Dred Scott v. Sandford, 60 U.S. 393 (1857), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that held the U.S. Constitution did not extend American citizenship to people of black African descent, and thus they could not enjoy the rights and privileges the Constitution conferred upon American citizens. The decision is widely considered the worst in the Supreme Court's history, being widely denounced for its overt racism, perceived judicial activism and poor legal reasoning, and for its crucial role in the start of the American Civil War four years later. Legal scholar Bernard Schwartz said that it "stands first in any list of the worst Supreme Court decisions". Chief Justice Charles Evans Hughes called it the Court's "greatest self-inflicted wound".

Dred Scott was an enslaved African American man who, along with his wife, Harriet, unsuccessfully sued for freedom for themselves and their two daughters, Eliza and Lizzie, in the Dred Scott v. Sandford case of 1857, popularly known as the "Dred Scott decision". The Scotts claimed that they should be granted their freedom because Dred had lived in Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory for four years, where slavery was illegal, and laws in those jurisdictions said that slaveholders gave up their rights to slaves if they stayed for an extended period.

The Territory of Louisiana or Louisiana Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1805, until June 4, 1812, when it was renamed the Missouri Territory. The territory was formed out of the District of Louisiana, which consisted of the portion of the Louisiana Purchase north of the 33rd parallel.
Adverse possession, sometimes colloquially described as "squatter's rights", is a legal principle in the Anglo-American common law under which a person who does not have legal title to a piece of property—usually land —may acquire legal ownership based on continuous possession or occupation of the property without the permission (licence) of its legal owner.
Riparian water rights is a system for allocating water among those who possess land along its path. It has its origins in English common law. Riparian water rights exist in many jurisdictions with a common law heritage, such as Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and states in the eastern United States.
Water right in water law is the right of a user to use water from a water source, e.g., a river, stream, pond or source of groundwater. In areas with plentiful water and few users, such systems are generally not complicated or contentious. In other areas, especially arid areas where irrigation is practiced, such systems are often the source of conflict, both legal and physical. Some systems treat surface water and ground water in the same manner, while others use different principles for each.

McLaren v Caldwell was a landmark decision of the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council that upheld provincial jurisdiction in matters of a local or private nature, as well as over property and civil rights. It has been described as "a decision in a non-constitutional legal context that had indirect non-legal, but profound, constitutional consequences."

The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Missouri is a trial level federal district court based in St. Louis, Missouri, with jurisdiction over fifty counties in the eastern half of Missouri. The court is one of ninety-four district-level courts which make up the first tier of the U.S. federal judicial system. Judges of this court preside over civil and criminal trials on federal matters that originate within the borders of its jurisdiction. It is organized into three divisions, with court held in St. Louis, Hannibal, and Cape Girardeau.
Navigable servitude is a doctrine in United States constitutional law that gives the federal government the right to regulate navigable waterways as an extension of the Commerce Clause in Article I, Section 8 of the constitution. It is also sometimes called federal navigational servitude.
Head v. Amoskeag Mfg. Co., 113 U.S. 9 (1885), was a U.S. Supreme Court case considering whether a dam constructed on privately owned land served a public purpose and whether having the owner of the dam compensate any adjacent landowner was a legal form of eminent domain.

In United States law, a federal enclave is a parcel of federal property within a state that is under the "Special Maritime and Territorial Jurisdiction of the United States". In 1960, the year of the latest comprehensive inquiry, 7% of federal property had enclave status. Of the land with federal enclave status, 57% was under "concurrent" state jurisdiction. The remaining 43%, on which some state laws do not apply, was scattered almost at random throughout the United States. In 1960, there were about 5,000 enclaves, with about one million people living on them. While a comprehensive inquiry has not been performed since 1960, these statistics are likely much lower today, since many federal enclaves were military bases that have been closed and transferred out of federal ownership.
Bryan v. Kennett, 113 U.S. 179 (1885), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that, under the treaty providing for the Louisiana Purchase, the United States would recognize property interests granted by the previous sovereign governments prior to the Purchase, even if the grant had been inchoate or incomplete.
Quincy v. Jackson, 113 U.S. 332 (1885), was a writ of error brought to reverse a judgment by the court below by Jackson, a relator, who recovered a judgment against the City of Quincy, Illinois, for the sum of $9,546.24, with costs of suit.
The Flood Control Act of 1928 authorized the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to design and construct projects for the control of floods on the Mississippi River and its tributaries as well as the Sacramento River in California. It was sponsored by Sen. Wesley L. Jones (R) of Washington and Rep. Frank R. Reid (R) of Illinois, in response to the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927.
Solid Waste Agency of Northern Cook County (SWANCC) v. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, 531 U.S. 159 (2001), was a decision by the US Supreme Court that interpreted a provision of the Clean Water Act. Section 404 of the Act requires permits for the discharge of dredged or fill materials into "navigable waters," which is defined by the Act as "waters of the United States." That provision was the basis for the federal wetlands-permitting program.
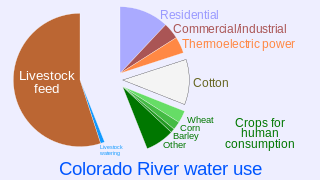
Water law in the United States refers to the Water resources law laws regulating water as a resource in the United States. Beyond issues common to all jurisdictions attempting to regulate water's uses, water law in the United States must contend with:
Shelley v. Kraemer, 334 U.S. 1 (1948), is a landmark United States Supreme Court case that held that racially restrictive housing covenants cannot legally be enforced.
Morris v. United States, 174 U.S. 196 (1899), is a 5-to-2 ruling by the United States Supreme Court which held that the bed under the Potomac River between the District of Columbia and the Commonwealth of Virginia belonged to the United States government rather than nearby private landowners on the District of Columbia side.

During the tenure of Morrison Waite as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, the Supreme Court heard an unprecedented volume and frequency of criminal cases. In just fourteen years, the Court heard 106 criminal cases, almost as many cases as the Supreme Court had heard in the period from its creation to the appointment of Waite as Chief Justice. Notable cases include United States v. Cruikshank (1875), United States v. Reese (1875), Reynolds v. United States (1878), Wilkerson v. Utah (1879), the Trade-Mark Cases (1879), Strauder v. West Virginia (1880), Pace v. Alabama (1883), United States v. Harris (1883), Ex parte Crow Dog (1883), Hurtado v. California (1884), Clawson v. United States (1885), Yick Wo v. Hopkins (1886), United States v. Kagama (1886), Ker v. Illinois (1886), and Mugler v. Kansas (1887).
United States v. John, 437 U.S. 634 (1978), was a case in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that lands designated as a reservation in Mississippi are "Indian country" as defined by statute, although the reservation was established nearly a century after Indian removal and related treaties. The court ruled that, under the Major Crimes Act, the State has no jurisdiction to try a Native American for crimes covered by that act that occurred on reservation land.







