See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Cygnus X. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Cygnus X may refer to:
Cygnus X was a trance music project from Germany named after the famous X-ray binary star Cygnus X-1. It began as a collaboration between Matthias Hoffmann and Ralf Hildenbeutel, who later left. Other projects of the pair include A.C. Boutsen, Brainchild and Dee.FX. Their sound extends from hard to ambient trance.
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Cygnus X. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
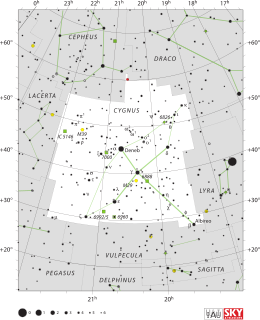
Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. Cygnus is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, and it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross. Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.

Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a galactic X-ray source in the constellation Cygnus, and the first such source widely accepted to be a black hole. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (2.3×103 Jansky). It remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon has 300 km "as upper bound to the linear dimension of the source region" of occasional X-ray bursts lasting only for about 1 ms.

The North America Nebula is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, close to Deneb. The remarkable shape of the nebula resembles that of the continent of North America, complete with a prominent Gulf of Mexico. It is sometimes incorrectly called the "North American Nebula".

Messier 29 or M 29, also known as NGC 6913, is an open cluster of star in the Cygnus constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764, and can be seen from Earth by using binoculars.

The Crescent Nebula is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, about 5000 light-years away from Earth. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1792. It is formed by the fast stellar wind from the Wolf-Rayet star WR 136 colliding with and energizing the slower moving wind ejected by the star when it became a red giant around 250,000 to 400,000 years ago. The result of the collision is a shell and two shock waves, one moving outward and one moving inward. The inward moving shock wave heats the stellar wind to X-ray-emitting temperatures.

The Cygnus Loop is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebula or Cirrus Nebula, emit in the visible electromagnetic range. Radio, infrared, and X-ray images reveal the complete loop.
Cygnus X-3 is a high-mass X-ray binary (HMXB), one of the stronger binary X-ray sources in the sky. It is often considered to be a microquasar, and it is believed to be a compact object in a binary system which is pulling in a stream of gas from an ordinary star companion. It is the only known HMXB containing a Wolf-Rayet star. It is invisible visually, but can be observed at radio, infrared, X-ray, and gamma-ray wavelengths.

The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus.

The Cygnus spacecraft is a single-use American automated cargo spacecraft developed by Orbital Sciences and now built and launched by Northrop Grumman as part of NASA's Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) developmental program. It is launched by Northrop Grumman's Antares rocket or ULA's Atlas V and is designed to transport supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) following the retirement of the American Space Shuttle. Since August 2000 ISS resupply missions have been regularly flown by Russian Progress, as well as by the European Automated Transfer Vehicle, and the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle. With the Cygnus spacecraft and the SpaceX Dragon, NASA seeks to increase its partnerships with domestic commercial aviation and aeronautics industry.
Cygnus OB2 #8A is a double-lined spectroscopic binary located near the centre of the Cygnus OB2 association located 5,500 light years away.

Sharpless 101 (Sh2-101) is a H II region emission nebula located in the constellation Cygnus. It is sometimes also called the Tulip Nebula because it appears to resemble the outline of a tulip when imaged photographically. It was catalogued by astronomer Stewart Sharpless in his 1959 catalog of nebulae. It lies at a distance of about 6,000 light-years (5.7×1016 km; 3.5×1016 mi) from Earth.
Charles Thomas Bolton is an American astronomer who was one of the first astronomers to present strong evidence of the existence of a stellar-mass black hole.

NGC 6819 is an open cluster located 7,200 light years away in the Cygnus constellation. It was discovered by Caroline Herschel on 12 May 1784.

Cygnus OB2 is an OB association that is home to some of the most massive and most luminous stars known, including suspected Luminous blue variable Cyg OB2 #12. It also includes one of the largest known stars, NML Cygni. The region is embedded within a wider one of star formation known as Cygnus X, which is one of the most luminous objects in the sky at radio wavelengths. The region is approximately 1,400 parsecs from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.

DR 21 is a large molecular cloud located in the constellation Cygnus, discovered in 1966 as a radio continuum source by Downes and Rinehart. DR 21 is located about 6,000 light-years (1,800 pc) from Earth and extends for 80 light-years (25 pc). The region contains a high rate of star formation and is associated with the Cygnus X star forming region. It has an estimated mass of 1,000,000 M☉.

Cygnus-X is a massive star formation region located in the constellation of Cygnus at a distance from the Sun of 1.4 kiloparsecs.
BD+43 3654 is a massive luminous blue supergiant runaway star in the constellation Cygnus.
Cygnus OB7 is an OB association in the Milky Way Galaxy in the Cygnus molecular cloud complex, which also contains the star-forming regions Cygnus X, the North America Nebula, and the Pelican Nebula. The Northern Coal Sack lies in the foreground of this region.