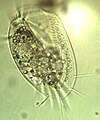
Tetrahymena is a genus of free-living ciliates that can also switch from commensalistic to pathogenic modes of survival. They are common in freshwater ponds. Tetrahymena species used as model organisms in biomedical research are T. thermophila and T. pyriformis.

Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature and therefore do not become healthy blood cells. Early on, there are typically no symptoms. Later symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bleeding, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia.

The heterotrichs are a class of ciliates. They typically have a prominent adoral zone of membranelles circling the mouth, used in locomotion and feeding, and shorter cilia on the rest of the body. Many species are highly contractile, and are typically compressed or conical in form. These include some of the largest protozoa, such as Stentor and Spirostomum, as well as many brightly pigmented forms, such as certain Blepharisma.
The plagiopylids are a small order of ciliates, including a few forms common in anaerobic habitats.

The Oligohymenophorea are a large class of ciliates. There is typically a ventral groove containing the mouth and distinct oral cilia, separate from those of the body. These include a paroral membrane to the right of the mouth and membranelles, usually three in number, to its left. The cytopharynx is inconspicuous and never forms the complex cyrtos found in similar classes. Body cilia generally arise from monokinetids, with dikinetids occurring in limited distribution over part of the body.

The peritrichs are a large and distinctive group of ciliates.

The Litostomatea are a class of ciliates. The group consists of three subclasses: Haptoria, Trichostomatia and Rhynchostomatia. Haptoria includes mostly carnivorous forms such as Didinium, a species of which preys primarily on the ciliate Paramecium. Trichostomatia (trichostomes) are mostly endosymbionts in the digestive tracts of vertebrates. These include the species Balantidium coli, which is the only ciliate parasitic in humans. The group Rhynchostomatia includes two free-living orders previously included among the Haptoria, but now known to be genetically distinct from them, the Dileptida and the Tracheliida.
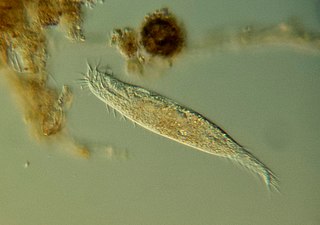
The hypotrichs are a group of ciliated protozoa, common in fresh water, salt water, soil and moss. Hypotrichs possess compound ciliary organelles called "cirri," which are made up of thick tufts of cilia, sparsely distributed on the ventral surface of the cell. The multiple fused cilia which form a cirrus function together as a unit, enabling the organism to crawl along solid substrates such as submerged debris or sediments. Hypotrichs typically possess a large oral aperture, bordered on one side by a wreath or collar of membranelles, forming an "adoral zone of membranelles," or AZM.

The stichotrichs are a group of ciliates, included among the spirotrichs. Like the hypotrichs, with which they were originally classified, they have body cilia fused into cirri, but these are mostly arranged into rows, running along the ventral surface or edges of the cell. Most stichotrichs are flattened and reasonably flexible. Stylonychia and Oxytricha are representative genera. Some evidence suggests that the hypotrichs may be paraphyletic to them, and that they in turn may be paraphyletic to the oligotrichs.

Miller–Dieker syndrome, Miller–Dieker lissencephaly syndrome (MDLS), and chromosome 17p13.3 deletion syndrome is a micro deletion syndrome characterized by congenital malformations. Congenital malformations are physical defects detectable in an infant at birth which can involve many different parts of the body including the brain, hearts, lungs, liver, bones, or intestinal tract. MDS is a contiguous gene syndrome - a disorder due to the deletion of multiple gene loci adjacent to one another. The disorder arises from the deletion of part of the small arm of chromosome 17p, leading to partial monosomy. There may be unbalanced translocations, or the presence of a ring chromosome 17.
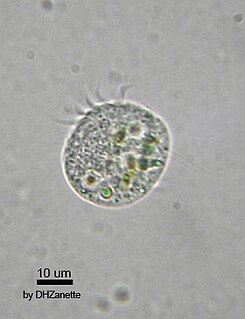
The oligotrichs are a group of ciliates, included among the spirotrichs. They have prominent oral cilia, which are arranged as a collar and lapel, in contrast to the choreotrichs where they form a complete circle. The body cilia are reduced to a girdle and ventral cilia. In Halteria and its relatives, they form bristles or cirri; however these forms may be closer relatives of the stichotrichs than of other oligotrichs. These organisms are very common in plankton communities, especially in marine systems. Usually found in concentrations of about 1 per ml, they are the most important herbivores in the sea, the first link in the food chain.

Uncharacterized hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells protein MDS032, also known as MDS032, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MDS032 gene.
Plagiopyla is a genus of ciliates. It includes nine species:
Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, Loxodes, is found in freshwater.
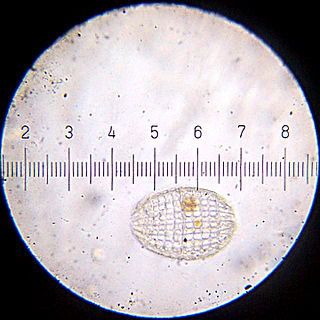
Prostomatea is a class of ciliates. It includes the genera Coleps and Pelagothrix.

The ciliates are a group of protozoans characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation.
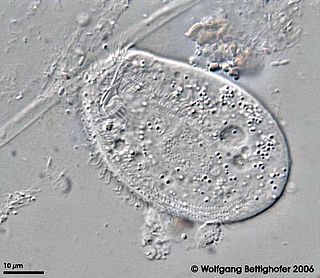
Chilodonella uncinata is a single-celled organism of the ciliate class of alveoles. As a ciliate, C. uncinata has cilia covering its body and a dual nuclear structure, the micronucleus and macronucleus. Unlike some other ciliates, C. uncinata contains millions of minichromosomes in its macronucleus while its micronucleus is estimated to contain 3 chromosomes. Childonella uncinata is the causative agent of Chilodonelloza, a disease that affects the gills and skin of fresh water fish, and may act as a faculitative parasite of mosquito larva.

Sterkiella histriomuscorum, formerly Oxytricha trifallax, is a ciliate species in the genus Sterkiella, known for its highly fragmented genomes which have been used as a model for ciliate genetics.

Colpidium colpoda are free-living ciliates commonly found in many freshwater environments including streams, rivers, lakes and ponds across the world. Colpidium colpoda is also frequently found inhabiting wastewater treatment plants. This species is used as an indicator of water quality and waste treatment plant performance.