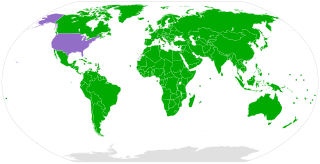
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals including: the conservation of biological diversity ; the sustainable use of its components; and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources.

The Environmental Modification Convention (ENMOD), formally the Convention on the Prohibition of Military or Any Other Hostile Use of Environmental Modification Techniques is an international treaty prohibiting the military or other hostile use of environmental modification techniques having widespread, long-lasting or severe effects. It opened for signature on 18 May 1977 in Geneva and entered into force on 5 October 1978.
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is an international environmental treaty adopted on 9 May 1992 and opened for signature at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro from 3 to 14 June 1992. It then entered into force on 21 March 1994, after a sufficient number of countries had ratified it. The UNFCCC objective is to "stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system". The framework sets non binding limits on greenhouse gas emissions for individual countries and contains no enforcement mechanisms. Instead, the framework outlines how specific international treaties may be negotiated to specify further action towards the objective of the UNFCCC

The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty, is the international agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea, which took place between 1973 and 1982. The Law of the Sea Convention defines the rights and responsibilities of nations with respect to their use of the world's oceans, establishing guidelines for businesses, the environment, and the management of marine natural resources. The Convention, concluded in 1982, replaced four 1958 treaties. UNCLOS came into force in 1994, a year after Guyana became the 60th nation to ratify the treaty. As of June 2016, 167 countries and the European Union have joined in the Convention. It is uncertain as to what extent the Convention codifies customary international law.

The United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification in Those Countries Experiencing Serious Drought and/or Desertification, Particularly in Africa (UNCCD) is a Convention to combat desertification and mitigate the effects of drought through national action programs that incorporate long-term strategies supported by international cooperation and partnership arrangements.

The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of 1961 is an international treaty that defines a framework for diplomatic relations between independent countries. It specifies the privileges of a diplomatic mission that enable diplomats to perform their function without fear of coercion or harassment by the host country. This forms the legal basis for diplomatic immunity. Its articles are considered a cornerstone of modern international relations. As of October 2018, it has been ratified by 192 states.

The Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) is an intergovernmental organization located at The Hague in the Netherlands. The PCA is not a court in the traditional sense but provides services of arbitral tribunal to resolve disputes that arise out of international agreements between member states, international organizations or private parties. The cases span a range of legal issues involving territorial and maritime boundaries, sovereignty, human rights, international investment, and international and regional trade. The PCA is constituted through two separate multilateral conventions with a combined membership of 121 states. The organization is not a United Nations agency,
but the PCA is an official United Nations Observer.

The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands. It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It is named after the city of Ramsar in Iran, where the Convention was signed in 1971.

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is a treaty concerning the international law on treaties between states. It was adopted on 23 May 1969 and opened for signature on 23 May 1969. The Convention entered into force on 27 January 1980. The VCLT has been ratified by 116 states as of January 2018. Some countries that have not ratified the Convention, such as the United States, recognize parts of it as a restatement of customary law and binding upon them as such.

The Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction was the first multilateral disarmament treaty banning the production of an entire category of weapons.

The Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were among the first formal statements of the laws of war and war crimes in the body of secular international law. A third conference was planned for 1914 and later rescheduled for 1915, but it did not take place due to the start of World War I.
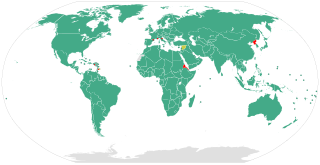
The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) is a multilateral treaty negotiated by member states of the United Nations (UN) and promoted by the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). It is the only legally binding international anti-corruption instrument. UNCAC requires state parties to the treaty to implement several anti-corruption measures that focus on five main areas: prevention, law enforcement, international cooperation, asset recovery, and technical assistance and information exchange.

The Bamako Convention is a treaty of African nations prohibiting the import of any hazardous waste. The Convention was negotiated by twelve nations of the Organisation of African Unity at Bamako, Mali in January, 1991, and came into force in 1998.
After the 2007 United Nations Climate Change Conference on the island Bali in Indonesia in December 2007 the participating nations adopted the Bali Road Map as a two-year process to finalizing a binding agreement in 2009 in Copenhagen. The conference encompassed meetings of several bodies, including the 13th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and the 3rd Meeting of the Parties to the Kyoto Protocol.

The 2008 United Nations Climate Change Conference took place at PIF Congress Centre, Poznań International Fair (PIF), in Poznań, Poland, between December 1 and December 12, 2008. Representatives from over 180 countries attended along with observers from intergovernmental and nongovernmental organizations.

A conference of the parties is the governing body of an international convention. Conventions with a COP include:

The United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP20 or CMP10 was held in Lima, Peru, from December 1 to 12, 2014. This was the 20th yearly session of the Conference of the Parties to the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 10th session of the Meeting of the Parties to the 1997 Kyoto Protocol. The conference delegates held negotiations towards a global climate agreement.

The 2016 United Nations Climate Change Conference was an international meeting of political leaders and activists to discuss environmental issues. It was held in Marrakech, Morocco, on 7-18 November 2016. The conference incorporated the twenty-second Conference of the Parties (COP22), the twelfth meeting of the parties for the Kyoto Protocol (CMP12), and the first meeting of the parties for the Paris Agreement (CMA1). The purpose of the conference was to discuss and implement plans about combatting climate change and to "[demonstrate] to the world that the implementation of the Paris Agreement is underway". Participants work together to come up with global solutions to climate change.
















