In signal processing, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction involves encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Compression can be either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information.
Compression may refer to:
Artifact, or artefact, may refer to:
Monkey's Audio is an algorithm and file format for lossless audio data compression. Lossless data compression does not discard data during the process of encoding, unlike lossy compression methods such as AAC, MP3, Vorbis and Musepack.

Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression is an audio signal processing operation that reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds thus reducing or compressing an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is commonly used in sound recording and reproduction, broadcasting, live sound reinforcement and in some instrument amplifiers.
An encoder is a device, circuit, transducer, software program, algorithm or person that converts information from one format or code to another, for the purpose of standardization, speed or compression.

dbx, Inc. is an American producer of professional audio recording equipment owned by Harman International Industries, a subsidiary of South Korean firm Samsung Electronics. It was founded by David E. Blackmer in 1971.
Forced induction is the process of delivering compressed air to the intake of an internal combustion engine. A forced induction engine uses a gas compressor to increase the pressure, temperature and density of the air. An engine without forced induction is considered a naturally aspirated engine.
True Audio (TTA) is a lossless compressor for multichannel 8, 16 and 24 bits audio data. .tta is the extension to filenames of audio files created by the True Audio codec.
WavPack is a free and open-source lossless audio compression format.

A portable media player (PMP) or digital audio player (DAP) is a portable consumer electronics device capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, and video files. The data is typically stored on a CD, DVD, BD, flash memory, microdrive, or hard drive. Most portable media players are equipped with a 3.5 mm headphone jack, which users can plug headphones into, or connect to a boombox or hifi system. In contrast, analogue portable audio players play music from non-digital media that use analogue signal storage, such as cassette tapes or vinyl records.
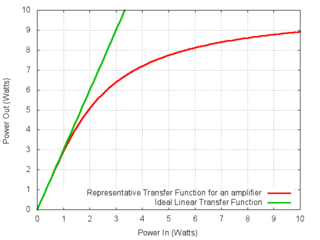
Gain compression is a reduction in "differential" or "slope" gain caused by nonlinearity of the transfer function of the amplifying device. This nonlinearity may be caused by heat due to power dissipation or by overdriving the active device beyond its linear region. It is a large-signal phenomenon of circuits.
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. They are commonly used to replace piston compressors where large volumes of high-pressure air are needed, either for large industrial applications or to operate high-power air tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, becoming less practical than piston types for smaller volume air compressors.
Vapour-compression refrigeration or vapor-compression refrigeration system (VCRS), in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air-conditioning of buildings and automobiles. It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators, large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats, refrigerated trucks and railroad cars, and a host of other commercial and industrial services. Oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical processing plants, and natural gas processing plants are among the many types of industrial plants that often utilize large vapor-compression refrigeration systems.
The SQX-Archiver is an open and free data compression and archival format. It can be used in one's own applications free of charge. The homepage provides an SDK, with source and compiled DLLs which are likewise unencumbered by license costs.
A stacker is a machine used in bulk material handling.
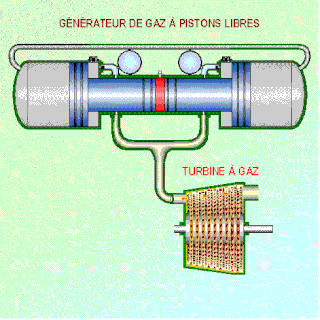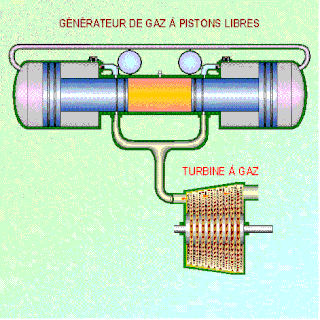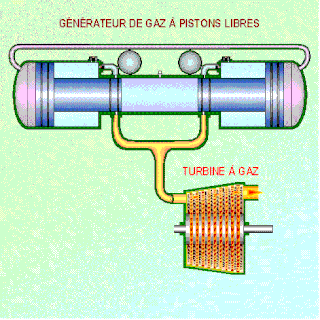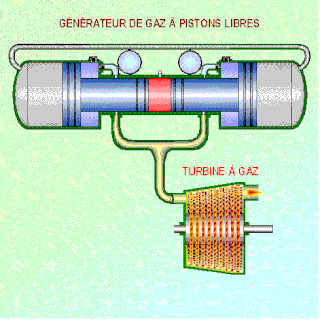
A free-piston engine is a linear, 'crankless' internal combustion engine, in which the piston motion is not controlled by a crankshaft but determined by the interaction of forces from the combustion chamber gases, a rebound device and a load device.

In sound recording and reproduction, audio mixing is the process of combining multitrack recordings into a final mono, stereo or surround sound product. In the process of combining the separate tracks, their relative levels are adjusted and balanced and various processes such as equalization and compression are commonly applied to individual tracks, groups of tracks, and the overall mix. In stereo and surround sound mixing, the placement of the tracks within the stereo field are adjusted and balanced. Audio mixing techniques and approaches vary widely and have a significant influence on the final product.
Harrison Mixbus is a digital audio workstation (DAW) available for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Linux operating systems and was released in 2009.









