
Thuringia, officially the Free State of Thuringia, is a state of Germany. In central Germany, it covers 16,171 square kilometres (6,244 sq mi), being the sixth smallest of the sixteen German States. It has a population of about 2.15 million inhabitants.
Altenburger Land is a district in Thuringia, Germany. It is bounded by the district of Greiz, the Burgenlandkreis (Saxony-Anhalt), and the districts Leipzig, Mittelsachsen and Zwickau in Saxony. The district is a member of the Central German Metropolitan Region.

The Federal Republic of Germany, as a federal state, consists of sixteen partly sovereign federated states. Since the German nation state was formed from an earlier collection of several states, it has a federal constitution, and the constituent states retain a measure of sovereignty.
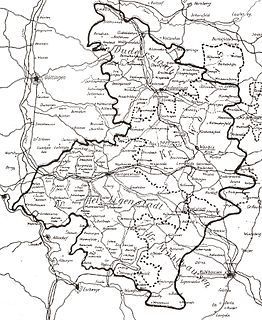
Eichsfeld is a district in Thuringia, Germany, and part of the historical region of Eichsfeld. It is bounded by the districts of Nordhausen, Kyffhäuserkreis and Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, and by the states of Hesse and Lower Saxony.
The Kyffhäuserkreis is a district in the northern part of Thuringia, Germany. Neighboring districts are the districts Mansfeld-Südharz, Saalekreis und Burgenlandkreis in Saxony-Anhalt, and the districts Sömmerda, Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis and Eichsfeld.

The Province of Saxony, also known as Prussian Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.
Silberberg is German for "Silver Mountain" or "Silver Hill" and may refer to:
Central Germany is an economic and cultural region in Germany. Its exact borders depend on context, but it is often defined as being a region within the federal states of Saxony, Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, or a smaller part of this region, such as the metropolitan area of Leipzig and Halle plus the surrounding counties.

Niederdorla is a village and a former municipality in the Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis district of Thuringia, Germany. It is the geographical center of Germany. Its nearest main city is Erfurt, which also is the capital city of Thuringia. Since 31 December 2012, it is part of the municipality Vogtei.
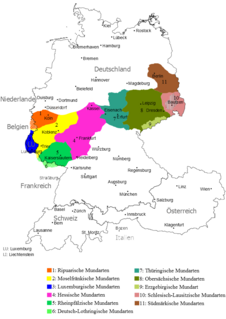
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon spoken mainly in the state of Saxony, therefore both are also regarded as one Thuringian-Upper Saxon dialect group. Thuringian dialects are among the Central German dialects with the highest number of speakers.
Germany is a country in west-central Europe, that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Germany has the second largest population in Europe and is seventh largest in area. The territory of Germany covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of waters.
The East Hesse Highlands describes a heavily wooded range of hills lying mainly in the German state of Hesse, but also extending a little way into Lower Saxony to the north, Thuringia to the east and Bavaria to the southeast. The region is sandwiched between the West Hesse Depression to the west, the Weser Uplands to the north, the Thuringian Basin to the northeast, the northwestern edge of the Thuringian Forest to the east, the Spessart to the south and the Wetterau to the southwest.
The Saxon Highlands and Uplands refer to a natural region mainly in the south of Saxony with small elements also in southeast Thuringia and northeast Bavaria. It comprises, from (south)west to (north)east, of the Vogtland, the Ore Mountains, Saxon Switzerland, the Upper Lusatian Plateau and the Zittau Hills.

The Helme is river in central Germany that is about 65 kilometres (40 mi) long and which forms a left-hand, western tributary of the Unstrut in the states of Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt.

A Naturschutzgebiet is a category of protected area within Germany's Federal Nature Conservation Act . Although often translated as 'Nature Reserve' in English, the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN) refers to them as 'Nature Conservation Areas'. It meets the criteria of an IUCN Category IV Habitat and Species Management Area.
The Drei-Länder-Stein is a boundary stone at the tripoint of the German federated states of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia near the Großer Ehrenberg mountain in the Harz.
The South Harz Nature Park is located in the county of Nordhausen in north Thuringia, Germany. The act designating this nature park in the Harz Mountains came into force on 31 December 2010 and thus founded the fifth nature park in Thuringia. It has an area of 267 km². The park is managed by the South Harz Tourist Association in conjunction with the Kyffhäuser Nature Park.

Vogtei is a municipality in the Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis district of Thuringia, Germany. It was formed on 31 December 2012 by the merger of the former municipalities Langula, Niederdorla and Oberdorla. The closest city ("Stadt"), and the only one that it borders, is Mühlhausen, which lies at its northern perimeter.
The Hesse Highlands, Hessian Highlands or Hessian Highlands and Lowlands, are a largely densely forested low mountain area in the German state of Hesse that lies between the Rhenish Massif and the western edge of the Thuringian Basin. The Hesse Highlands are both part of the German Central Uplands and the Rhine-Weser Watershed.

A Dreiherrenstein or Dreiherrnstein is the topographic name of a historical tripoint, especially in the German-speaking lands of central Europe, i.e. a place where the border of three princely territories met, together with any enclosures or border fortifications. The word means literally "Three Lords' Stone".













