
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.

A carburetor or carburettor is a device that mixes air and fuel for internal combustion engines in the proper air–fuel ratio for combustion. It is sometimes colloquially shortened to carb in the UK and North America or carby in Australia. To carburate or carburet means to mix the air and fuel or to equip with a carburetor for that purpose.
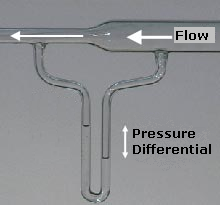
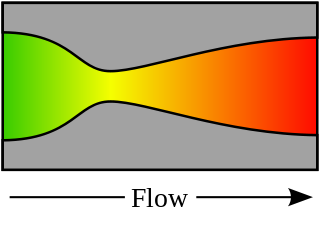
In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy. The principle is named after Daniel Bernoulli who published it in his book Hydrodynamica in 1738. Although Bernoulli deduced that pressure decreases when the flow speed increases, it was Leonhard Euler who derived Bernoulli's equation in its usual form in 1752. The principle is only applicable for isentropic flows: when the effects of irreversible processes and non-adiabatic processes are small and can be neglected.

A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellant mass for forming its high-speed propulsive jet. Rocket engines are reaction engines, obtaining thrust in accordance with Newton's third law. Most rocket engines use combustion, although non-combusting forms also exist. Vehicles propelled by rocket engines are commonly called rockets. Since they need no external material to form their jet, rocket engines can perform in a vacuum and thus can be used to propel spacecraft and ballistic missiles.

A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow as it exits an enclosed chamber or pipe.

Centrifugal compressors, sometimes called radial compressors, are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery.

Cyanosis is the bluish or purplish discolouration of the skin or mucous membranes due to the tissues near the skin surface having low oxygen saturation. Based on Lundsgaard and Van Slyke's work, it is classically described as occurring if 5.0 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin or greater is present. This was based on an estimate of capillary saturation based on a mean of arterial versus peripheral venous blood gas measurements. Since estimation of hypoxia is usually now based either on arterial blood gas measurement or pulse oximetry, this is probably an overestimate, with evidence that levels of 2.0 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin may reliably produce cyanosis. Since, however, the presence of cyanosis is dependent upon there being an absolute quantity of deoxyhemoglobin, the bluish color is more readily apparent in those with high hemoglobin counts than it is with those with anemia. Also, the bluer the color, the more difficult it is to detect on deeply pigmented skin. When signs of cyanosis first appear, such as on the lips or fingers, intervention should be made within 3–5 minutes because a severe hypoxia or severe circulatory failure may have induced the cyanosis.

A gas-filled tube, also known as a discharge tube, is an arrangement of electrodes in a gas within an insulating, temperature-resistant envelope. Gas-filled tubes exploit phenomena related to electric discharge in gases, and operate by ionizing the gas with an applied voltage sufficient to cause electrical conduction by the underlying phenomena of the Townsend discharge. A gas-discharge lamp is an electric light using a gas-filled tube; these include fluorescent lamps, metal-halide lamps, sodium-vapor lamps, and neon lights. Specialized gas-filled tubes such as krytrons, thyratrons, and ignitrons are used as switching devices in electric devices.
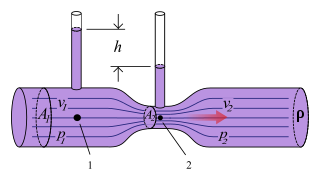
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of a pipe. The Venturi effect is named after Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822), an Italian physicist.

A hose is a flexible hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes, or more generally tubing. The shape of a hose is usually cylindrical.
A propelling nozzle is a nozzle that converts the internal energy of a working gas into propulsive force; it is the nozzle, which forms a jet, that separates a gas turbine, being gas generator, from a jet engine.

In petroleum and natural gas extraction, a Christmas tree, or "tree", is an assembly of valves, spools, and fittings used to regulate the flow of pipes in an oil well, gas well, water injection well, water disposal well, gas injection well, condensate well and other types of wells. It was named for its resemblance to the series of starting lights at a drag racing strip.

A chokehold, choke, stranglehold or, in Judo, shime-waza is a general term for a grappling hold that critically reduces or prevents either air (choking) or blood (strangling) from passing through the neck of an opponent. The restriction may be of one or both and depends on the hold used and the reaction of the victim. The lack of blood or air often leads to unconsciousness or even death if the hold is maintained. Chokeholds are used in martial arts, combat sports, self-defense, law enforcement and in military hand to hand combat applications. They are considered superior to brute-force manual strangling, which generally requires a large disparity in physical strength to be effective. Rather than using the fingers or arms to attempt to crush the neck, chokeholds effectively use leverage such as figure-four holds or collar holds that use the clothes to assist in the constriction.
A compressor map is a chart created for a compressor in a gas turbine engine. Complete maps are based on compressor rig test results or predicted by a special computer program. Alternatively the map of a similar compressor can be suitably scaled.
Choked flow is a compressible flow effect. The parameter that becomes "choked" or "limited" is the fluid velocity.
Accidental release source terms are the mathematical equations that quantify the flow rate at which accidental releases of liquid or gaseous pollutants into the ambient environment can occur at industrial facilities such as petroleum refineries, petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants, oil and gas transportation pipelines, chemical plants, and many other industrial activities. Governmental regulations in many countries require that the probability of such accidental releases be analyzed and their quantitative impact upon the environment and human health be determined so that mitigating steps can be planned and implemented.
A rocket engine nozzle is a propelling nozzle used in a rocket engine to expand and accelerate the combustion gases produced by burning propellants so that the exhaust gases exit the nozzle at hypersonic velocities.

Well completion is the process of making a well ready for production. This principally involves preparing the bottom of the hole to the required specifications, running in the production tubing and its associated down hole tools as well as perforating and stimulating as required. Sometimes, the process of running in and cementing the casing is also included. After a well has been drilled, should the drilling fluids be removed, the well would eventually close in upon itself. Casing ensures that this will not happen while also protecting the wellstream from outside incumbents, like water or sand.
Swirl valve technology has been developed by Twister BV of the Netherlands primarily for the gas processing market. This technology is similar to the swirl tube and can also be applied for liquid/liquid separation applications such as oil/water separation and for oil degassing. It is currently being used for optimising existing Joule–Thomson (JT-LTS) systems to minimise liquid carryover. The swirl valve is exactly the same as a Joule-Thomson (JT) choke valve, but it enhances the performance of downstream separators for the same pressure drop, by maximising droplet coalescence. The technology can be applied where a low temperature separator is undersized, or when a lower pressure drop over a JT valve is needed with a similar dew pointing performance. It can also be applied for reducing glycol/chemical inhibition liquid mist carry-over problems.














