
The Orinoco River is one of the longest rivers in South America at 2,140 kilometres (1,330 mi). Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers 880,000 square kilometres (340,000 sq mi), with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the third largest river in the world by discharge volume of water. The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the llanos of Colombia. The environment in the Orinoco's basin is extremely diverse; it hosts a wide variety of flora and fauna.

The Rio Negro is the largest left tributary of the Amazon River, the largest blackwater river in the world, and one of the world's ten largest rivers by average discharge.
San Juan River may refer to:

The Essequibo River is the largest river in Guyana, and the largest river between the Orinoco and Amazon. Rising in the Acarai Mountains near the Brazil-Guyana border, the Essequibo flows to the north for 1,014 kilometres (630 mi) through forest and savanna into the Atlantic Ocean. With a total drainage basin of 69,300 sq.km (26,757sq.mi) with average discharge of 74,303 cu ft/s.

A blackwater river is a type of river with a slow-moving channel flowing through forested swamps or wetlands. As vegetation decays, tannins leach into the water, making a transparent, acidic water that is darkly stained, resembling tea. Most major blackwater rivers are in the Amazon Basin and the Southern United States. The term is used in fluvial studies, geology, geography, ecology, and biology. Not all dark rivers are blackwater in that technical sense. Some rivers in temperate regions, which drain or flow through areas of dark black loam, are simply black due to the color of the soil; these rivers are black mud rivers. There are also black mud estuaries.

The Apure River is a river of southwestern Venezuela, formed by the confluence of the Sarare and Uribante near Guasdualito, in Venezuela, at 7°15′N70°40′W, and flowing across the llanos into the Orinoco. It provides significant transportation in the area.

The Cordillera de Mérida is a series of mountain ranges, or massif, in northwestern Venezuela. The Cordillera de Mérida is a northeastern extension of the Andes Mountains and the most important branch of Venezuelan Andes. The ranges run southwest-northeast between the Venezuelan-Colombian border and the Venezuelan Coastal Ranges. The Táchira depression separates the Cordillera de Mérida from the Cordillera Oriental, which forms the Colombia-Venezuela border.

The Meta River is a major left tributary of the Orinoco River in eastern Colombia and southern Venezuela, South America. The Meta originates in the Eastern Ranges of the Andes and flows through the Meta Department, Colombia as the confluence of the Humea, Guatiquía and Guayuriba rivers. It flows east-northeastward across the Llanos Orientales of Colombia following the direction of the Meta Fault. The Meta forms the northern boundary of Vichada Department, first with Casanare Department, then with Arauca Department, and finally with Venezuela, down to Puerto Carreño where it flows into the Orinoco.

The Ventuari River is the largest tributary of the Orinoco in southern Venezuela. The Ventuari flows from south-central Venezuela in the Guiana Highlands southwest into the Orinoco River. It is 520 km (320 mi) long and its major tributary is the Manapiare River.

The department of Norte de Santander in northwestern Colombia, and its capital, Cúcuta, contains several rivers. The rivers are mostly part of the Maracaibo Lake basin, with the southeastern section located in the Magdalena River basin. Important fluvial elements are the Zulia, Catatumbo and Pamplonita Rivers. The entity in charge of taking care of these hydrology of Norte de Santander is Corponor.

The violaceous jay is a species of bird in the family Corvidae, the crows and their allies.

The river tyrannulet is a species of bird in the family Tyrannidae, the tyrant flycatchers. It is found in Peru, Venezuela and Brazil; also river extensions into Ecuador, Colombia-(border) and Bolivia.
Carrao River is a river of Venezuela. It is part of the Orinoco River basin. It is well known for one of its major tributaries, the Churun River, which feeds Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall. Another major tributary is the Ahonda River. The Carrao River flows primarily through Canaima National Park. As it starts to flow north, the Carrao River widens and meets the small town of Canaima, a vacationing destination. It flows north again, but it eventually narrows. As it continues its course west, it drains into the Caroní River, a major tributary of the Orinoco River in Venezuela.

Portuguesa River is a river of Venezuela. It is part of the Orinoco River basin, and is a tributary of the Apure River.

Caparo River is a river of Venezuela. It is part of the Orinoco River basin and a tributary of the Sioca River, itself a tributary of the Apure River.

Uonquén Airport is an airport serving Uonquén, a village in the Bolívar state of Venezuela. The well-marked grass runway is adjacent to the village.
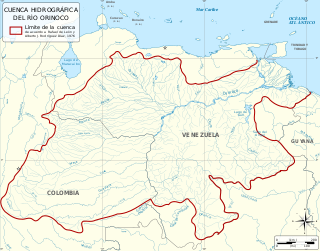
The Orinoco Basin is the part of South America drained by the Orinoco river and its tributaries. The Orinoco watershed covers an area of about 990000 km2, making it the third largest in South America, covering most of Venezuela and eastern part of Colombia.















