Computing is any activity that uses computers to manage, process, and communicate information. It includes development of both hardware and software. Computing is a critical, integral component of modern industrial technology. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, software engineering, computer science, information systems, and information technology.

A computer mouse is a hand-held pointing device that detects two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of a pointer on a display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface. The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was in 1968. Originally wired to a computer, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range radio communication with the connected system. Mice originally used a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion, but modern mice often have optical sensors that have no moving parts. In addition to moving a cursor, computer mice have one or more buttons to allow operations such as selection of a menu item on a display. Mice often also feature other elements, such as touch surfaces and "wheels", which enable additional control and dimensional input.

Lausanne is the capital city and biggest town of the canton of Vaud in Romandy, Switzerland. A municipality, it is situated on the shores of Lake Geneva. It faces the French town of Évian-les-Bains, with the Jura Mountains to its north-west. Lausanne is located 62 kilometres northeast of Geneva.

James Arthur Gosling, OC is a Canadian computer scientist, best known as the founder and lead designer behind the Java programming language.
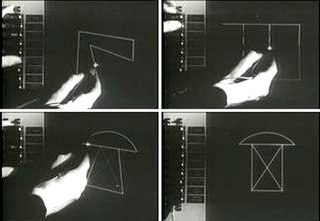
Sketchpad was a computer program written by Ivan Sutherland in 1963 in the course of his PhD thesis, for which he received the Turing Award in 1988, and the Kyoto Prize in 2012. It pioneered the way for human–computer interaction (HCI). Sketchpad is considered to be the ancestor of modern computer-aided design (CAD) programs as well as a major breakthrough in the development of computer graphics in general. For example, the graphical user interface (GUI) was derived from the Sketchpad as well as modern object oriented programming. Ivan Sutherland demonstrated with it that computer graphics could be used for both artistic and technical purposes in addition to showing a novel method of human-computer interaction.
Thinking Machines Corporation was a supercomputer manufacturer and artificial intelligence (AI) company, founded in Waltham, Massachusetts, in 1983 by Sheryl Handler and W. Daniel "Danny" Hillis to turn Hillis's doctoral work at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) on massively parallel computing architectures into a commercial product named the Connection Machine. The company moved in 1984 from Waltham to Kendall Square in Cambridge, Massachusetts, close to the MIT AI Lab. Thinking Machines made some of the most powerful supercomputers of the time, and by 1993 the four fastest computers in the world were Connection Machines. The firm filed for bankruptcy in 1994; its hardware and parallel computing software divisions were acquired in time by Sun Microsystems.

A framebuffer is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing a complete frame of data. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor.

Jean-Daniel Nicoud, is a Swiss computer scientist, noted for inventing of a computer mouse with an optical encoder and the CALM Common Assembly Language for microprocessors.

The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a museum established in 1996 in Mountain View, California, US. The museum is dedicated to preserving and presenting the stories and artifacts of the information age, and exploring the computing revolution and its impact on society.

The College of Computing at the Georgia Institute of Technology has roots stretching back to an Information Science degree established in 1964. In 1988, Georgia Tech president John Patrick Crecine elevated the School of Information and Computer Science to become the College of Computing, making Georgia Tech the second university to do so, after Carnegie Mellon University created their School of Computer Science.

Martin Odersky is a German computer scientist and professor of programming methods at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland. He specializes in code analysis and programming languages. He designed the Scala programming language and Generic Java both with others. He implemented the GJ compiler, and his implementation became the basis of javac, the Java compiler. In 2007, he was inducted as a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery.
Alain Wegmann is a Swiss computer scientist, professor of Systemic Modeling at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), and Information Technology and Services consultant, known for the development of the Systemic Enterprise Architecture Methodology (SEAM).
Bernard M. E. Moret is a Swiss-American computer scientist, an emeritus professor of Computer Science at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland. He is known for his work in computational phylogenetics, and in particular for mathematics and methods for computing phylogenetic trees using genome rearrangement events.

The Musée Bolo is an exhibition at the School of Computer And Communication Sciences at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Lausanne, Romandy, Switzerland. Each exhibit has a different theme such as original microcomputers, video game consoles, and computers organized by country. Posters next to each display case explain the exhibits. Currently it houses around fifty computers. It contains the private collection of the hardware engineer Yves Bolognini.

The Lausanne campus or Dorigny university campus is a large area in Switzerland where the University of Lausanne (UNIL), the École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) and several other institutions are located. It is in Dorigny, towards the west of Lausanne, on the shores of Lake Geneva. The site is about 2.2 kilometres wide and 31,000 people study and work there.
Anastasia Ailamaki is a Cyprus-born, Greek full professor at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland, appointed December 12, 2007. As of 2008 she leads the Data-Intensive Applications and Systems (DIAS) laboratory at the Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL). The DIAS lab conducts a research in communication between database software and both the application layer and the underlying hardware platforms.
IBM Q System One is the world's first-ever circuit-based commercial quantum computer, introduced by IBM in January 2019. IBM Q System One is a 20-qubit computer.
cadwork informatik AG is a multinational software company headquartered in Basel, Switzerland. It develops and markets software products primarily for the construction industry. These products include timber industry products in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) as well as products in building information model (BIM) and virtual design and construction (VDC). These products are suitable for designers, structural engineers, construction engineers, civil engineering draftspeople, building contractors, and in the case of BIMTeam VDC, the construction crews.