
Computing is any activity that uses computers to manage, process, and communicate information for various purposes. It includes development of both hardware and software. Computing is a critical, integral component of modern industrial technology. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, software engineering, computer science, information systems, and information technology.

A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor or main processor, is the electronic circuitry within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions. The computer industry has used the term "central processing unit" at least since the early 1960s. Traditionally, the term "CPU" refers to a processor, more specifically to its processing unit and control unit (CU), distinguishing these core elements of a computer from external components such as main memory and I/O circuitry.

Client–server model is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks or workloads between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and service requesters, called clients. Often clients and servers communicate over a computer network on separate hardware, but both client and server may reside in the same system. A server host runs one or more server programs which share their resources with clients. A client does not share any of its resources, but requests a server's content or service function. Clients therefore initiate communication sessions with servers which await incoming requests. Examples of computer applications that use the client–server model are Email, network printing, and the World Wide Web.

Mainframe computers or mainframes are computers used primarily by large organizations for critical applications; bulk data processing, such as census, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning; and transaction processing. They are larger and have more processing power than some other classes of computers: minicomputers, servers, workstations, and personal computers.

Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes.
The Semantic Web is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The standards promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, most fundamentally the Resource Description Framework (RDF). According to the W3C, "The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and community boundaries". The Semantic Web is therefore regarded as an integrator across different content, information applications and systems.

In computing, a server is a computer program or a device that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called "clients". This architecture is called the client–server model, and a single overall computation is distributed across multiple processes or devices. Servers can provide various functionalities, often called "services", such as sharing data or resources among multiple clients, or performing computation for a client. A single server can serve multiple clients, and a single client can use multiple servers. A client process may run on the same device or may connect over a network to a server on a different device. Typical servers are database servers, file servers, mail servers, print servers, web servers, game servers, and application servers.
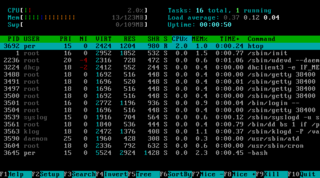
In computing, a process is the instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many threads. It contains the program code and its activity. Depending on the operating system (OS), a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently.

Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) involves a multiprocessor computer hardware and software architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single, shared main memory, have full access to all input and output devices, and are controlled by a single operating system instance that treats all processors equally, reserving none for special purposes. Most multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture. In the case of multi-core processors, the SMP architecture applies to the cores, treating them as separate processors.
A management information system (MIp) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization.
Information systems (IS) are formal, sociotechnical, organizational systems designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. In a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people, structure, and technology.

A system bus is a single computer bus that connects the major components of a computer system, combining the functions of a data bus to carry information, an address bus to determine where it should be sent, and a control bus to determine its operation. The technique was developed to reduce costs and improve modularity, and although popular in the 1970s and 1980s, more modern computers use a variety of separate buses adapted to more specific needs.
A penetration test, colloquially known as a pen test or pentest, is an authorized simulated cyberattack on a computer system, performed to evaluate the security of the system. The test is performed to identify both weaknesses, including the potential for unauthorized parties to gain access to the system's features and data, as well as strengths, enabling a full risk assessment to be completed.

Microsoft NetMeeting is a discontinued VoIP and multi-point videoconferencing client included in many versions of Microsoft Windows. It uses the H.323 protocol for videoconferencing, and is interoperable with OpenH323-based clients such as Ekiga, OpenH323, and Internet Locator Service (ILS) as reflector. It also uses a slightly modified version of the T.120 Protocol for whiteboarding, application sharing, and file transfers.

Videotelephony comprises the technologies for the reception and transmission of audio-video signals by users at different locations, for communication between people in real-time. A videophone is a telephone with a video display, capable of simultaneous video and audio for communication between people in real-time. Videoconferencing implies the use of this technology for a group or organizational meeting rather than for individuals, in a videoconference. Telepresence may refer either to a high-quality videotelephony system or to meetup technology, which goes beyond video into robotics. Videoconferencing has also been called "visual collaboration" and is a type of groupware.
The term "software multitenancy" refers to a software architecture in which a single instance of software runs on a server and serves multiple tenants. Systems designed in such manner are often called shared. A tenant is a group of users who share a common access with specific privileges to the software instance. With a multitenant architecture, a software application is designed to provide every tenant a dedicated share of the instance - including its data, configuration, user management, tenant individual functionality and non-functional properties. Multitenancy contrasts with multi-instance architectures, where separate software instances operate on behalf of different tenants.

A computer network is a digital telecommunications network which allows nodes to share resources. In computer networks, computing devices exchange data with each other using connections between nodes. These data links are established over cable media such as wires or optic cables, or wireless media such as Wi-Fi.
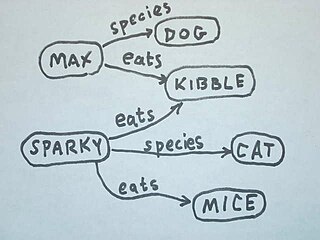
In software, semantic technology encodes meanings separately from data and content files, and separately from application code.

Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. The term is generally used to describe data centers available to many users over the Internet. Large clouds, predominant today, often have functions distributed over multiple locations from central servers. If the connection to the user is relatively close, it may be designated an edge server.















