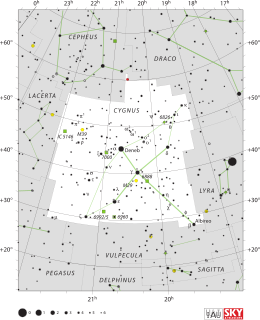
Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. Cygnus is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, and it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross. Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.

Swans are birds of the family Anatidae within the genus Cygnus. The swans' close relatives include the geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form the tribe Cygnini. Sometimes, they are considered a distinct subfamily, Cygninae. There are six or seven living species of swan in the genus Cygnus; in addition, there is another species known as the coscoroba swan, although this species is no longer considered one of the true swans. Swans usually mate for life, although “divorce” sometimes occurs, particularly following nesting failure, and if a mate dies, the remaining swan will take up with another. The number of eggs in each clutch ranges from three to eight.

The whooper swan, pronounced hooper swan, is a large Northern Hemisphere swan. It is the Eurasian counterpart of the North American trumpeter swan, and the type species for the genus Cygnus. Francis Willughby and John Ray's Ornithology of 1676 referred to this swan as "the Elk, Hooper, or wild Swan". The scientific name is from cygnus, the Latin for "swan".

Cygnus A (3C 405) is a radio galaxy, and one of the strongest radio sources in the sky. It was discovered by Grote Reber in 1939. In 1951, Cygnus A, along with Cassiopeia A, and Puppis A were the first "radio stars" identified with an optical source. Of these, Cygnus A became the first radio galaxy; the other two being nebulae inside the Milky Way. In 1953 Roger Jennison and M K Das Gupta showed it to be a double source. Like all radio galaxies, it contains an active galactic nucleus. The super massive black hole at the core has a mass of (2.5±0.7)×109 M☉.

The Cygnus Loop is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebula or Cirrus Nebula, emit in the visible electromagnetic range. Radio, infrared, and X-ray images reveal the complete loop.
Cygnus X-3 is a high-mass X-ray binary (HMXB), one of the stronger binary X-ray sources in the sky. It is often considered to be a microquasar, and it is believed to be a compact object in a binary system which is pulling in a stream of gas from an ordinary star companion. It is the only known HMXB containing a Wolf-Rayet star. It is invisible visually, but can be observed at radio, infrared, X-ray, and gamma-ray wavelengths.

The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus.

The R30: 30th Anniversary Tour was a concert tour by Canadian rock band Rush that celebrated the 30th anniversary of the band's definitive formation in July 1974 after Neil Peart replaced original drummer John Rutsey. It was also in support of the covers EP Feedback. The tour started at the Starwood Amphitheatre in Nashville, Tennessee on May 26, 2004 and culminated at Sportpaleis Ahoy in Rotterdam, The Netherlands on October 1. The show on September 24, 2004 at the Festhalle in Frankfurt, Germany was recorded and released as a DVD titled R30: 30th Anniversary World Tour in November 2005.

Rush's Test for Echo Tour was in support of the band's studio album Test for Echo. It was the band's first tour with no opening act on any date, and was billed as "An Evening With Rush." The tour kicked off October 19, 1996 at the Knickerbocker Arena in Albany, New York and culminated on July 4, 1997 at the Corel Centre in Ottawa, Ontario. This was the only concert tour in which Rush played the song "2112" in its entirety. This marks the last tour until 2002 because of tragedies in Neil Peart's life.

Rush's Counterparts Tour was in support of the band's studio album Counterparts. The tour kicked off January 22, 1994 at the Civic Center in Pensacola, Florida and culminated on May 7, 1994 at Maple Leaf Gardens in Toronto. Opening acts for this tour were Candlebox, The Melvins, Primus, The Doughboys, and I Mother Earth.

The Cygnus spacecraft is a single-use American automated cargo spacecraft developed by Orbital Sciences and now built and launched by Northrop Grumman as part of NASA's Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) developmental program. It is launched by Northrop Grumman's Antares rocket or ULA's Atlas V and is designed to transport supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) following the retirement of the American Space Shuttle. Since August 2000 ISS resupply missions have been regularly flown by Russian Progress, as well as by the European Automated Transfer Vehicle, and the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle. With the Cygnus spacecraft and the SpaceX Dragon, NASA seeks to increase its partnerships with domestic commercial aviation and aeronautics industry.

Sharpless 101 (Sh2-101) is a H II region emission nebula located in the constellation Cygnus. It is sometimes also called the Tulip Nebula because it appears to resemble the outline of a tulip when imaged photographically. It was catalogued by astronomer Stewart Sharpless in his 1959 catalog of nebulae. It lies at a distance of about 6,000 light-years (5.7×1016 km; 3.5×1016 mi) from Earth.

Cygnus OB2 is an OB association that is home to some of the most massive and most luminous stars known, including suspected Luminous blue variable Cyg OB2 #12. It also includes one of the largest known stars, NML Cygni. The region is embedded within a wider one of star formation known as Cygnus X, which is one of the most luminous objects in the sky at radio wavelengths. The region is approximately 1,400 parsecs from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.

Cygnus CRS Orb-2, also known as Orbital Sciences CRS Flight 2, was the third flight of the Orbital Sciences' unmanned resupply spacecraft Cygnus, its third flight to the International Space Station, and the fourth launch of the company's Antares launch vehicle. The mission launched from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport on 13 July 2014.

Cygnus-X is a massive star formation region located in the constellation of Cygnus at a distance from the Sun of 1.4 kiloparsecs.

NanoRacks LLC is a private company that develops products and offers services for the commercial utilization of space.
Cygnus OB7 is an OB association in the Milky Way Galaxy in the Cygnus molecular cloud complex, which also contains the star-forming regions Cygnus X, the North America Nebula, and the Pelican Nebula. The Northern Coal Sack lies in the foreground of this region.














