, 63 km northwest of Karystos and 10 km north of Kalamos, across the gulf. The Greek National Road 44 passes through the town.

The Triarchy of Negroponte was a crusader state established on the island of Euboea after the partition of the Byzantine Empire following the Fourth Crusade. Partitioned into three baronies run by a few interrelated Lombard families, the island soon fell under the influence of the Republic of Venice. From circa 1390, the island became a regular Venetian colony as the Kingdom of Negroponte.

Ochi is a mountain in the southeasternmost part of the island of Euboea, Greece. Its maximum elevation is 1,398 m. There are forests on the northern slopes while most of the mountain range is covered with grassland and bushes. It is 6 km northeast of the coastal town Karystos, 90 km southeast of the island capital Chalcis and 65 km east of Athens.

Vathy is a town and a community in the municipal unit of Avlida in the Euboea regional unit, Greece. It is situated on the Greek mainland, near the South Euboean Gulf, 6 km south of Chalcis. The Greek National Road 44 passes west of the town. The community Vathy consists of the town Vathy and the villages Mikro Vathy, Paralia and Ritsona.
Carystus, in Greek mythology, was the eponym of the town of Carystus on Euboea. He was the son of Chiron and a nymph Chariclo, brother of Hippe, Endeïs and Ocyrhoe. Carystus was the father of Zarex, and also a certain Aristaeus.
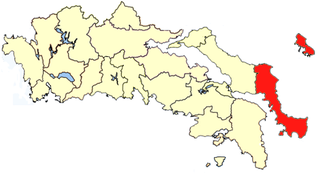
Karystia was one of the provinces of the Euboea Prefecture, Greece. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Karystos, Kymi-Aliveri, and Skyros. It was abolished in 2006.
Carystus or Karystos was a town in ancient Laconia, in the district Aegytis, near the frontiers of Laconia. Its wine was celebrated by the poet Alcman. William Martin Leake, a 19th century explorer and classicist, supposed that Carystus stood at the site known as "Huts of Giorgitzes", but modern scholars treat its site as unlocated.
Styra was a town of ancient Euboea, on the west coast, north of Carystus, and nearly opposite the promontory of Cynosura in Attica. The town stood near the shore in the inner part of the bay, in the middle of which is the island Aegileia, now called Stouronisi. Styra is mentioned by Homer along with Carystus in the Catalogue of Ships in the Iliad. Its inhabitants were originally Dryopians, though they denied this origin, and claimed to be descended from the deme of Steiria in Attica. In the First Persian War (490 BCE) the Persians landed at Aegileia, which belonged to Styra, the prisoners whom they had taken at Eretria. In the Second Persian War (480-479 BCE) the Styrians fought at the battles of Artemisium, Salamis, and Plataeae. They sent two ships to the naval engagements, and at Plataeae they and the Eretrians amounted together to 600 men. They afterwards became the subjects of Athens, and paid a yearly tribute of 1200 drachmae. The Athenian fleet was stationed here in 356 BCE. Strabo relates that the town was destroyed in the "Maliac War" by the Athenian Phaedrus, and its territory given to the Eretrians; but as the Maliac War is not mentioned elsewhere, we ought probably to substitute Lamian War for it.
Marmarium or Marmarion was a town of ancient Euboea. According to Strabo, Marmarium was situated upon the coast near Carystus, opposite Halae Araphenides in Attica. The quarries at Marmarium produced a celebrated green marble, with white zones – the Cipollino marble of the Romans.








